Technology
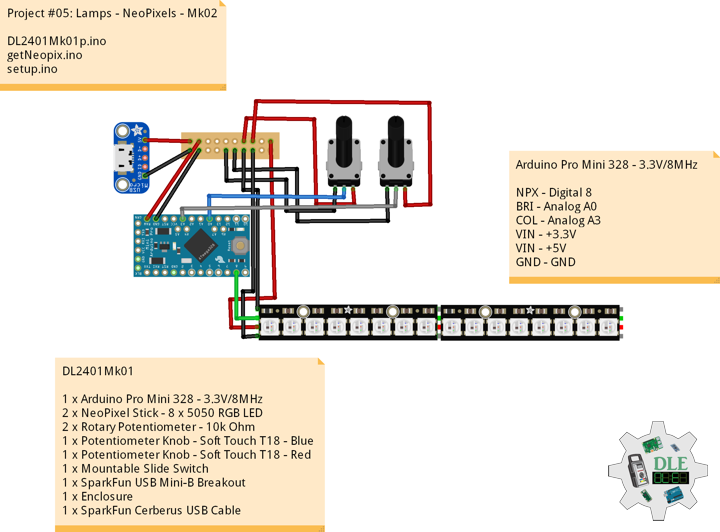
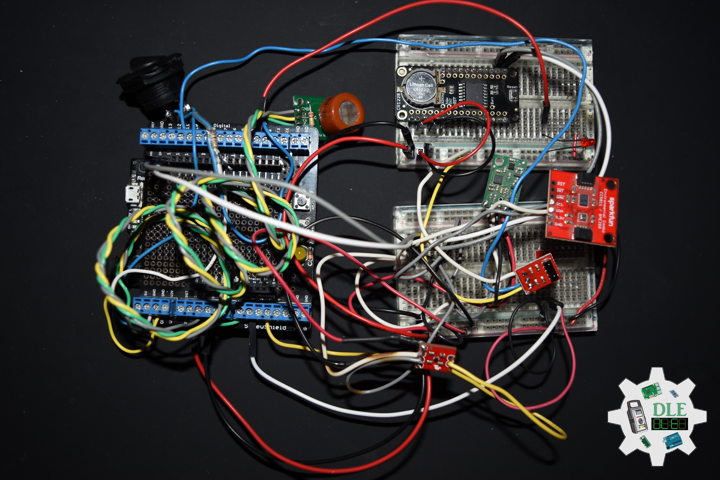
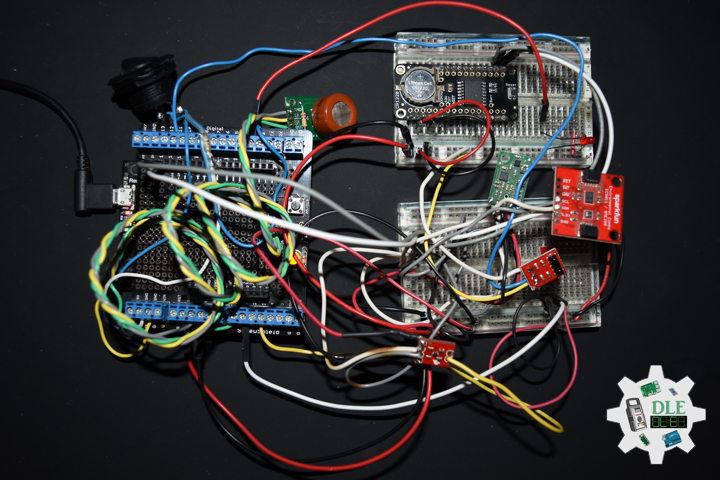
Project #05: Lamps – NeoPixels – Mk02
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Lamps #NeoPixels #Keyboard #Adafruit #SparkFun #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
——
NeoPixels
The WS2812 Integrated Light Source, or NeoPixel in Adafruit parlance, is the latest advance in the quest for a simple, scalable and affordable full-color LED. Red, green and blue LEDs are integrated alongside a driver chip into a tiny surface-mount package controlled through a single wire. They can be used individually, chained into longer strings or assembled into still more interesting form-factors.
NeoPixels don’t just light up on their own; they require a microcontroller, such as Arduino, and some programming. We provide some sample code to get you started. To create your own effects and animation, you’ll need some programming practice. If this is a new experience, work through some of the beginning Arduino tutorials to get a feel for the language.
NeoPixel Stick – 8 x 5050 RGB LED
Make your own little LED strip arrangement with this stick of NeoPixel LEDs. We crammed 8 of the tiny 5050 smart RGB LEDs onto a PCB with mounting holes and a chainable design. Use only one microcontroller pin to control as many as you can chain together. Each LED is addressable as the driver chip is inside the LED. Each one has constant current drive so the color will be very consistent even if the voltage varies, and no external choke resistors are required making the design slim. Power the whole thing with 5VDC and you’re ready to rock. The LEDs are “Chainable” by connecting the output of one stick into the input of another. There is a single data line with a very timing-specific protocol.
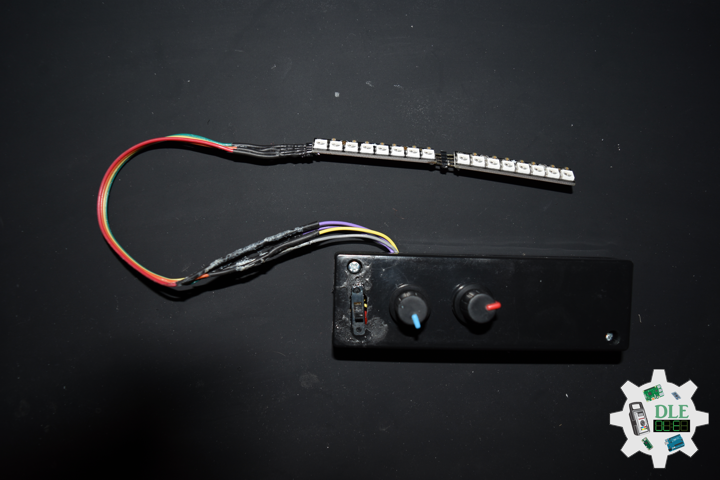
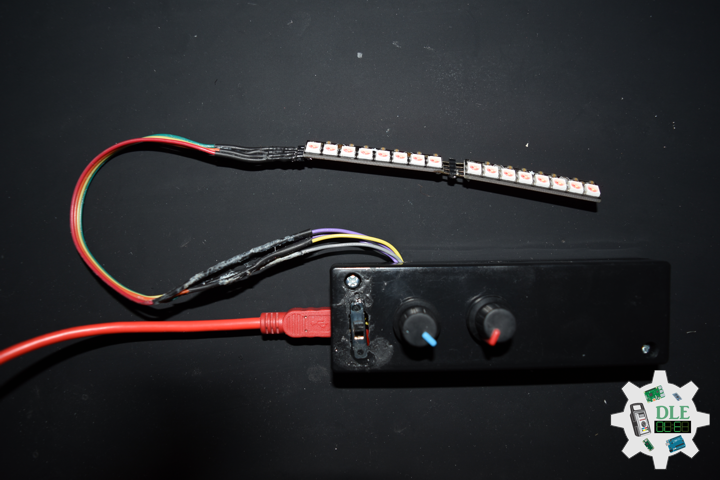
DL2401Mk01
1 x Arduino Pro Mini 328 – 3.3V/8MHz
2 x NeoPixel Stick – 8 x 5050 RGB LED
2 x Rotary Potentiometer – 10k Ohm
1 x Potentiometer Knob – Soft Touch T18 – Blue
1 x Potentiometer Knob – Soft Touch T18 – Red
1 x Mountable Slide Switch
1 x SparkFun USB Mini-B Breakout
1 x Enclosure
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
Arduino Pro Mini 328 – 3.3V/8MHz
NPX – Digital 8
BRI – Analog A0
COL – Analog A3
VIN – +3.3V
VIN – +5V
GND – GND
——
DL2401Mk01p.ino
/****** Don Luc Electronics © ******
Software Version Information
Project #05: Lamps - NeoPixels - Mk02
05-02
DL2401Mk01p.ino
1 x Arduino Pro Mini 328 - 3.3V/8MHz
2 x NeoPixel Stick - 8 x 5050 RGB LED
2 x Rotary Potentiometer - 10k Ohm
1 x Potentiometer Knob - Soft Touch T18 - Blue
1 x Potentiometer Knob - Soft Touch T18 - Red
1 x Mountable Slide Switch
1 x SparkFun USB Mini-B Breakout
1 x Enclosure
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// NeoPixel
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
// NeoPixels
#define PIN 8
// How many NeoPixels are attached to the Arduino => 16
#define NUMPIXELS 16
Adafruit_NeoPixel pixels = Adafruit_NeoPixel(NUMPIXELS, PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
// Color
// Red
int red = 0;
// Green
int green = 0;
// Blue
int blue = 0;
// 2 x Panel Mount 1K potentiometer
// Brighten
const int iSensorBrighten = A0;
int BrightenValue = 0;
int sensorMin = 1023; // minimum sensor value
int sensorMax = 0; // maximum sensor value
// Color
const int iSensorColor = A3;
int y = 0;
int ColorVal = 0;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "05-02";
void loop() {
// Color
isRangeColor();
// Brighten
isNeopix();
}
getNeopix.ino
// Neopix
void isNeopix() {
for(int i=0; i<NUMPIXELS; i++){
// Neopix
BrightenValue = analogRead( iSensorBrighten );
// Apply the calibration to the sensor reading
BrightenValue = map(BrightenValue, sensorMin, sensorMax, 0, 255);
// In case the sensor value is outside the range seen during calibration
BrightenValue = constrain(BrightenValue, 0, 255);
pixels.setBrightness( BrightenValue );
// The pixels.Color takes RGB values, from 0,0,0 up to 255,255,255
pixels.setPixelColor(i, pixels.Color(red,green,blue));
// This sends the updated pixel color to the hardware
pixels.show();
}
}
// Range Color
void isRangeColor() {
// Range Color
ColorVal = analogRead( iSensorColor );
y = (ColorVal / 127);
switch ( y ) {
case 0:
// White
red = 255;
green = 255;
blue = 255;
break;
case 1:
// Yellow
red = 255;
green = 255;
blue = 0;
isNeopix();
break;
case 2:
// Pink
red = 255;
green = 153;
blue = 203;
isNeopix();
break;
case 3:
// Blue
red = 0;
green = 102;
blue = 204;
isNeopix();
isNeopix();
break;
case 4:
// Green
red = 0;
green = 255;
blue = 0;
isNeopix();
break;
case 5:
// Orange
red = 255;
green = 102;
blue = 0;
isNeopix();
break;
case 6:
// Violet
red = 204;
green = 102;
blue = 204;
isNeopix();
break;
case 7:
// Red
red = 255;
green = 0;
blue = 0;
isNeopix();
break;
}
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// This initializes the NeoPixel library
pixels.begin();
delay(50);
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Teacher, Instructor, E-Mentor, R&D and Consulting
- Programming Language
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi, Arm, Silicon Labs, Espressif, Etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Automation
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- RTOS
- eHealth Sensors, Biosensor, and Biometric
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Consulting
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2024
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@thesass2063
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
Teacher, Instructor, E-Mentor, R&D and Consulting
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Teacher #Instructor #EMentor #RD #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
Teacher, Instructor, E-Mentor, R&D and Consulting
- Programming Language
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi, Arm, Silicon Labs, Espressif, Etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Automation
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- RTOS
- eHealth Sensors, Biosensor, and Biometric
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Consulting
I am a highly skilled programming language, microcontrollers, IoT, robotics and etc; with over 45 years of experience in various industries. I graduated from McGill University, Montréal, Québec, Canada with B.Sc. and D.D.S. degrees. I started consulting with small and medium-sized businesses in my native Canada in the mid-eighties and by the mid-nineties I was consulting for large corporate clients like Fannie Mae, KPMG Peat Marwick, Chase Manhattan Foreign Trade Division (Hong Kong), Warner Lambert and a variety of other firms in the Washington, DC and New York City area. Later on I worked with clients in Europe, Mexico, and Latin America.
I have worked, lived and traveled all over the world and I am a trilingual (English, French, and Spanish).
Over the years I have been the CTO of various early stage IT startups, the owner of an IT consulting company (desktop, web, mobile, microcontroller and embedded systems) with clients worldwide, in charge of R&D projects to integrate hardware and software solutions in innovative ways, director of technology for a business software development company, designer and integrator of electronic hardware and head developer on a variety of software and technology projects.
I have seen many trends come and go, good and bad, and lived through many major industry changes. I do deplore some of the current state of the industry, and applaud some of the new trends. My wife had been telling me for years to write about the the industry as we discuss things a lot and she always tells me that I was born to teach, or preach when I get excited about a subject. Since my motto has always been to learn something new daily, and that a wasted day is one where you learn nothing new, I decided to share some of that hard-earned let’s call it “Wisdom” for lack of a better term.
I know that I am considered as a dinosaur in this business where you are considered old when you hit 25, but there are some of us old fogies at over twice that, that are still active and can still provide a full contribution to this or these fields. Besides consulting and custom programming, I also offer electronic hardware integration and design, hardware/software integration as well as R&D services. I provide my services worldwide and can work from my office or yours depending on your project’s needs.
Schedule of Services Teacher, Instructor and E-Mentor
- Beginner: These beginner-friendly microcontrollers are easy to use and program with just a computer or laptop, a USB cable, and some open-source software.
- Intermediate: Internet of Things (IoT).
- Advanced: Robotics, engineering, fashion, medical, environmental, performing arts, etc…
- Projects: TBD
- Research & Development: TBD
- Consulting: TBD
Luc Paquin – 2024
The Electronic, Programming Language, Microcontrollers, IoT, Robotics Experts.
Curriculum Vitae 2024
https://www.donluc.com/luc/LucPaquinCVEng2024Mk01.pdf
Luc Paquin – Programming Language 2024
https://www.donluc.com/luc/LucPaquinProgrammingLanguage2024Mk01.pdf
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2023
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@thesass2063
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
Why “The Alpha Geek”?
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #AlphaGeek #Geek #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
Why “The Alpha Geek”?
I have said “Once a Geek always a Geek” so many time in describing myself. Since I was a small child the main goal in my life has been to learn new things daily. While I write this, on the whiteboard in front of my me in my office, is written in large letters “What new things have you learned today?”. It is a reminder to myself that the day will not be complete until something new is learned. Luckily for me in my line of business you would have to work very hard not to learn something new on a daily basis.
With that attitude in mind since childhood it was very difficult not to grow up and become a full-fledged Geek at an early age. In my early teens I was into photography and processing and printing my own B&W photos in a darkroom I had built with the help of my Mom in our basement in Canada. That was one of my many interests at the time and I can’t even remember how many different “Geeky” things I have done over the years. I got into electronics when I could not afford to buy a proper darkroom timer and I saw some article, probably in some electronics magazine, that explained how to build a simple timer that blinks a LED at one second intervals. After a trip, probably to Radio Shack, to buy a 555 timer IC, a LED, some resistors, wires and a small perforated circuit board. After that I was hooked on electronics projects from that day.
Some years later, while I was an undergrad at university, I was learning mainframe programming in Fortran and assembler programming for some mini-computer I do not remember. Since they were giving us only a few minutes of mainframe processor time a semester a bunch of friends and I bought one of the original Apple 1 kits and I built it for the group and we used that for a few years to supplement our mainframe time. Then followed a Timex Sinclair, a Commodore 64, a Portable Commodore 64, a 128, a PC XT clone with a huge 10Mb hard drive and then hundreds of PCs, laptops, Palm PDAs, tablets and electronic computing devices and gadgets of all kinds.
When I started consulting in 1983 a major part of my time was spent integrating and repairing computer hardware and I even worked for a few years repairing systems nobody else could fix. Nowadays besides programming some business applications on a variety of platforms I still spend a lot of time integrating specialized hardware with software and designing electronic devices of all kind. Since I started with that first simple electronics project over 45 years ago, the Geek in me is still going strong and even though the “Geek” badge is generally used describing the younger crowds I think that a grizzled grey-haired Geek veteran like me deserves the title of “Alpha Geek”. Experience should count for something…
If you noticed I capitalize “Geek” as I think it is a term of respect and not one of derision. I hope that all the Geeks out there will love visiting this blog that will grow to host many projects and features. I also hope that it will help in convert Geeks-in-Training to full-fledged card-carrying Geeks like that first project did for me so long ago.
In the meantime enjoy your stay and let’s Geek Out!
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Teacher, Instructor, E-Mentor, R&D and Consulting
- Programming Language
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi, Arm, Silicon Labs, Espressif, Etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Automation
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- RTOS
- eHealth Sensors, Biosensor, and Biometric
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Consulting
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2023
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@thesass2063
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
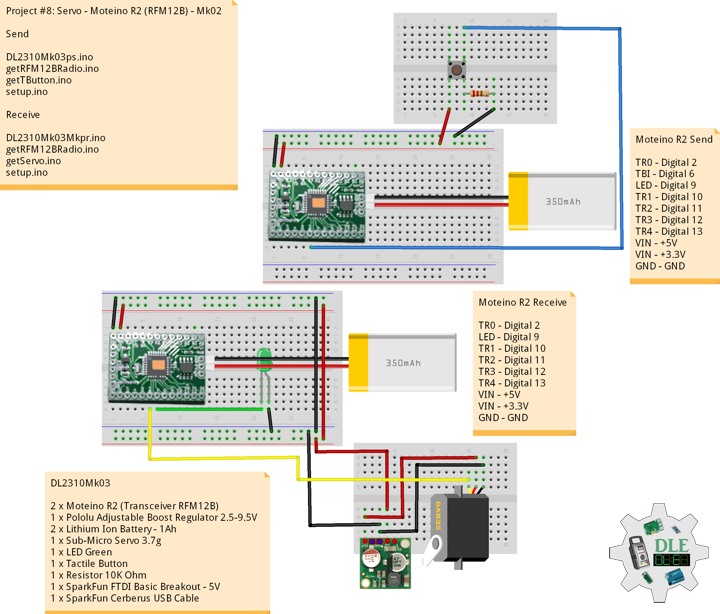
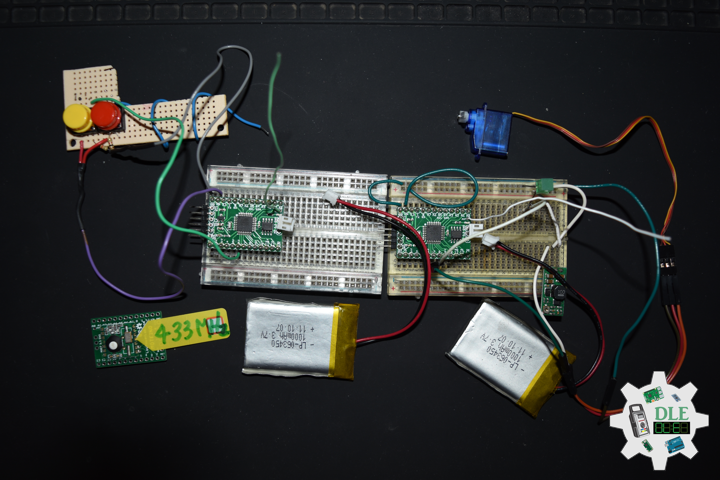
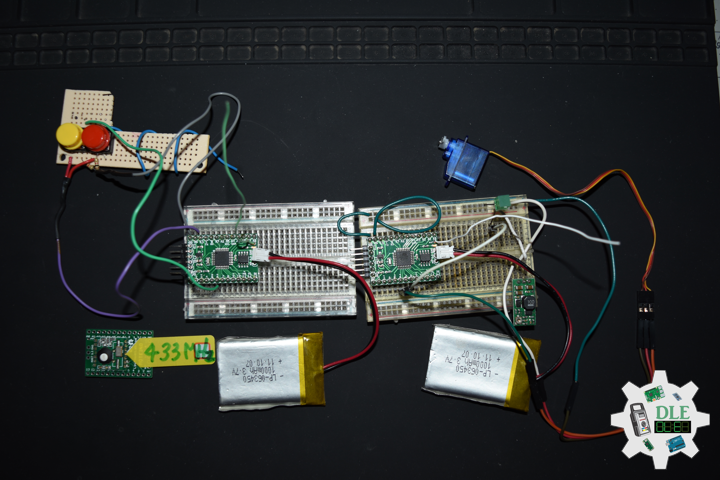
Project #8: Servo – Moteino R2 (RFM12B) – Mk02
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Servo #Moteino #Transceiver #RadioFrequency #Pololu #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
Moteino
Moteino began as a low power wireless Arduino compatible development platform based on the popular ATmega328p chip used in the Arduino UNO. There are now several Moteino development boards including MoteinoMEGA based on the Atmega1284P and MoteinoM0 based on the SAMD21G18 Cortex M0+. For programming you will need an external FTDI-Adapter to load sketches, the advantages being lower cost, smaller size.
Servo Motor
A servo motor is a rotary actuator or linear actuator that allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity and acceleration. It consists of a suitable motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback. It also requires a relatively sophisticated controller, often a dedicated module designed specifically for use with servo motors.
Servo motors have been around for a long time and are utilized in many applications. They are small in size but pack a big punch and are very energy-efficient. These features allow them to be used to operate remote-controlled or radio-controlled toy cars, robots and airplanes. Servo motors are also used in industrial applications, robotics, in-line manufacturing, pharmaceutics and food services.
Pololu Adjustable Boost Regulator 2.5-9.5 Volt
This powerful, adjustable boost regulator can generate an output voltage as high as 9.5 Volt from an input voltage as low as 1.5 Volt, all in a compact. A trimmer potentiometer lets you set the boost regulator’s output voltage to a value between 2.5 and 9.5 Volt.
DL2310Mk03
2 x Moteino R2 (Transceiver RFM12B)
1 x Pololu Adjustable Boost Regulator 2.5-9.5V
2 x Lithium Ion Battery – 1Ah
1 x Sub-Micro Servo 3.7g
1 x LED Green
1 x Tactile Button
1 x Resistor 10K Ohm
1 x SparkFun FTDI Basic Breakout – 5V
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
Moteino R2 (Send)
TR0 – Digital 2
TBI – Digital 6
LED – Digital 9
TR1 – Digital 10
TR2 – Digital 11
TR3 – Digital 12
TR4 – Digital 13
VIN – +5V
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
——
DL2310Mk03ps.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #8: Servo - Radio Frequency - Mk02
6-02
Send
DL2310Mk03ps.ino
2 x Moteino R2 (Transceiver RFM12B)
1 x Pololu Adjustable Boost Regulator 2.5-9.5V
2 x Lithium Ion Battery - 1Ah
1 x Sub-Micro Servo 3.7g
1 x LED Green
1 x Tactile Button
1 x Resistor 10K Ohm
1 x SparkFun FTDI Basic Breakout - 5V
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// RFM12B Radio
#include <RFM12B.h>
// Sleep
#include <avr/sleep.h>
// You will need to initialize the radio by telling it what ID
// it has and what network it's on
// The NodeID takes values from 1-127, 0 is reserved for sending
// broadcast messages (send to all nodes)
// The Network ID takes values from 0-255
// By default the SPI-SS line used is D10 on Atmega328.
// You can change it by calling .SetCS(pin) where pin can be {8,9,10}
// Network ID used for this unit
#define NODEID 2
// The network ID we are on
#define NETWORKID 99
// The node ID we're sending to
#define GATEWAYID 1
// # of ms to wait for an ack
#define ACK_TIME 50
// Serial
#define SERIAL_BAUD 115200
// Encryption is OPTIONAL
// to enable encryption you will need to:
// - provide a 16-byte encryption KEY (same on all nodes that talk encrypted)
// - to call .Encrypt(KEY) to start encrypting
// - to stop encrypting call .Encrypt(NULL)
uint8_t KEY[] = "ABCDABCDABCDABCD";
// Wait this many ms between sending packets
int interPacketDelay = 50;
// Input
char input = 0;
// Need an instance of the RFM12B Radio Module
RFM12B radio;
// Send Size
byte sendSize = 0;
// Payload
char payload[100];
// Request ACK
bool requestACK = false;
// LED
int iLED = 9;
// The number of the Tactile Button pin
int iTButton = 6;
// Variable for reading the button status
int TButtonState = 0;
// The previous reading from the input pin
int lastTButtonState = LOW;
// The following variables are unsigned longs
// because the time, measured in
// milliseconds, will quickly become a bigger
// number than can be stored in an int.
// The last time the output pin was toggled
unsigned long lastDebounceTime = 0;
// The debounce time; increase if the output flickers
unsigned long debounceDelay = 50;
// String
String zzzzzz = "";
int iSER = 0;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "8-02";
void loop()
{
// Tactile Button
isTButton();
// is RFM12B Radio
isRFM12BRadio();
// Inter Packet Delay
delay(interPacketDelay);
}
getRFM12BRadio.ino
// RFM12B Radio
void isSetupRFM12BRadio(){
// RFM12B Radio
radio.Initialize(NODEID, RF12_433MHZ, NETWORKID);
// Encryption
radio.Encrypt(KEY);
// Sleep right away to save power
radio.Sleep();
// Transmitting
Serial.println("Transmitting...\n\n");
}
// is RFM12 BRadio
void isRFM12BRadio(){
// zzzzzz ""
zzzzzz = "";
// zzzzz = "<SER|" + iSER + "|*";
zzzzzz = "<SER|";
zzzzzz = zzzzzz + iSER;
zzzzzz = zzzzzz + "|*";
// sendSize Length
sendSize = zzzzzz.length();
// sendSize
payload[sendSize];
// sendSize, charAt
for(byte i = 0; i < sendSize+1; i++){
payload[i] = zzzzzz.charAt(i);
}
// payload
Serial.print(payload);
// Request ACK
requestACK = sendSize;
// Wakeup
radio.Wakeup();
// Turn the LED on HIGH
digitalWrite( iLED , HIGH);
// Send
radio.Send(GATEWAYID, payload, sendSize, requestACK);
// Request ACK
if (requestACK)
{
Serial.print(" - waiting for ACK...");
if (waitForAck()){
Serial.print("Ok!");
}
else Serial.print("nothing...");
}
// Turn the LED on LOW
digitalWrite( iLED , LOW);
// Sleep
radio.Sleep();
// Serial
Serial.println();
}
// Wait a few milliseconds for proper ACK, return true if received
static bool waitForAck(){
// Now
long now = millis();
// ACK
while (millis() - now <= ACK_TIME){
if (radio.ACKReceived(GATEWAYID)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
getTButton.ino
// Tactile Button
void isTButton(){
// Read the state of the Button value:
int reading = digitalRead(iTButton);
// Check to see if you just pressed the TButton
// (i.e. the input went from LOW to HIGH), and you've waited long enough
// since the last press to ignore any noise:
// If the TButton changed, due to noise or pressing:
if (reading != lastTButtonState) {
// Reset the debouncing timer
lastDebounceTime = millis();
}
if ((millis() - lastDebounceTime) > debounceDelay) {
// Whatever the reading is at, it's been there for
// longer than the debounce
// delay, so take it as the actual current state:
// if the button state has changed:
if (reading != TButtonState) {
TButtonState = reading;
// Check if the TButton is pressed. If it is, the TButtonState is HIGH:
if (TButtonState == HIGH) {
iSER = 1;
} else {
iSER = 0;
}
}
}
// Save the reading. Next time through the loop,
// it'll be the lastTButtonState:
lastTButtonState = reading;
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup(){
// Serial
Serial.begin(SERIAL_BAUD);
// LED
pinMode( iLED , OUTPUT);
// Initialize the Button pin as an input
pinMode(iTButton, INPUT);
// Setup RFM12B Radio
isSetupRFM12BRadio();
}
Moteino R2 (Receive)
TR0 – Digital 2
LED – Digital 9
TR1 – Digital 10
TR2 – Digital 11
TR3 – Digital 12
TR4 – Digital 13
VIN – +5V
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
—
DL2310Mk03Mkpr.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #8: Servo - Radio Frequency - Mk02
6-02
Receive
DL2310Mk03pr.ino
2 x Moteino R2 (RFM12B)
1 x Pololu Adjustable Boost Regulator 2.5-9.5V
2 x Lithium Ion Battery - 1Ah
1 x Sub-Micro Servo 3.7g
1 x LED Green
1 x Tactile Button
1 x Resistor 10K Ohm
1 x SparkFun FTDI Basic Breakout - 5V
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// RFM12B Radio
#include <RFM12B.h>
// Servo
#include <Servo.h>
// You will need to initialize the radio by telling it what ID
// it has and what network it's on
// The NodeID takes values from 1-127, 0 is reserved for sending
// broadcast messages (send to all nodes)
// The Network ID takes values from 0-255
// By default the SPI-SS line used is D10 on Atmega328.
// You can change it by calling .SetCS(pin) where pin can be {8,9,10}
// Network ID used for this unit
#define NODEID 1
// The network ID we are on
#define NETWORKID 99
// Serial
#define SERIAL_BAUD 115200
// Encryption is OPTIONAL
// to enable encryption you will need to:
// - provide a 16-byte encryption KEY (same on all nodes that talk encrypted)
// - to call .Encrypt(KEY) to start encrypting
// - to stop encrypting call .Encrypt(NULL)
uint8_t KEY[] = "ABCDABCDABCDABCD";
// Need an instance of the RFM12B Radio Module
RFM12B radio;
// Message
String msg = "";
// Servo
int iSER = 0;
String sSER = "";
int firstClosingBracket = 0;
// LED
int iLED = 9;
int iLEDG = 7;
// Servo control
Servo serv;
const int pinServo = 6;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "8-02";
void loop() {
// is RFM12B Radio
isRFM12BRadio();
}
getRFM12BRadio.ino
// RFM12B Radio
void isSetupRFM12BRadio()
{
// RFM12B Radio
radio.Initialize(NODEID, RF12_433MHZ, NETWORKID);
// Encryption
radio.Encrypt(KEY);
// Transmitting
Serial.println("Listening...");
}
// is RFM12 BRadio
void isRFM12BRadio()
{
// Receive
if (radio.ReceiveComplete())
{
// CRC Pass
if (radio.CRCPass())
{
// Serial
Serial.print('[');
Serial.print(radio.GetSender());
Serial.print("] ");
// Message
msg = "";
// Can also use radio.GetDataLen() if you don't like pointers
for (byte i = 0; i < *radio.DataLen; i++)
{
Serial.print((char)radio.Data[i]);
msg = msg + (char)radio.Data[i];
}
// Turn the LED on HIGH
digitalWrite( iLED , HIGH);
// Servo
isServo();
// ACK Requested
if (radio.ACKRequested())
{
// Send ACK
radio.SendACK();
Serial.print(" - ACK Sent");
}
// Turn the LED on LOW
digitalWrite( iLED , LOW);
}
else
{
// BAD-CRC
Serial.print("BAD-CRC");
}
// Serial
Serial.println();
}
}
getServo.ino
// Servo
void isServo(){
// Message
//Serial.println( msg );
// msg = "<SER|0|*";
firstClosingBracket = 0;
// "<SER|"
firstClosingBracket = msg.indexOf('|');
//Serial.println( msg );
msg.remove(0, 5);
//Serial.println( msg );
// Servo
firstClosingBracket = msg.indexOf('|');
sSER = msg;
sSER.remove(firstClosingBracket);
//Serial.println( sSER );
iSER = sSER.toInt();
//Serial.println( iSER );
int x = iSER;
if (x == 1) {
digitalWrite(iLEDG, HIGH);
// Set servo to unlock
serv.write( 0 );
delay(15);
} else {
digitalWrite(iLEDG, LOW);
// Set servo to lock
serv.write( 90 );
delay(15);
}
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// Serial
Serial.begin(SERIAL_BAUD);
// LED
pinMode( iLED , OUTPUT);
pinMode( iLEDG , OUTPUT);
// Attach Servo
serv.attach( pinServo );
// RFM12B Radio
isSetupRFM12BRadio();
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Teacher, Instructor, E-Mentor, R&D and Consulting
- Programming Language
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi, Arm, Silicon Labs, Espressif, Etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Automation
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- RTOS
- eHealth Sensors, Biosensor, and Biometric
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Consulting
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2023
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@thesass2063
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
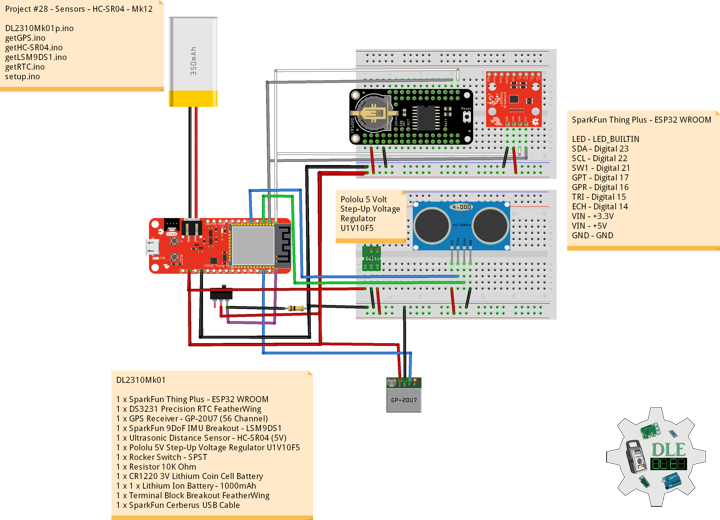
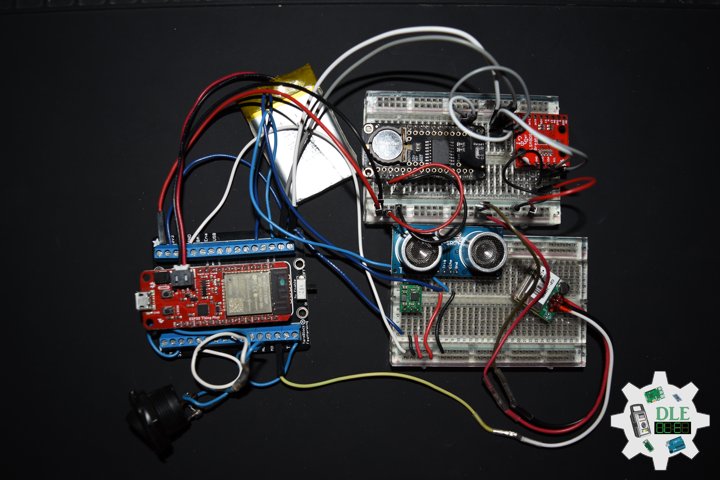
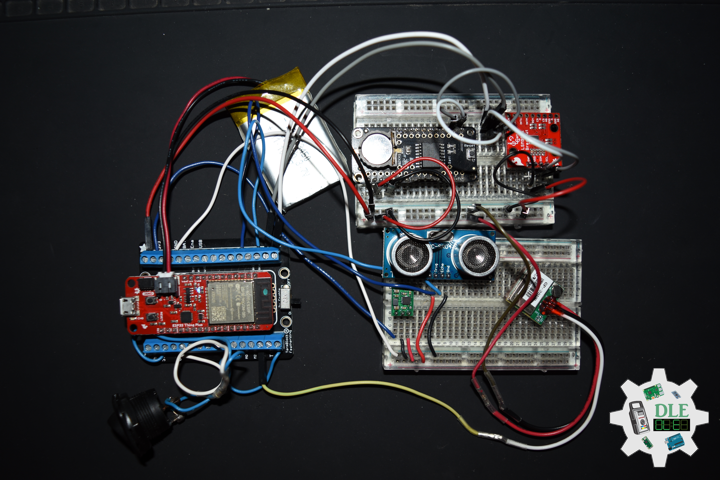
Project #28 – Sensors – HC-SR04 – Mk12
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Sensors #LSM9DS1 #IMU #GPSReceiver #Adafruit #SparkFun #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
Pololu 5 Volt Step-Up Voltage Regulator U1V10F5
This tiny U1V10F5 switching step-up voltage regulator efficiently generates 5 Volt from input voltages as low as 0.5 Volt. Unlike most boost regulators, the U1V10F5 automatically switches to a linear down-regulation mode when the input voltage exceeds the output.
Ultrasonic Distance Sensor – HC-SR04 (5 Volt)
This is the HC-SR04 ultrasonic distance sensor. This economical sensor provides 2 Centimetres to 400 Centimetres of non-contact measurement functionality with a ranging accuracy that can reach up to 3 Millimetres. Each HC-SR04 module includes an ultrasonic transmitter, a receiver and a control circuit. There are only four pins that you need to worry about on the HC-SR04: VCC (Power), Trig (Trigger), Echo (Receive), and GND (Ground). This sensor has additional control circuitry that can prevent inconsistent “Bouncy” data depending on the application.
DL2310Mk01
1 x SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x GPS Receiver – GP-20U7 (56 Channel)
1 x SparkFun 9DoF IMU Breakout – LSM9DS1
1 x Ultrasonic Distance Sensor – HC-SR04 (5V)
1 x Pololu 5V Step-Up Voltage Regulator U1V10F5
1 x Rocker Switch – SPST
1 x Resistor 10K Ohm
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x 1 x Lithium Ion Battery – 1000mAh
1 x Terminal Block Breakout FeatherWing
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
LED – LED_BUILTIN
SDA – Digital 23
SCL – Digital 22
SW1 – Digital 21
GPT – Digital 17
GPR – Digital 16
TRI – Digital 15
ECH – Digital 14
VIN – +3.3V
VIN – +5V
GND – GND
——
DL2310Mk01p.ino
/****** Don Luc Electronics © ******
Software Version Information
Project #28 - Sensors - HC-SR04 - Mk12
28-12
DL2310Mk01p.ino
1 x SparkFun Thing Plus - ESP32 WROOM
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x GPS Receiver - GP-20U7 (56 Channel)
1 x SparkFun 9DoF IMU Breakout - LSM9DS1
1 x Ultrasonic Distance Sensor - HC-SR04 (5V)
1 x Pololu 5V Step-Up Voltage Regulator U1V10F5
1 x Rocker Switch - SPST
1 x Resistor 10K Ohm
1 x Lithium Ion Battery - 1000mAh
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x Terminal Block Breakout FeatherWing
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// Bluetooth LE keyboard
#include <BleKeyboard.h>
// Two Wire Interface (TWI/I2C)
#include <Wire.h>
// Serial Peripheral Interface
#include <SPI.h>
// DS3231 Precision RTC
#include <RTClib.h>
// GPS Receiver
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
// ESP32 Hardware Serial
#include <HardwareSerial.h>
// LSM9DS1 9DOF Sensor
#include <SparkFunLSM9DS1.h>
// Bluetooth LE Keyboard
BleKeyboard bleKeyboard;
String sKeyboard = "";
// Send Size
byte sendSize = 0;
// DS3231 Precision RTC
RTC_DS3231 rtc;
String dateRTC = "";
String timeRTC = "";
// GPS Receiver
#define gpsRXPIN 16
// This one is unused and doesnt have a conection
#define gpsTXPIN 17
// The TinyGPS++ object
TinyGPSPlus gps;
// Latitude
float TargetLat;
// Longitude
float TargetLon;
// GPS Date, Time
// GPS Date
String TargetDat;
// GPS Time
String TargetTim;
// GPS Status
String GPSSt = "";
// ESP32 HardwareSerial
HardwareSerial tGPS(2);
// LSM9DS1 9DOF Sensor
LSM9DS1 imu;
#define PRINT_CALCULATED
// Earth's magnetic field varies by location. Add or subtract
// a declination to get a more accurate heading. Calculate
// your's here: http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/geomag-web/#declination
// Declination (degrees) in El Centro, CA
#define DECLINATION 10.4
// Gyro
float fGyroX;
float fGyroY;
float fGyroZ;
// Accel
float fAccelX;
float fAccelY;
float fAccelZ;
// Mag
float fMagX;
float fMagY;
float fMagZ;
// Attitude
float fRoll;
float fPitch;
float fHeading;
// HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
int iTrig = 15;
int iEcho = 14;
// Stores the distance measured by the distance sensor
float distance = 0;
// The number of the Rocker Switch pin
int iSwitch = 21;
// Variable for reading the button status
int SwitchState = 0;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "28-12";
void loop() {
// Date and Time RTC
isRTC ();
// isGPS
isGPS();
// GPS Keyboard
isGPSKeyboard();
// Gyro
isGyro();
// Accel
isAccel();
// Mag
isMag();
// Attitude
isAttitude();
// HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
isHCSR04();
// Read the state of the Switch value:
SwitchState = digitalRead(iSwitch);
// Check if the button is pressed. If it is, the SwitchState is HIGH:
if (SwitchState == HIGH) {
// Bluetooth LE Keyboard
isBluetooth();
}
// Delay 1 Second
delay(1000);
}
getBleKeyboard.ino
// Ble Keyboard
// Bluetooth
// isBluetooth
void isBluetooth() {
// ESP32 BLE Keyboard
if(bleKeyboard.isConnected()) {
// Send Size Length
sendSize = sKeyboard.length();
// Send Size, charAt
for(byte i = 0; i < sendSize+1; i++){
// Write
bleKeyboard.write(sKeyboard.charAt(i));
delay(50);
}
bleKeyboard.write(KEY_RETURN);
}
}
getGPS.ino
// GPS Receiver
// Setup GPS
void isSetupGPS() {
// Setup GPS
//tGPS.begin( 9600 );
// Setup GPS
tGPS.begin( 9600 , SERIAL_8N1 , gpsRXPIN , gpsTXPIN );
}
// isGPS
void isGPS(){
// Receives NEMA data from GPS receiver
// This sketch displays information every time a new sentence is correctly encoded
while ( tGPS.available() > 0)
if (gps.encode( tGPS.read() ))
{
// GPS Vector Pointer Target
displayInfo();
// GPS Date, Time
displayDTS();
}
if (millis() > 5000 && gps.charsProcessed() < 10)
{
while(true);
}
}
// GPS Vector Pointer Target
void displayInfo(){
// Location
if (gps.location.isValid())
{
// Latitude
TargetLat = gps.location.lat();
// Longitude
TargetLon = gps.location.lng();
// GPS Status 2
GPSSt = "Yes";
}
else
{
// GPS Status 0
GPSSt = "No";
TargetLat = 0;
TargetLon = 0;
}
}
// GPS Date, Time
void displayDTS(){
// Date
TargetDat = "";
if (gps.date.isValid())
{
// Date
// Year
TargetDat += String(gps.date.year(), DEC);
TargetDat += "/";
// Month
TargetDat += String(gps.date.month(), DEC);
TargetDat += "/";
// Day
TargetDat += String(gps.date.day(), DEC);
}
// Time
TargetTim = "";
if (gps.time.isValid())
{
// Time
// Hour
TargetTim += String(gps.time.hour(), DEC);
TargetTim += ":";
// Minute
TargetTim += String(gps.time.minute(), DEC);
TargetTim += ":";
// Secound
TargetTim += String(gps.time.second(), DEC);
}
}
// GPS Keyboard
void isGPSKeyboard(){
// GPS Keyboard
// bleKeyboard
// GPS Vector Pointer Target
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + GPSSt + "|" + String(TargetLat)
+ "|" + String(TargetLon) + "|";
// bleKeyboard
// GPS Date, Time
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + TargetDat + "|" +
TargetTim + "|";
}
getHC-SR04.ino
// HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
// Setup HC-SR04
void isSetupHCSR04() {
// The trigger iTrig will output pulses of electricity
pinMode(iTrig, OUTPUT);
// The echo iEcho will measure the duration of pulses coming back from the distance sensor
pinMode(iEcho, INPUT);
}
// HC-SR04
void isHCSR04() {
// Variable to store the distance measured by the sensor
distance = isDistance();
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(distance) + " cm|*";
}
// Distance
float isDistance() {
// Variable to store the time it takes for a ping to bounce off an object
float echoTime;
// Variable to store the distance calculated from the echo time
float calculatedDistance;
// Send out an ultrasonic pulse that's 10ms long
digitalWrite(iTrig, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(iTrig, LOW);
// Use the pulseIn command to see how long it takes for the
// pulse to bounce back to the sensor
echoTime = pulseIn(iEcho, HIGH);
// Calculate the distance of the object that reflected the pulse
// (half the bounce time multiplied by the speed of sound)
// cm = 58.0
calculatedDistance = echoTime / 58.0;
// Send back the distance that was calculated
return calculatedDistance;
}
getLSM9DS1.ino
// LSM9DS1 9DOF Sensor
// Gyro
void isGyro(){
// Update the sensor values whenever new data is available
if ( imu.gyroAvailable() )
{
// To read from the gyroscope, first call the
// readGyro() function. When it exits, it'll update the
// gx, gy, and gz variables with the most current data.
imu.readGyro();
// If you want to print calculated values, you can use the
// calcGyro helper function to convert a raw ADC value to
// DPS. Give the function the value that you want to convert.
fGyroX = imu.calcGyro(imu.gx);
fGyroY = imu.calcGyro(imu.gy);
fGyroZ = imu.calcGyro(imu.gz);
// bleKeyboard
// Gyro
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(fGyroX) + "|" + String(fGyroY)
+ "|" + String(fGyroZ) + "|";
}
}
// Accel
void isAccel(){
// Update the sensor values whenever new data is available
if ( imu.accelAvailable() )
{
// To read from the accelerometer, first call the
// readAccel() function. When it exits, it'll update the
// ax, ay, and az variables with the most current data.
imu.readAccel();
// If you want to print calculated values, you can use the
// calcAccel helper function to convert a raw ADC value to
// g's. Give the function the value that you want to convert.
fAccelX = imu.calcAccel(imu.ax);
fAccelY = imu.calcAccel(imu.ay);
fAccelZ = imu.calcAccel(imu.az);
// bleKeyboard
// Accel
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(fAccelX) + "|" + String(fAccelY)
+ "|" + String(fAccelZ) + "|";
}
}
// Mag
void isMag(){
// Update the sensor values whenever new data is available
if ( imu.magAvailable() )
{
// To read from the magnetometer, first call the
// readMag() function. When it exits, it'll update the
// mx, my, and mz variables with the most current data.
imu.readMag();
// If you want to print calculated values, you can use the
// calcMag helper function to convert a raw ADC value to
// Gauss. Give the function the value that you want to convert.
fMagX = imu.calcMag(imu.mx);
fMagY = imu.calcMag(imu.my);
fMagZ = imu.calcMag(imu.mz);
// bleKeyboard
// Mag
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(fMagX) + "|" + String(fMagY)
+ "|" + String(fMagZ) + "|";
}
}
// Attitude
void isAttitude(){
// Attitude
// Roll
fRoll = atan2(fAccelY, fAccelZ);
// Pitch
fPitch = atan2(-fAccelX, sqrt(fAccelY * fAccelY + fAccelZ * fAccelZ));
// Heading
if (fMagY == 0) {
fHeading = (fMagX < 0) ? PI : 0;
}
else {
fHeading = atan2(fMagX, fMagY);
}
fHeading -= DECLINATION * PI / 180;
if (fHeading > PI) fHeading -= (2 * PI);
else if (fHeading < -PI) fHeading += (2 * PI);
// Convert everything from radians to degrees:
fHeading *= 180.0 / PI;
fPitch *= 180.0 / PI;
fRoll *= 180.0 / PI;
// bleKeyboard
// Attitude
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(fHeading) + "|" + String(fPitch)
+ "|" + String(fRoll) + "|";
}
getRTC.ino
// Date & Time
// DS3231 Precision RTC
void isSetupRTC() {
// DS3231 Precision RTC
if (! rtc.begin()) {
//Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC");
//Serial.flush();
while (1) delay(10);
}
if (rtc.lostPower()) {
//Serial.println("RTC lost power, let's set the time!");
// When time needs to be set on a new device, or after a power loss, the
// following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
// This line sets the RTC with an explicit date & time, for example to set
// January 21, 2014 at 3am you would call:
//rtc.adjust(DateTime(2023, 8, 10, 11, 0, 0));
}
}
// Date and Time RTC
void isRTC () {
// Date and Time
dateRTC = "";
timeRTC = "";
DateTime now = rtc.now();
// Date
dateRTC = now.year(), DEC;
dateRTC = dateRTC + "/";
dateRTC = dateRTC + now.month(), DEC;
dateRTC = dateRTC + "/";
dateRTC = dateRTC + now.day(), DEC;
// Time
timeRTC = now.hour(), DEC;
timeRTC = timeRTC + ":";
timeRTC = timeRTC + now.minute(), DEC;
timeRTC = timeRTC + ":";
timeRTC = timeRTC + now.second(), DEC;
// bleKeyboard
sKeyboard = "SEN|" + sver + "|" + String(dateRTC)
+ "|" + String(timeRTC) + "|";
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Bluetooth LE keyboard
bleKeyboard.begin();
// Wire - Inialize I2C Hardware
Wire.begin();
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Date & Time RTC
// DS3231 Precision RTC
isSetupRTC();
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// GPS Receiver
// Setup GPS
isSetupGPS();
// LSM9DS1 9DOF Sensor
imu.begin();
// Setup HC-SR04
isSetupHCSR04();
// Initialize the Switch pin as an input
pinMode(iSwitch, INPUT);
// Initialize digital pin LED_BUILTIN as an output
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
// Turn the LED on HIGH
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH);
// Delay 5 Second
delay( 5000 );
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Teacher, Instructor, E-Mentor, R&D and Consulting
- Programming Language
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi, Arm, Silicon Labs, Espressif, Etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Automation
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- RTOS
- eHealth Sensors, Biosensor, and Biometric
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Consulting
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2023
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@thesass2063
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
Project #28 – Sensors – LSM9DS1 – Mk11
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Sensors #LSM9DS1 #IMU #GPSReceiver #Adafruit #SparkFun #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
SparkFun 9DoF IMU Breakout – LSM9DS1
The SparkFun LSM9DS1 Breakout is a versatile, motion-sensing System-In-A-Chip. It houses a 3-axis accelerometer, 3-axis gyroscope, and 3-axis magnetometer, nine degrees of freedom (9DOF) on a single board. The LSM9DS1 from STMicroelectronics is equipped with a digital interface, but even that is flexible. This IMU-In-A-Chip is so cool we put it on the quarter-sized breakout board you are currently viewing.
The LSM9DS1 is one of only a handful of IC’s that can measure three key properties of movement, angular velocity, acceleration, and heading, in a single IC. By measuring these three properties, you can gain a great deal of knowledge about an object’s movement and orientation. The LSM9DS1 measures each of these movement properties in three dimensions. That means it produces nine pieces of data: acceleration in x/y/z, angular rotation in x/y/z, and magnetic force in x/y/z. The LSM9DS1 Breakout has labels indicating the accelerometer and gyroscope axis orientations, which share a right-hand rule relationship with each other.
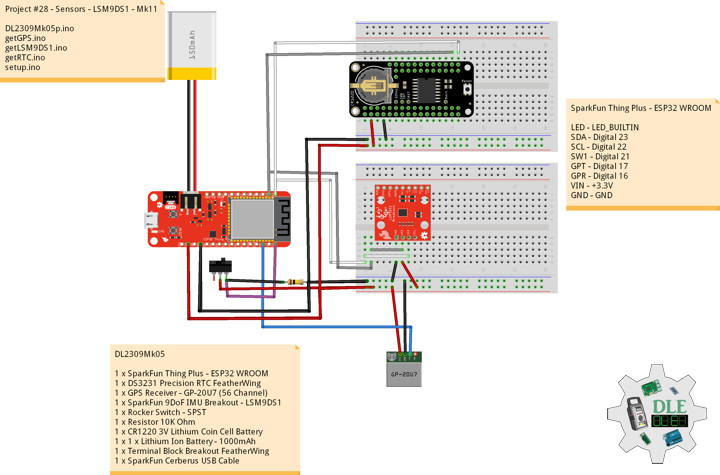
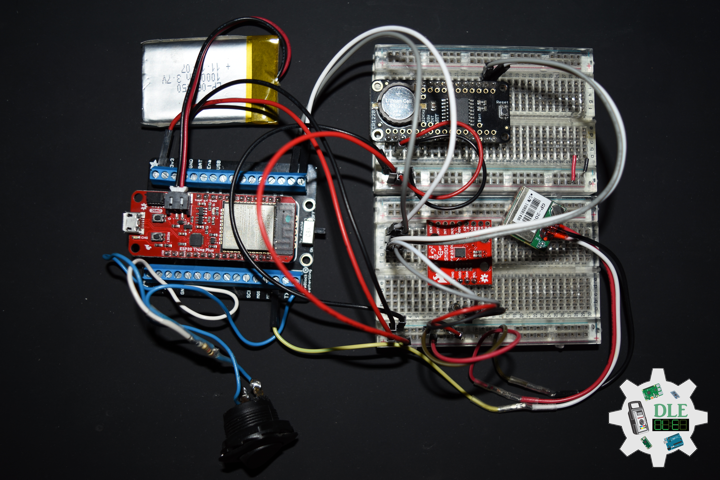
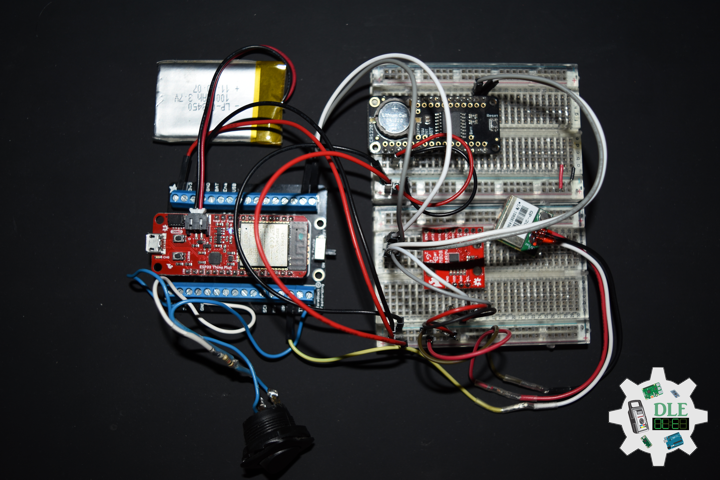
DL2309Mk05
1 x SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x GPS Receiver – GP-20U7 (56 Channel)
1 x SparkFun 9DoF IMU Breakout – LSM9DS1
1 x Rocker Switch – SPST
1 x Resistor 10K Ohm
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x 1 x Lithium Ion Battery – 1000mAh
1 x Terminal Block Breakout FeatherWing
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
LED – LED_BUILTIN
SDA – Digital 23
SCL – Digital 22
SW1 – Digital 21
GPT – Digital 17
GPR – Digital 16
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
——
DL2309Mk05p.ino
/****** Don Luc Electronics © ******
Software Version Information
Project #28 - Sensors - LSM9DS1 - Mk11
28-11
DL2309Mk05p.ino
1 x SparkFun Thing Plus - ESP32 WROOM
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x GPS Receiver - GP-20U7 (56 Channel)
1 x SparkFun 9DoF IMU Breakout - LSM9DS1
1 x Rocker Switch - SPST
1 x Resistor 10K Ohm
1 x Lithium Ion Battery - 1000mAh
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x Terminal Block Breakout FeatherWing
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// Bluetooth LE keyboard
#include <BleKeyboard.h>
// Two Wire Interface (TWI/I2C)
#include <Wire.h>
// Serial Peripheral Interface
#include <SPI.h>
// DS3231 Precision RTC
#include <RTClib.h>
// GPS Receiver
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
// ESP32 Hardware Serial
#include <HardwareSerial.h>
// LSM9DS1 9DOF Sensor
#include <SparkFunLSM9DS1.h>
// Bluetooth LE Keyboard
BleKeyboard bleKeyboard;
String sKeyboard = "";
// Send Size
byte sendSize = 0;
// DS3231 Precision RTC
RTC_DS3231 rtc;
String dateRTC = "";
String timeRTC = "";
// GPS Receiver
#define gpsRXPIN 16
// This one is unused and doesnt have a conection
#define gpsTXPIN 17
// The TinyGPS++ object
TinyGPSPlus gps;
// Latitude
float TargetLat;
// Longitude
float TargetLon;
// GPS Date, Time
// GPS Date
String TargetDat;
// GPS Time
String TargetTim;
// GPS Status
String GPSSt = "";
// ESP32 HardwareSerial
HardwareSerial tGPS(2);
// LSM9DS1 9DOF Sensor
LSM9DS1 imu;
#define PRINT_CALCULATED
// Earth's magnetic field varies by location. Add or subtract
// a declination to get a more accurate heading. Calculate
// your's here: http://www.ngdc.noaa.gov/geomag-web/#declination
// Declination (degrees) in El Centro, CA
#define DECLINATION 10.4
// Gyro
float fGyroX;
float fGyroY;
float fGyroZ;
// Accel
float fAccelX;
float fAccelY;
float fAccelZ;
// Mag
float fMagX;
float fMagY;
float fMagZ;
// Attitude
float fRoll;
float fPitch;
float fHeading;
// The number of the Rocker Switch pin
int iSwitch = 21;
// Variable for reading the button status
int SwitchState = 0;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "28-11";
void loop() {
// Date and Time RTC
isRTC ();
// isGPS
isGPS();
// GPS Keyboard
isGPSKeyboard();
// Gyro
isGyro();
// Accel
isAccel();
// Mag
isMag();
// Attitude
isAttitude();
// Read the state of the Switch value:
SwitchState = digitalRead(iSwitch);
// Check if the button is pressed. If it is, the SwitchState is HIGH:
if (SwitchState == HIGH) {
// Bluetooth LE Keyboard
isBluetooth();
}
// Delay 1 Second
delay(1000);
}
getBleKeyboard.ino
// Ble Keyboard
// Bluetooth
// isBluetooth
void isBluetooth() {
// ESP32 BLE Keyboard
if(bleKeyboard.isConnected()) {
// Send Size Length
sendSize = sKeyboard.length();
// Send Size, charAt
for(byte i = 0; i < sendSize+1; i++){
// Write
bleKeyboard.write(sKeyboard.charAt(i));
delay(50);
}
bleKeyboard.write(KEY_RETURN);
}
}
getGPS.ino
// GPS Receiver
// Setup GPS
void setupGPS() {
// Setup GPS
//tGPS.begin( 9600 );
// Setup GPS
tGPS.begin( 9600 , SERIAL_8N1 , gpsRXPIN , gpsTXPIN );
}
// isGPS
void isGPS(){
// Receives NEMA data from GPS receiver
// This sketch displays information every time a new sentence is correctly encoded
while ( tGPS.available() > 0)
if (gps.encode( tGPS.read() ))
{
// GPS Vector Pointer Target
displayInfo();
// GPS Date, Time
displayDTS();
}
if (millis() > 5000 && gps.charsProcessed() < 10)
{
while(true);
}
}
// GPS Vector Pointer Target
void displayInfo(){
// Location
if (gps.location.isValid())
{
// Latitude
TargetLat = gps.location.lat();
// Longitude
TargetLon = gps.location.lng();
// GPS Status 2
GPSSt = "Yes";
}
else
{
// GPS Status 0
GPSSt = "No";
TargetLat = 0;
TargetLon = 0;
}
}
// GPS Date, Time
void displayDTS(){
// Date
TargetDat = "";
if (gps.date.isValid())
{
// Date
// Year
TargetDat += String(gps.date.year(), DEC);
TargetDat += "/";
// Month
TargetDat += String(gps.date.month(), DEC);
TargetDat += "/";
// Day
TargetDat += String(gps.date.day(), DEC);
}
// Time
TargetTim = "";
if (gps.time.isValid())
{
// Time
// Hour
TargetTim += String(gps.time.hour(), DEC);
TargetTim += ":";
// Minute
TargetTim += String(gps.time.minute(), DEC);
TargetTim += ":";
// Secound
TargetTim += String(gps.time.second(), DEC);
}
}
// GPS Keyboard
void isGPSKeyboard(){
// GPS Keyboard
// bleKeyboard
// GPS Vector Pointer Target
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + GPSSt + "|" + String(TargetLat)
+ "|" + String(TargetLon) + "|";
// bleKeyboard
// GPS Date, Time
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + TargetDat + "|" +
TargetTim + "|";
}
getLSM9DS1.ino
// LSM9DS1 9DOF Sensor
// Gyro
void isGyro(){
// Update the sensor values whenever new data is available
if ( imu.gyroAvailable() )
{
// To read from the gyroscope, first call the
// readGyro() function. When it exits, it'll update the
// gx, gy, and gz variables with the most current data.
imu.readGyro();
// If you want to print calculated values, you can use the
// calcGyro helper function to convert a raw ADC value to
// DPS. Give the function the value that you want to convert.
fGyroX = imu.calcGyro(imu.gx);
fGyroY = imu.calcGyro(imu.gy);
fGyroZ = imu.calcGyro(imu.gz);
// bleKeyboard
// Gyro
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(fGyroX) + "|" + String(fGyroY)
+ "|" + String(fGyroZ) + "|";
}
}
// Accel
void isAccel(){
// Update the sensor values whenever new data is available
if ( imu.accelAvailable() )
{
// To read from the accelerometer, first call the
// readAccel() function. When it exits, it'll update the
// ax, ay, and az variables with the most current data.
imu.readAccel();
// If you want to print calculated values, you can use the
// calcAccel helper function to convert a raw ADC value to
// g's. Give the function the value that you want to convert.
fAccelX = imu.calcAccel(imu.ax);
fAccelY = imu.calcAccel(imu.ay);
fAccelZ = imu.calcAccel(imu.az);
// bleKeyboard
// Accel
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(fAccelX) + "|" + String(fAccelY)
+ "|" + String(fAccelZ) + "|";
}
}
// Mag
void isMag(){
// Update the sensor values whenever new data is available
if ( imu.magAvailable() )
{
// To read from the magnetometer, first call the
// readMag() function. When it exits, it'll update the
// mx, my, and mz variables with the most current data.
imu.readMag();
// If you want to print calculated values, you can use the
// calcMag helper function to convert a raw ADC value to
// Gauss. Give the function the value that you want to convert.
fMagX = imu.calcMag(imu.mx);
fMagY = imu.calcMag(imu.my);
fMagZ = imu.calcMag(imu.mz);
// bleKeyboard
// Mag
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(fMagX) + "|" + String(fMagY)
+ "|" + String(fMagZ) + "|";
}
}
// Attitude
void isAttitude(){
// Attitude
// Roll
fRoll = atan2(fAccelY, fAccelZ);
// Pitch
fPitch = atan2(-fAccelX, sqrt(fAccelY * fAccelY + fAccelZ * fAccelZ));
// Heading
if (fMagY == 0) {
fHeading = (fMagX < 0) ? PI : 0;
}
else {
fHeading = atan2(fMagX, fMagY);
}
fHeading -= DECLINATION * PI / 180;
if (fHeading > PI) fHeading -= (2 * PI);
else if (fHeading < -PI) fHeading += (2 * PI);
// Convert everything from radians to degrees:
fHeading *= 180.0 / PI;
fPitch *= 180.0 / PI;
fRoll *= 180.0 / PI;
// bleKeyboard
// Attitude
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(fHeading) + "|" + String(fPitch)
+ "|" + String(fRoll) + "|*";
}
getRTC.ino
// Date & Time
// DS3231 Precision RTC
void setupRTC() {
// DS3231 Precision RTC
if (! rtc.begin()) {
//Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC");
//Serial.flush();
while (1) delay(10);
}
if (rtc.lostPower()) {
//Serial.println("RTC lost power, let's set the time!");
// When time needs to be set on a new device, or after a power loss, the
// following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
// This line sets the RTC with an explicit date & time, for example to set
// January 21, 2014 at 3am you would call:
//rtc.adjust(DateTime(2023, 8, 10, 11, 0, 0));
}
}
// Date and Time RTC
void isRTC () {
// Date and Time
dateRTC = "";
timeRTC = "";
DateTime now = rtc.now();
// Date
dateRTC = now.year(), DEC;
dateRTC = dateRTC + "/";
dateRTC = dateRTC + now.month(), DEC;
dateRTC = dateRTC + "/";
dateRTC = dateRTC + now.day(), DEC;
// Time
timeRTC = now.hour(), DEC;
timeRTC = timeRTC + ":";
timeRTC = timeRTC + now.minute(), DEC;
timeRTC = timeRTC + ":";
timeRTC = timeRTC + now.second(), DEC;
// bleKeyboard
sKeyboard = "SEN|" + sver + "|" + String(dateRTC)
+ "|" + String(timeRTC) + "|";
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Bluetooth LE keyboard
bleKeyboard.begin();
// Wire - Inialize I2C Hardware
Wire.begin();
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Date & Time RTC
// DS3231 Precision RTC
setupRTC();
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// GPS Receiver
// Setup GPS
setupGPS();
// LSM9DS1 9DOF Sensor
imu.begin();
// Initialize the Switch pin as an input
pinMode(iSwitch, INPUT);
// Initialize digital pin LED_BUILTIN as an output
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
// Turn the LED on HIGH
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH);
// Delay 5 Second
delay( 5000 );
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Teacher, Instructor, E-Mentor, R&D and Consulting
- Programming Language
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi, Arm, Silicon Labs, Espressif, Etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Automation
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- RTOS
- eHealth Sensors, Biosensor, and Biometric
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Consulting
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2023
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@thesass2063
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
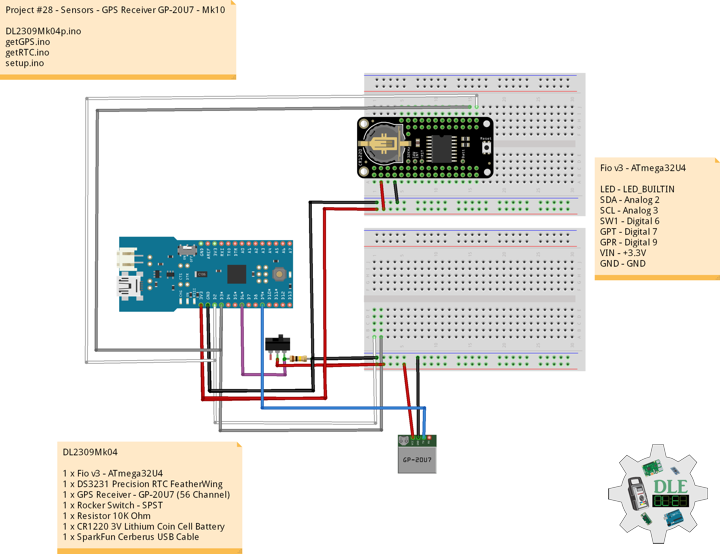
Project #28 – Sensors – GPS Receiver GP-20U7 – Mk10
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Sensors #GPSReceiver #Adafruit #SparkFun #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
GPS Receiver – GP-20U7
The GP-20U7 is a compact GPS receiver with a built-in high performances All-In-One GPS chipset. The GP-20U7 accurately provides position, velocity, and time readings as well possessing high sensitivity and tracking capabilities. Thanks to the low power consumption this receiver requires, the GP-20U7 is ideal for portable applications such as tablet PCs, smart phones, and other devices requiring positioning capability. This 56-Channel GPS module, that supports a standard NMEA-0183 and uBlox 7 protocol, has low power consumption of 40mA@3.3V (max), an antenna on board, and -162dBm tracking sensitivity. With 56 channels in search mode and 22 channels “All-In-View” tracking, the GP-20U7 is quite the work horse for its size.
DL2309Mk04
1 x Fio v3 – ATmega32U4
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x GPS Receiver – GP-20U7 (56 Channel)
1 x Rocker Switch – SPST
1 x Resistor 10K Ohm
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
Fio v3 – ATmega32U4
LED – LED_BUILTIN
SDA – Digital 2
SCL – Digital 3
SW1 – Digital 6
GPT – Digital 7
GPR – Digital 9
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
——
DL2309Mk04p.ino
/****** Don Luc Electronics © ******
Software Version Information
Project #28 - Sensors - GPS Receiver GP-20U7 - Mk10
28-10
DL2309Mk04p.ino
1 x Fio v3 - ATmega32U4
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x GPS Receiver - GP-20U7 (56 Channel)
1 x Rocker Switch - SPST
1 x Resistor 10K Ohm
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// DS3231 Precision RTC
#include <RTClib.h>
// Two Wire Interface (TWI/I2C)
#include <Wire.h>
// Keyboard
#include <Keyboard.h>
// GPS Receiver
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
// Software Serial
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Keyboard
String sKeyboard = "";
// DS3231 Precision RTC
RTC_DS3231 rtc;
String dateRTC = "";
String timeRTC = "";
// GPS Receiver
#define gpsRXPIN 9
// This one is unused and doesnt have a conection
#define gpsTXPIN 7
// The TinyGPS++ object
TinyGPSPlus gps;
// Latitude
float TargetLat;
// Longitude
float TargetLon;
// GPS Date, Time
// GPS Date
String TargetDat;
// GPS Time
String TargetTim;
// GPS Status
String GPSSt = "";
// The serial connection to the GPS device
SoftwareSerial tGPS(gpsRXPIN, gpsTXPIN);
// The number of the Rocker Switch pin
int iSwitch = 6;
// Variable for reading the button status
int SwitchState = 0;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "28-10";
void loop() {
// Date and Time RTC
isRTC ();
// isGPS
isGPS();
// GPS Keyboard
isGPSKeyboard();
// Read the state of the Switch value:
SwitchState = digitalRead(iSwitch);
// Check if the button is pressed. If it is, the SwitchState is HIGH:
if (SwitchState == HIGH) {
Keyboard.println(sKeyboard);
}
// Delay 1 Second
delay(1000);
}
getGPS.ino
// GPS Receiver
// Setup GPS
void setupGPS() {
// Setup GPS
tGPS.begin( 9600 );
}
// isGPS
void isGPS(){
// Receives NEMA data from GPS receiver
// This sketch displays information every time a new sentence is correctly encoded
while ( tGPS.available() > 0)
if (gps.encode( tGPS.read() ))
{
// GPS Vector Pointer Target
displayInfo();
// GPS Date, Time
displayDTS();
}
if (millis() > 5000 && gps.charsProcessed() < 10)
{
while(true);
}
}
// GPS Vector Pointer Target
void displayInfo(){
// Location
if (gps.location.isValid())
{
// Latitude
TargetLat = gps.location.lat();
// Longitude
TargetLon = gps.location.lng();
// GPS Status 2
GPSSt = "Yes";
}
else
{
// GPS Status 0
GPSSt = "No";
TargetLat = 0;
TargetLon = 0;
}
}
// GPS Date, Time
void displayDTS(){
// Date
TargetDat = "";
if (gps.date.isValid())
{
// Date
// Year
TargetDat += String(gps.date.year(), DEC);
TargetDat += "/";
// Month
TargetDat += String(gps.date.month(), DEC);
TargetDat += "/";
// Day
TargetDat += String(gps.date.day(), DEC);
}
// Time
TargetTim = "";
if (gps.time.isValid())
{
// Time
// Hour
TargetTim += String(gps.time.hour(), DEC);
TargetTim += ":";
// Minute
TargetTim += String(gps.time.minute(), DEC);
TargetTim += ":";
// Secound
TargetTim += String(gps.time.second(), DEC);
}
}
// GPS Keyboard
void isGPSKeyboard(){
// GPS Keyboard
// Keyboard
// GPS Vector Pointer Target
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + GPSSt + "|" + String(TargetLat)
+ "|" + String(TargetLon) + "|";
// Keyboard
// GPS Date, Time
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + TargetDat + "|" +
TargetTim + "|*";
}
getRTC.ino
// Date & Time
// DS3231 Precision RTC
void setupRTC() {
// DS3231 Precision RTC
if (! rtc.begin()) {
//Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC");
//Serial.flush();
while (1) delay(10);
}
if (rtc.lostPower()) {
//Serial.println("RTC lost power, let's set the time!");
// When time needs to be set on a new device, or after a power loss, the
// following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
// This line sets the RTC with an explicit date & time, for example to set
// January 21, 2014 at 3am you would call:
//rtc.adjust(DateTime(2023, 8, 10, 11, 0, 0));
}
}
// Date and Time RTC
void isRTC () {
// Date and Time
dateRTC = "";
timeRTC = "";
DateTime now = rtc.now();
// Date
dateRTC = now.year(), DEC;
dateRTC = dateRTC + "/";
dateRTC = dateRTC + now.month(), DEC;
dateRTC = dateRTC + "/";
dateRTC = dateRTC + now.day(), DEC;
// Time
timeRTC = now.hour(), DEC;
timeRTC = timeRTC + ":";
timeRTC = timeRTC + now.minute(), DEC;
timeRTC = timeRTC + ":";
timeRTC = timeRTC + now.second(), DEC;
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = "SEN|" + sver + "|" + String(dateRTC) + "|" +
String(timeRTC) + "|";
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Wire - Inialize I2C Hardware
Wire.begin();
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Date & Time RTC
// DS3231 Precision RTC
setupRTC();
// Initialize control over the keyboard:
Keyboard.begin();
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// GPS Receiver
// Setup GPS
setupGPS();
// Initialize the Switch pin as an input
pinMode(iSwitch, INPUT);
// Initialize digital pin LED_BUILTIN as an output
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
// Turn the LED on HIGH
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH);
// Delay 5 Second
delay( 5000 );
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Programming Language
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- RTOS
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor, E-Mentor, STEAM, and Arts-Based Training
- Programming Language
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2023
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@thesass2063
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
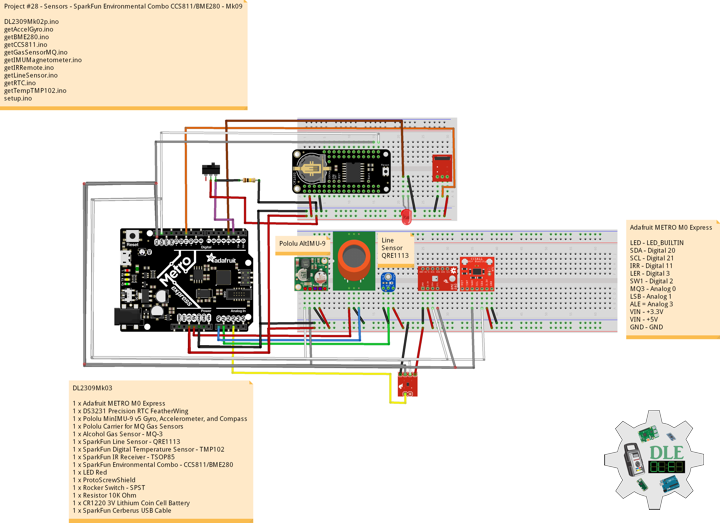
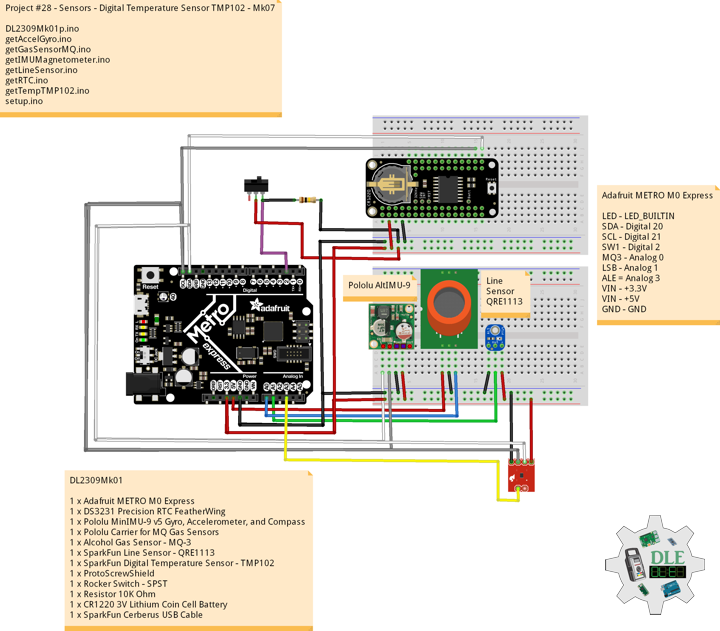
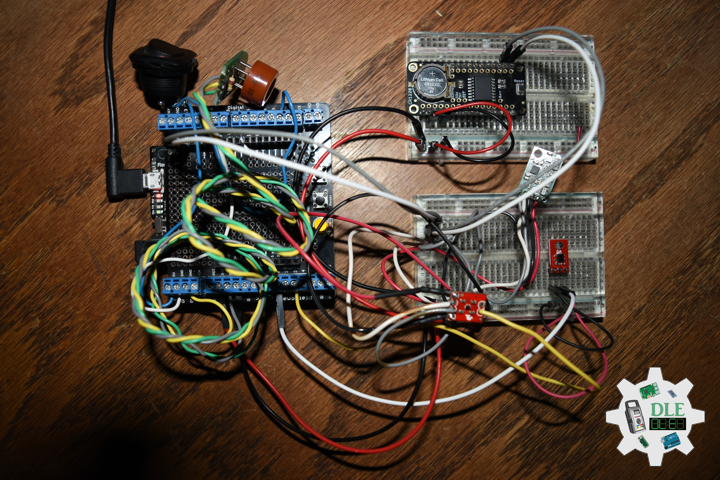
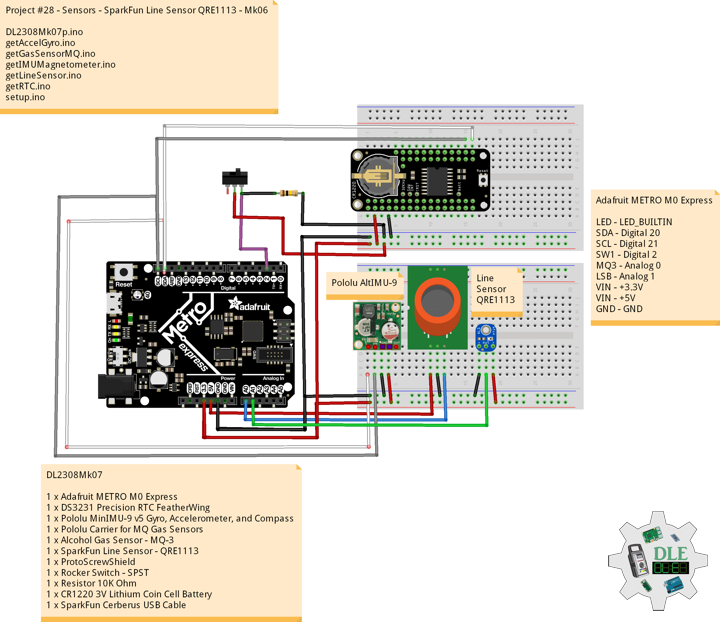
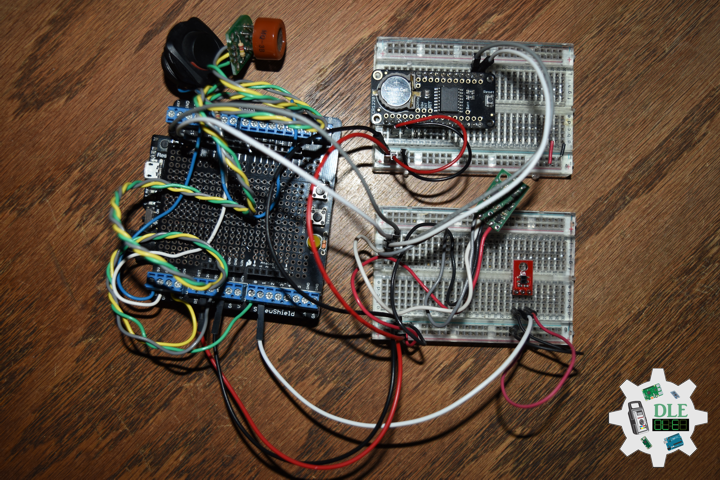
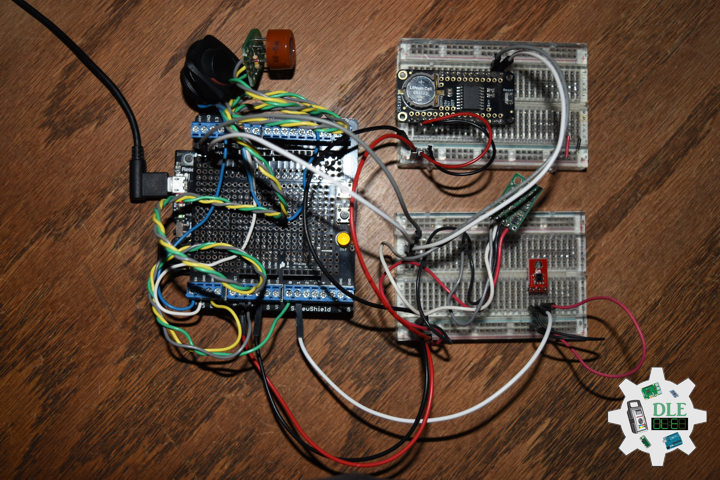
Project #28 – Sensors – SparkFun Environmental Combo CCS811/BME280 – Mk09
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Sensors #CCS811 #BME280 #TSOP85 #TMP102 #LineSensor #AlcoholGasSensor #MinIMU9 #Pololu #Adafruit #SparkFun #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
SparkFun Environmental Combo – CCS811/BME280
The SparkFun CCS811/BME280 Environmental Combo Breakout takes care of all your atmospheric-quality sensing needs with the popular CCS811 and BME280 ICs. This unique breakout provides a variety of environmental data, including barometric pressure, humidity, temperature, TVOCs and equivalent eCO2 levels.
The CCS811 is an exceedingly popular sensor, providing readings for equivalent eCO2 in the parts per million (PPM) and total volatile organic compounds in the parts per billion (PPB). The CCS811 also has a feature that allows it to fine-tune its readings if it has access to the current humidity and temperature. Luckily for us, the BME280 provides humidity, temperature and barometric pressure. This allows the sensors to work together to give us more accurate readings than they’d be able to provide on their own. We also made it easy to interface with them via I2C.
DL2309Mk03
1 x Adafruit METRO M0 Express
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x Pololu MinIMU-9 v5 Gyro, Accelerometer, and Compass
1 x Pololu Carrier for MQ Gas Sensors
1 x Alcohol Gas Sensor – MQ-3
1 x SparkFun Line Sensor – QRE1113
1 x SparkFun Digital Temperature Sensor – TMP102
1 x SparkFun IR Receiver – TSOP85
1 x SparkFun Environmental Combo – CCS811/BME280
1 x LED Red
1 x ProtoScrewShield
1 x Rocker Switch – SPST
2 x Resistor 10K Ohm
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
Adafruit METRO M0 Express
LED – LED_BUILTIN
SDA – Digital 20
SCL – Digital 21
IRR – Digital 11
LER – Digital 3
SW1 – Digital 2
MQ3 – Analog 0
LSB – Analog 1
ALE = Analog 3
VIN – +3.3V
VIN – +5V
GND – GND
——
DL2309Mk03p.ino
/****** Don Luc Electronics © ******
Software Version Information
Project #28 - Sensors - SparkFun Environmental Combo CCS811/BME280 - Mk09
28-09
DL2309Mk03p.ino
1 x Adafruit METRO M0 Express
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x Pololu MinIMU-9 v5 Gyro, Accelerometer, and Compass
1 x Pololu Carrier for MQ Gas Sensors
1 x Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
1 x SparkFun Line Sensor - QRE1113
1 x SparkFun Digital Temperature Sensor - TMP102
1 x SparkFun IR Receiver - TSOP85
1 x SparkFun Environmental Combo - CCS811/BME280
1 x LED Red
1 x ProtoScrewShield
1 x Rocker Switch - SPST
2 x Resistor 10K Ohm
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// DS3231 Precision RTC
#include <RTClib.h>
// Two Wire Interface (TWI/I2C)
#include <Wire.h>
// Keyboard
#include <Keyboard.h>
// Includes and variables for IMU integration
// STMicroelectronics LSM6DS33 Gyroscope and Accelerometer
#include <LSM6.h>
// STMicroelectronics LIS3MDL Magnetometer
#include <LIS3MDL.h>
// SparkFun Digital Temperature Sensor TMP102
#include <SparkFunTMP102.h>
// SparkFun IR Receiver - TSOP85
#include <IRremote.h>
// SparkFun BME280 - Temperature, Humidity, Barometric Pressure, and Altitude
#include <SparkFunBME280.h>
// SparkFun CCS811 - eCO2 & tVOC
#include <SparkFunCCS811.h>
// Keyboard
String sKeyboard = "";
// DS3231 Precision RTC
RTC_DS3231 rtc;
String dateRTC = "";
String timeRTC = "";
// Pololu 9DoF IMU
// STMicroelectronics LSM6DS33 Gyroscope and Accelerometer
LSM6 imu;
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
// Accelerometer
int imuAX;
int imuAY;
int imuAZ;
// Gyroscopes
int imuGX;
int imuGY;
int imuGZ;
// STMicroelectronics LIS3MDL Magnetometer
LIS3MDL mag;
// Magnetometer
int magX;
int magY;
int magZ;
// Gas Sensors MQ
// Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
int iMQ3 = A0;
int iMQ3Raw = 0;
int iMQ3ppm = 0;
// SparkFun Line Sensor - QRE1113 (Analog)
int iLine = A1;
int iLineSensor = 0;
// SparkFun Digital Temperature Sensor TMP102
const int ALERT_PIN = A3;
TMP102 sensor0;
float temperature;
boolean alertPinState;
boolean alertRegisterState;
// SparkFun IR Receiver - TSOP85
int RECV_PIN = 11;
IRrecv irrecv(RECV_PIN);
decode_results results;
String IRValue = "";
int iLEDRed = 3;
// SparkFun BME280 - Temperature, Humidity, Barometric Pressure, and Altitude
BME280 myBME280;
float BMEtempC = 0;
float BMEhumid = 0;
float BMEpressure = 0;
float BMEaltitudeM = 0;
// SparkFun CCS811 - eCO2 & tVOC
// Default I2C Address
#define CCS811_ADDR 0x5B
CCS811 myCCS811(CCS811_ADDR);
float CCS811CO2 = 0;
float CCS811TVOC = 0;
// The number of the Rocker Switch pin
int iSwitch = 2;
// Variable for reading the button status
int SwitchState = 0;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "28-09";
void loop() {
// Date and Time RTC
isRTC ();
// Pololu Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
isIMU();
// Pololu Magnetometer
isMag();
// Gas Sensors MQ
isGasSensor();
// SparkFun Line Sensor
isLineSensor();
// SparkFun Temperature TMP102
isTMP102();
// SparkFun IR Receiver - TSOP85
isIR();
// SparkFun BME280 - Temperature, Humidity, Barometric Pressure, and Altitude
isBME280();
// SparkFun CCS811 - eCO2 & tVOC
isCCS811();
// Read the state of the Switch value:
SwitchState = digitalRead(iSwitch);
// Check if the button is pressed. If it is, the SwitchState is HIGH:
if (SwitchState == HIGH) {
Keyboard.println(sKeyboard);
}
// Delay 1 Second
delay(1000);
}
getAccelGyro.ino
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
// Setup IMU
void setupIMU() {
// Setup IMU
imu.init();
// Default
imu.enableDefault();
}
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
void isIMU() {
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
imu.read();
// Accelerometer x, y, z
imuAX = imu.a.x;
imuAY = imu.a.y;
imuAZ = imu.a.z;
// Gyroscopes x, y, z
imuGX = imu.g.x;
imuGY = imu.g.y;
imuGZ = imu.g.z;
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(imuAX) + "|" + String(imuAY) + "|"
+ String(imuAZ) + "|";
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(imuGX) + "|" + String(imuGY) + "|"
+ String(imuGZ) + "|";
}
getBME280.ino
// SparkFun BME280 - Temperature, Humidity, Barometric Pressure, and Altitude
// isBME280 - Temperature, Humidity, Barometric Pressure, and Altitude
void isBME280(){
// Temperature Celsius
BMEtempC = myBME280.readTempC();
// Humidity
BMEhumid = myBME280.readFloatHumidity();
// Barometric Pressure
BMEpressure = myBME280.readFloatPressure();
// Altitude Meters
BMEaltitudeM = (myBME280.readFloatAltitudeMeters(), 2);
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(BMEtempC) + "|" + String(BMEhumid) + "|" +
String(BMEpressure) + "|" + String(BMEaltitudeM) + "|";
}
getCCS811.ino
// CCS811 - eCO2 & tVOC
// isCCS811 - eCO2 & tVOC
void isCCS811(){
// This sends the temperature & humidity data to the CCS811
myCCS811.setEnvironmentalData(BMEhumid, BMEtempC);
// Calling this function updates the global tVOC and eCO2 variables
myCCS811.readAlgorithmResults();
// eCO2 Concentration
CCS811CO2 = myCCS811.getCO2();
// tVOC Concentration
CCS811TVOC = myCCS811.getTVOC();
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(CCS811CO2) + "|" + String(CCS811TVOC) + "|*";
}
getGasSensorMQ.ino
// Gas Sensors MQ
// Gas Sensor
void isGasSensor() {
// Read in analog value from each gas sensors
// Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
iMQ3ppm = isMQ3( iMQ3Raw );
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(iMQ3ppm) + "|";
}
// Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
int isMQ3(double rawValue) {
double RvRo = rawValue;
// % BAC = breath mg/L * 0.21
double bac = RvRo * 0.21;
return bac;
}
getIMUMagnetometer.ino
// IMU Magnetometer
// Setup Magnetometer
void setupMag() {
// Setup Magnetometer
mag.init();
// Default
mag.enableDefault();
}
// Magnetometer
void isMag() {
// Magnetometer
mag.read();
// Magnetometer x, y, z
magX = mag.m.x;
magY = mag.m.y;
magZ = mag.m.z;
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(magX) + "|" + String(magY) + "|"
+ String(magZ) + "|";
}
getIRRemote.ino
// SparkFun IR Receiver - TSOP85
// Setup
void isSetupIR(){
// Initialize digital pin LED Red as an output
pinMode(iLEDRed, OUTPUT);
// Start the receiver
irrecv.enableIRIn();
}
//
void isIR(){
if (irrecv.decode(&results))
{
// LED Red HIGH
digitalWrite(iLEDRed, HIGH);
//Serial.print("IR RECV Code = 0x ");
//Serial.println(results.value, HEX);
IRValue = "0x ";
IRValue = IRValue + String(results.value, HEX);
// LED Red LOW
digitalWrite(iLEDRed, LOW);
// IR Resume
irrecv.resume();
}
else {
IRValue = "0";
}
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(IRValue) + "|";
}
getLineSensor.ino
// Line Sensor
// isLine Sensor
void isLineSensor(){
// Line Sensor
iLineSensor = analogRead(iLine);
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(iLineSensor) + "|";
}
getRTC.ino
// Date & Time
// DS3231 Precision RTC
void setupRTC() {
// DS3231 Precision RTC
if (! rtc.begin()) {
//Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC");
//Serial.flush();
while (1) delay(10);
}
if (rtc.lostPower()) {
//Serial.println("RTC lost power, let's set the time!");
// When time needs to be set on a new device, or after a power loss, the
// following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
// This line sets the RTC with an explicit date & time, for example to set
// January 21, 2014 at 3am you would call:
//rtc.adjust(DateTime(2023, 8, 10, 11, 0, 0));
}
}
// Date and Time RTC
void isRTC () {
// Date and Time
dateRTC = "";
timeRTC = "";
DateTime now = rtc.now();
// Date
dateRTC = now.year(), DEC;
dateRTC = dateRTC + "/";
dateRTC = dateRTC + now.month(), DEC;
dateRTC = dateRTC + "/";
dateRTC = dateRTC + now.day(), DEC;
// Time
timeRTC = now.hour(), DEC;
timeRTC = timeRTC + ":";
timeRTC = timeRTC + now.minute(), DEC;
timeRTC = timeRTC + ":";
timeRTC = timeRTC + now.second(), DEC;
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = "SEN|" + sver + "|" + String(dateRTC) + "|" +
String(timeRTC) + "|";
}
getTempTMP102.ino
// SparkFun Digital Temperature Sensor TMP102
// Setup TMP102
void isSetupTMP102(){
// Declare alertPin as an input
pinMode(ALERT_PIN,INPUT);
// Begin
//It will return true on success or false on failure to communicate
if(!sensor0.begin())
{
while(1);
}
// set the Conversion Rate
//0-3: 0:0.25Hz, 1:1Hz, 2:4Hz, 3:8Hz
sensor0.setConversionRate(2);
//set Extended Mode.
//0:12-bit Temperature(-55C to +128C) 1:13-bit Temperature(-55C to +150C)
sensor0.setExtendedMode(0);
// Set T_HIGH, the upper limit to trigger the alert on
// Set T_HIGH in C
sensor0.setHighTempC(29.4);
// Set T_LOW, the lower limit to shut turn off the alert
// set T_LOW in C
sensor0.setLowTempC(27.67);
}
// is TMP102
void isTMP102(){
// Turn sensor on to start temperature measurement.
// Current consumtion typically ~10uA.
sensor0.wakeup();
// read temperature data C
temperature = sensor0.readTempC();
// Check for Alert
// Read the Alert from pin
alertPinState = digitalRead(ALERT_PIN);
// Read the Alert from register
alertRegisterState = sensor0.alert();
// Place sensor in sleep mode to save power.
// Current consumtion typically <0.5uA.
sensor0.sleep();
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(temperature) + "|" +
String(alertPinState) + "|" + String(alertRegisterState) + "|";
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Wire - Inialize I2C Hardware
Wire.begin();
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Date & Time RTC
// DS3231 Precision RTC
setupRTC();
// Initialize control over the keyboard:
Keyboard.begin();
// Pololu Setup IMU
setupIMU();
// Pololu Setup Magnetometer
setupMag();
// Setup TMP102
isSetupTMP102();
// SetupTSOP85
isSetupIR();
// SparkFun BME280 - Temperature, Humidity, Barometric Pressure, and Altitude
myBME280.begin();
// CCS811 - eCO2 & tVOC
myCCS811.begin();
// Initialize the Switch pin as an input
pinMode(iSwitch, INPUT);
// Initialize digital pin LED_BUILTIN as an output
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
// Turn the LED on HIGH
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH);
// Delay 5 Second
delay( 5000 );
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Programming Language
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- RTOS
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor, E-Mentor, STEAM, and Arts-Based Training
- Programming Language
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2023
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@thesass2063
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
Project #28 – Sensors – Digital Temperature Sensor TMP102 – Mk07
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Sensors #TMP102 #LineSensor #AlcoholGasSensor #MinIMU9 #Pololu #Adafruit #SparkFun #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
SparkFun Digital Temperature Sensor – TMP102
The TMP102 is an easy-to-use digital temperature sensor from Texas Instruments. The TMP102 breakout allows you to easily incorporate the digital temperature sensor into your project. While some temperature sensors use an analog voltage to represent the temperature, the TMP102 uses the I2C bus of the Arduino to communicate the temperature. Needless to say, this is a very handy sensor that doesn’t require much setup.
The TMP102 is capable of reading temperatures to a resolution of 0.0625°C, and is accurate up to 0.5°C. The breakout has built-in 4.7k Ohm pull-up resistors for I2C communications and runs from 1.4V to 3.6V. I2C communication uses an open drain signaling, so there is no need to use level shifting.
DL2309Mk01
1 x Adafruit METRO M0 Express
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x Pololu MinIMU-9 v5 Gyro, Accelerometer, and Compass
1 x Pololu Carrier for MQ Gas Sensors
1 x Alcohol Gas Sensor – MQ-3
1 x SparkFun Line Sensor – QRE1113
1 x SparkFun Digital Temperature Sensor – TMP102
1 x ProtoScrewShield
1 x Rocker Switch – SPST
2 x Resistor 10K Ohm
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
Adafruit METRO M0 Express
LED – LED_BUILTIN
SDA – Digital 20
SCL – Digital 21
SW1 – Digital 2
MQ3 – Analog 0
LSB – Analog 1
ALE = Analog 3
VIN – +3.3V
VIN – +5V
GND – GND
——
DL2309Mk01p.ino
/****** Don Luc Electronics © ******
Software Version Information
Project #28 - Sensors - Digital Temperature Sensor TMP102 - Mk07
28-07
DL2309Mk01p.ino
1 x Adafruit METRO M0 Express
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x Pololu MinIMU-9 v5 Gyro, Accelerometer, and Compass
1 x Pololu Carrier for MQ Gas Sensors
1 x Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
1 x SparkFun Line Sensor - QRE1113
1 x SparkFun Digital Temperature Sensor - TMP102
1 x ProtoScrewShield
1 x Rocker Switch - SPST
2 x Resistor 10K Ohm
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// DS3231 Precision RTC
#include <RTClib.h>
// Two Wire Interface (TWI/I2C)
#include <Wire.h>
// Keyboard
#include <Keyboard.h>
// Includes and variables for IMU integration
// STMicroelectronics LSM6DS33 Gyroscope and Accelerometer
#include <LSM6.h>
// STMicroelectronics LIS3MDL Magnetometer
#include <LIS3MDL.h>
// SparkFun Digital Temperature Sensor TMP102
#include <SparkFunTMP102.h>
// Keyboard
String sKeyboard = "";
// DS3231 Precision RTC
RTC_DS3231 rtc;
String dateRTC = "";
String timeRTC = "";
// Pololu 9DoF IMU
// STMicroelectronics LSM6DS33 Gyroscope and Accelerometer
LSM6 imu;
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
// Accelerometer
int imuAX;
int imuAY;
int imuAZ;
// Gyroscopes
int imuGX;
int imuGY;
int imuGZ;
// STMicroelectronics LIS3MDL Magnetometer
LIS3MDL mag;
// Magnetometer
int magX;
int magY;
int magZ;
// Gas Sensors MQ
// Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
int iMQ3 = A0;
int iMQ3Raw = 0;
int iMQ3ppm = 0;
// SparkFun Line Sensor - QRE1113 (Analog)
int iLine = A1;
int iLineSensor = 0;
// SparkFun Digital Temperature Sensor TMP102
const int ALERT_PIN = A3;
TMP102 sensor0;
float temperature;
boolean alertPinState;
boolean alertRegisterState;
// The number of the Rocker Switch pin
int iSwitch = 2;
// Variable for reading the button status
int SwitchState = 0;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "28-07";
void loop() {
// Date and Time RTC
isRTC ();
// Pololu Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
isIMU();
// Pololu Magnetometer
isMag();
// Gas Sensors MQ
isGasSensor();
// SparkFun Line Sensor
isLineSensor();
// SparkFun Temperature TMP102
isTMP102();
// Read the state of the Switch value:
SwitchState = digitalRead(iSwitch);
// Check if the button is pressed. If it is, the SwitchState is HIGH:
if (SwitchState == HIGH) {
Keyboard.println(sKeyboard);
}
// Delay 1 Second
delay(1000);
}
getAccelGyro.ino
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
// Setup IMU
void setupIMU() {
// Setup IMU
imu.init();
// Default
imu.enableDefault();
}
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
void isIMU() {
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
imu.read();
// Accelerometer x, y, z
imuAX = imu.a.x;
imuAY = imu.a.y;
imuAZ = imu.a.z;
// Gyroscopes x, y, z
imuGX = imu.g.x;
imuGY = imu.g.y;
imuGZ = imu.g.z;
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(imuAX) + "|" + String(imuAY) + "|"
+ String(imuAZ) + "|";
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(imuGX) + "|" + String(imuGY) + "|"
+ String(imuGZ) + "|";
}
getGasSensorMQ.ino
// Gas Sensors MQ
// Gas Sensor
void isGasSensor() {
// Read in analog value from each gas sensors
// Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
iMQ3ppm = isMQ3( iMQ3Raw );
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(iMQ3ppm) + "|";
}
// Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
int isMQ3(double rawValue) {
double RvRo = rawValue;
// % BAC = breath mg/L * 0.21
double bac = RvRo * 0.21;
return bac;
}
getIMUMagnetometer.ino
// IMU Magnetometer
// Setup Magnetometer
void setupMag() {
// Setup Magnetometer
mag.init();
// Default
mag.enableDefault();
}
// Magnetometer
void isMag() {
// Magnetometer
mag.read();
// Magnetometer x, y, z
magX = mag.m.x;
magY = mag.m.y;
magZ = mag.m.z;
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(magX) + "|" + String(magY) + "|"
+ String(magZ) + "|";
}
getLineSensor.ino
// Line Sensor
// isLine Sensor
void isLineSensor(){
// Line Sensor
iLineSensor = analogRead(iLine);
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(iLineSensor) + "|";
}
getRTC.ino
// Date & Time
// DS3231 Precision RTC
void setupRTC() {
// DS3231 Precision RTC
if (! rtc.begin()) {
//Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC");
//Serial.flush();
while (1) delay(10);
}
if (rtc.lostPower()) {
//Serial.println("RTC lost power, let's set the time!");
// When time needs to be set on a new device, or after a power loss, the
// following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
// This line sets the RTC with an explicit date & time, for example to set
// January 21, 2014 at 3am you would call:
//rtc.adjust(DateTime(2023, 8, 10, 11, 0, 0));
}
}
// Date and Time RTC
void isRTC () {
// Date and Time
dateRTC = "";
timeRTC = "";
DateTime now = rtc.now();
// Date
dateRTC = now.year(), DEC;
dateRTC = dateRTC + "/";
dateRTC = dateRTC + now.month(), DEC;
dateRTC = dateRTC + "/";
dateRTC = dateRTC + now.day(), DEC;
// Time
timeRTC = now.hour(), DEC;
timeRTC = timeRTC + ":";
timeRTC = timeRTC + now.minute(), DEC;
timeRTC = timeRTC + ":";
timeRTC = timeRTC + now.second(), DEC;
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = "SEN|" + sver + "|" + String(dateRTC) + "|" +
String(timeRTC) + "|";
}
getTempTMP102.ino
// SparkFun Digital Temperature Sensor TMP102
// Setup TMP102
void isSetupTMP102(){
// Declare alertPin as an input
pinMode(ALERT_PIN,INPUT);
// Begin
//It will return true on success or false on failure to communicate
if(!sensor0.begin())
{
while(1);
}
// set the Conversion Rate
//0-3: 0:0.25Hz, 1:1Hz, 2:4Hz, 3:8Hz
sensor0.setConversionRate(2);
//set Extended Mode.
//0:12-bit Temperature(-55C to +128C) 1:13-bit Temperature(-55C to +150C)
sensor0.setExtendedMode(0);
// Set T_HIGH, the upper limit to trigger the alert on
// Set T_HIGH in C
sensor0.setHighTempC(29.4);
// Set T_LOW, the lower limit to shut turn off the alert
// set T_LOW in C
sensor0.setLowTempC(27.67);
}
// is TMP102
void isTMP102(){
// Turn sensor on to start temperature measurement.
// Current consumtion typically ~10uA.
sensor0.wakeup();
// read temperature data C
temperature = sensor0.readTempC();
// Check for Alert
// Read the Alert from pin
alertPinState = digitalRead(ALERT_PIN);
// Read the Alert from register
alertRegisterState = sensor0.alert();
// Place sensor in sleep mode to save power.
// Current consumtion typically <0.5uA.
sensor0.sleep();
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(temperature) + "|" +
String(alertPinState) + "|" + String(alertRegisterState) + "|*";
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Wire - Inialize I2C Hardware
Wire.begin();
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Date & Time RTC
// DS3231 Precision RTC
setupRTC();
// Initialize control over the keyboard:
Keyboard.begin();
// Pololu Setup IMU
setupIMU();
// Pololu Setup Magnetometer
setupMag();
// Setup TMP102
isSetupTMP102();
// Initialize the Switch pin as an input
pinMode(iSwitch, INPUT);
// Initialize digital pin LED_BUILTIN as an output
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
// Turn the LED on HIGH
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH);
// Delay 5 Second
delay( 5000 );
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Programming Language
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- RTOS
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor, E-Mentor, STEAM, and Arts-Based Training
- Programming Language
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2023
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@thesass2063
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
Project #28 – Sensors – SparkFun Line Sensor QRE1113 – Mk06
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Sensors #LineSensor #AlcoholGasSensor #MinIMU9 #Pololu #Adafruit #SparkFun #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
SparkFun Line Sensor QRE1113 (Analog)
This version of the QRE1113 breakout board features an easy-to-use analog output, which will vary depending on the amount of IR light reflected back to the sensor. This tiny board is perfect for line sensing applications and can be used in both 3.3V and 5V systems.
The board’s QRE1113 IR reflectance sensor is comprised of two parts – an IR emitting LED and an IR sensitive phototransistor. When you apply power to the VCC and GND pins the IR LED inside the sensor will illuminate. A 100 Ohm resistor is on-board and placed in series with the LED to limit current. A 10k Ohm resistor pulls the output pin high, but when the light from the LED is reflected back onto the phototransistor the output will begin to go lower. The more IR light sensed by the phototransistor, the lower the output voltage of the breakout board.
These sensors are widely used in line following robots, white surfaces reflect much more light than black, so, when directed towards a white surface, the voltage output will be lower than that on a black surface.
DL2308Mk07
1 x Adafruit METRO M0 Express
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x Pololu MinIMU-9 v5 Gyro, Accelerometer, and Compass
1 x Pololu Carrier for MQ Gas Sensors
1 x Alcohol Gas Sensor – MQ-3
1 x SparkFun Line Sensor – QRE1113
1 x ProtoScrewShield
1 x Rocker Switch – SPST
2 x Resistor 10K Ohm
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
Adafruit METRO M0 Express
LED – LED_BUILTIN
SDA – Digital 20
SCL – Digital 21
SW1 – Digital 2
MQ3 – Analog 0
LSB – Analog 1
VIN – +3.3V
VIN – +5V
GND – GND
——
DL2308Mk07p.ino
/****** Don Luc Electronics © ******
Software Version Information
Project #28 - Sensors - SparkFun Line Sensor QRE1113 - Mk06
28-06
DL2308Mk07p.ino
1 x Adafruit METRO M0 Express
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x Pololu MinIMU-9 v5 Gyro, Accelerometer, and Compass
1 x Pololu Carrier for MQ Gas Sensors
1 x Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
1 x SparkFun Line Sensor - QRE1113
1 x ProtoScrewShield
1 x Rocker Switch - SPST
2 x Resistor 10K Ohm
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// DS3231 Precision RTC
#include <RTClib.h>
// Two Wire Interface (TWI/I2C)
#include <Wire.h>
// Keyboard
#include <Keyboard.h>
// Includes and variables for IMU integration
// STMicroelectronics LSM6DS33 Gyroscope and Accelerometer
#include <LSM6.h>
// STMicroelectronics LIS3MDL Magnetometer
#include <LIS3MDL.h>
// Keyboard
String sKeyboard = "";
// DS3231 Precision RTC
RTC_DS3231 rtc;
String dateRTC = "";
String timeRTC = "";
// Pololu 9DoF IMU
// STMicroelectronics LSM6DS33 Gyroscope and Accelerometer
LSM6 imu;
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
// Accelerometer
int imuAX;
int imuAY;
int imuAZ;
// Gyroscopes
int imuGX;
int imuGY;
int imuGZ;
// STMicroelectronics LIS3MDL Magnetometer
LIS3MDL mag;
// Magnetometer
int magX;
int magY;
int magZ;
// Gas Sensors MQ
// Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
int iMQ3 = A0;
int iMQ3Raw = 0;
int iMQ3ppm = 0;
// SparkFun Line Sensor - QRE1113 (Analog)
int iLine = A1;
int iLineSensor = 0;
// The number of the Rocker Switch pin
int iSwitch = 2;
// Variable for reading the button status
int SwitchState = 0;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "28-06";
void loop() {
// Date and Time RTC
isRTC ();
// Pololu Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
isIMU();
// Pololu Magnetometer
isMag();
// Gas Sensors MQ
isGasSensor();
// SparkFun Line Sensor
isLineSensor();
// Read the state of the Switch value:
SwitchState = digitalRead(iSwitch);
// Check if the button is pressed. If it is, the SwitchState is HIGH:
if (SwitchState == HIGH) {
Keyboard.println(sKeyboard);
}
// Delay 1 Second
delay(1000);
}
getAccelGyro.ino
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
// Setup IMU
void setupIMU() {
// Setup IMU
imu.init();
// Default
imu.enableDefault();
}
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
void isIMU() {
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
imu.read();
// Accelerometer x, y, z
imuAX = imu.a.x;
imuAY = imu.a.y;
imuAZ = imu.a.z;
// Gyroscopes x, y, z
imuGX = imu.g.x;
imuGY = imu.g.y;
imuGZ = imu.g.z;
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(imuAX) + "|" + String(imuAY) + "|"
+ String(imuAZ) + "|";
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(imuGX) + "|" + String(imuGY) + "|"
+ String(imuGZ) + "|";
}
getGasSensorMQ.ino
// Gas Sensors MQ
// Gas Sensor
void isGasSensor() {
// Read in analog value from each gas sensors
// Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
iMQ3ppm = isMQ3( iMQ3Raw );
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(iMQ3ppm) + "|";
}
// Alcohol Gas Sensor - MQ-3
int isMQ3(double rawValue) {
double RvRo = rawValue;
// % BAC = breath mg/L * 0.21
double bac = RvRo * 0.21;
return bac;
}
getIMUMagnetometer.ino
// IMU Magnetometer
// Setup Magnetometer
void setupMag() {
// Setup Magnetometer
mag.init();
// Default
mag.enableDefault();
}
// Magnetometer
void isMag() {
// Magnetometer
mag.read();
// Magnetometer x, y, z
magX = mag.m.x;
magY = mag.m.y;
magZ = mag.m.z;
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(magX) + "|" + String(magY) + "|"
+ String(magZ) + "|";
}
getLineSensor.ino
// Line Sensor
// isLine Sensor
void isLineSensor(){
// Line Sensor
iLineSensor = analogRead(iLine);
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = sKeyboard + String(iLineSensor) + "|*";
}
getRTC.ino
// Date & Time
// DS3231 Precision RTC
void setupRTC() {
// DS3231 Precision RTC
if (! rtc.begin()) {
//Serial.println("Couldn't find RTC");
//Serial.flush();
while (1) delay(10);
}
if (rtc.lostPower()) {
//Serial.println("RTC lost power, let's set the time!");
// When time needs to be set on a new device, or after a power loss, the
// following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
// This line sets the RTC with an explicit date & time, for example to set
// January 21, 2014 at 3am you would call:
//rtc.adjust(DateTime(2023, 8, 10, 11, 0, 0));
}
}
// Date and Time RTC
void isRTC () {
// Date and Time
dateRTC = "";
timeRTC = "";
DateTime now = rtc.now();
// Date
dateRTC = now.year(), DEC;
dateRTC = dateRTC + "/";
dateRTC = dateRTC + now.month(), DEC;
dateRTC = dateRTC + "/";
dateRTC = dateRTC + now.day(), DEC;
// Time
timeRTC = now.hour(), DEC;
timeRTC = timeRTC + ":";
timeRTC = timeRTC + now.minute(), DEC;
timeRTC = timeRTC + ":";
timeRTC = timeRTC + now.second(), DEC;
// Keyboard
sKeyboard = "SEN|" + sver + "|" + String(dateRTC) + "|" +
String(timeRTC) + "|";
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Wire - Inialize I2C Hardware
Wire.begin();
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Date & Time RTC
// DS3231 Precision RTC
setupRTC();
// Initialize control over the keyboard:
Keyboard.begin();
// Pololu Setup IMU
setupIMU();
// Pololu Setup Magnetometer
setupMag();
// Initialize the Switch pin as an input
pinMode(iSwitch, INPUT);
// Initialize digital pin LED_BUILTIN as an output
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
// Turn the LED on HIGH
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH);
// Delay 5 Second
delay( 5000 );
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Programming Language
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- RTOS
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor, E-Mentor, STEAM, and Arts-Based Training
- Programming Language
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2023
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@thesass2063
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc