——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #RadioFrequency #Bluetooth #Accelerometer #Magnetometer #Gyroscope #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
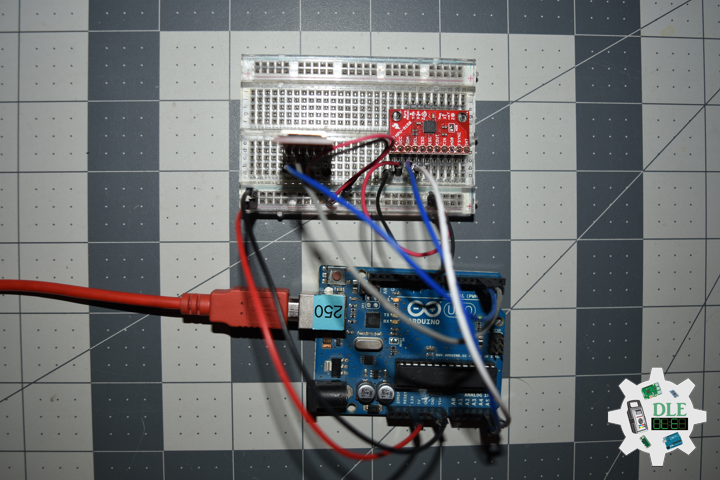
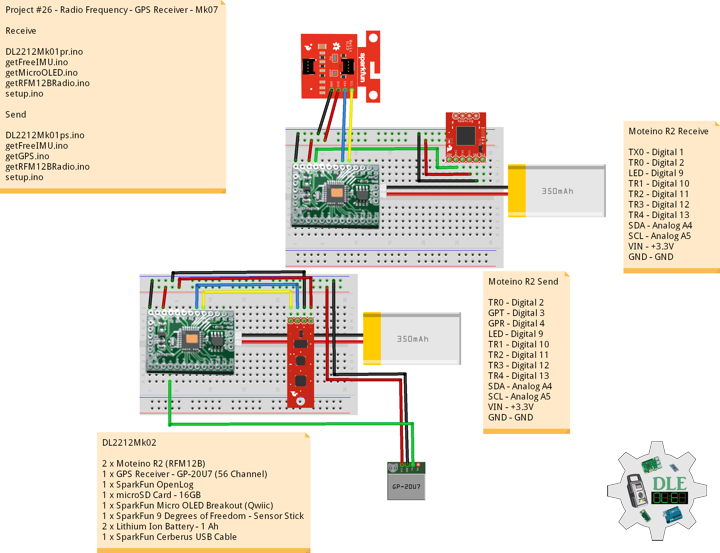
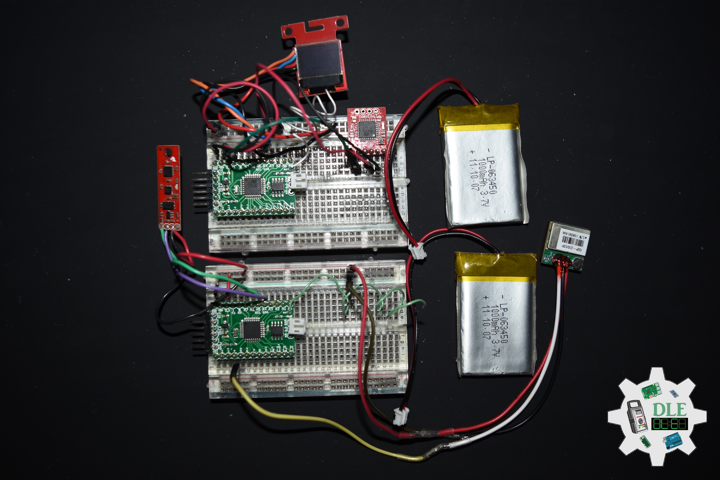
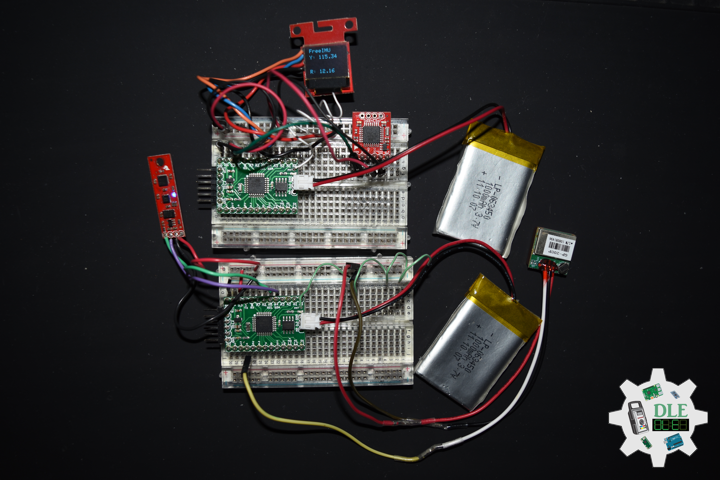
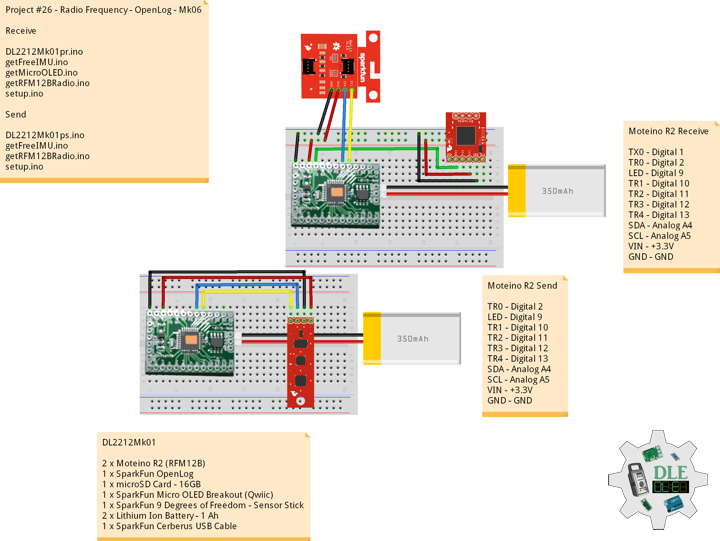
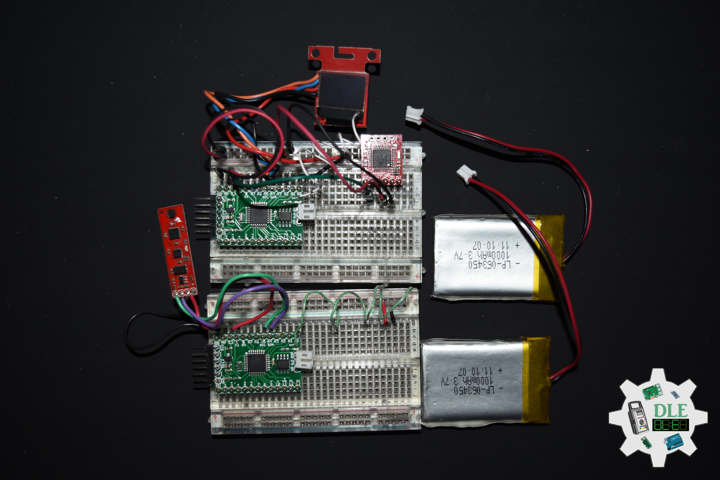
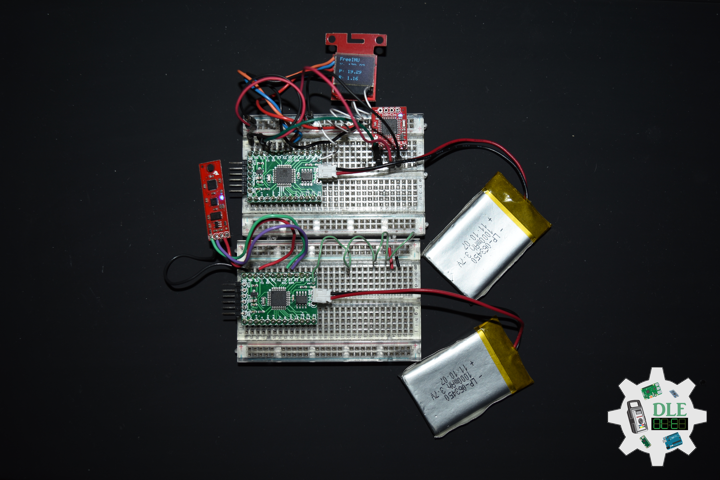
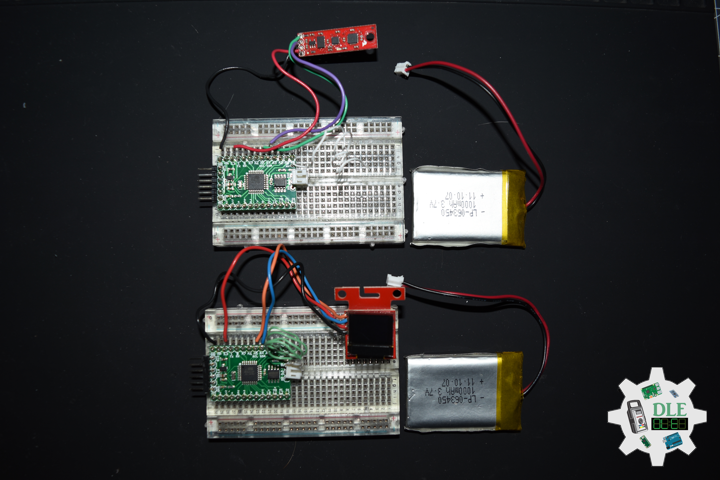
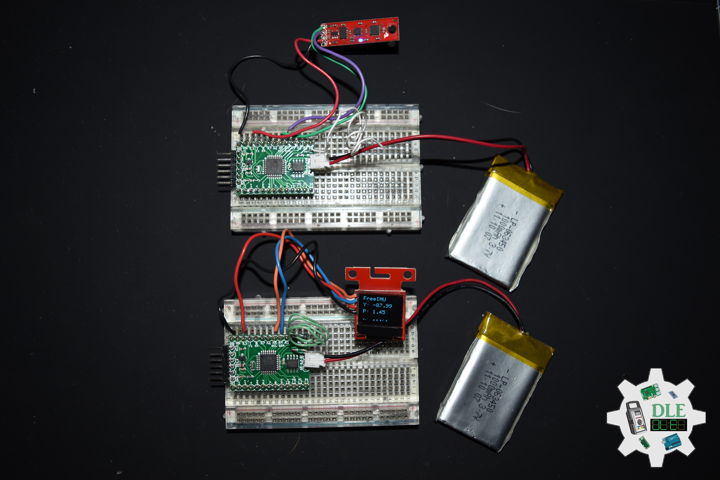
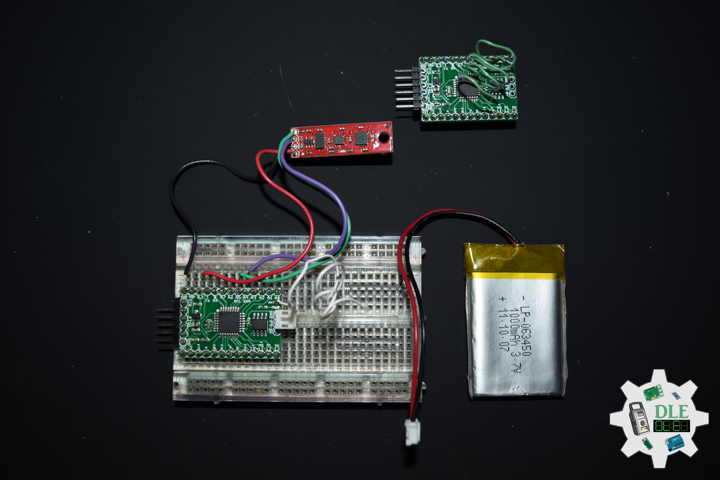
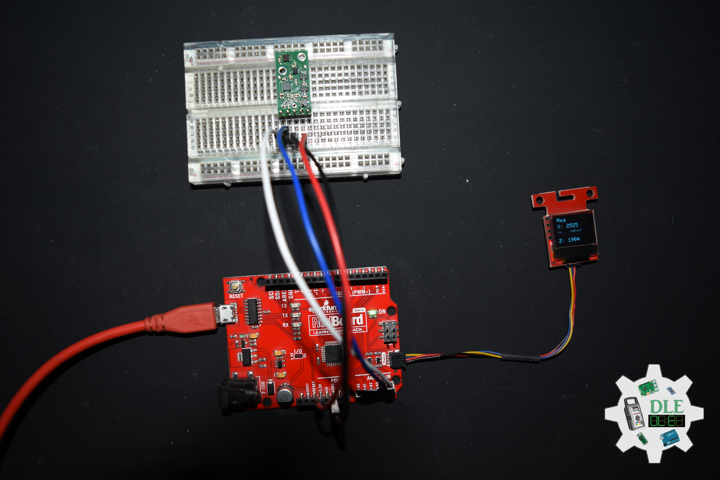
Moteino
Moteino began as a low power wireless Arduino compatible development platform based on the popular ATmega328p chip used in the Arduino UNO. Moteinos are compatible and can communicate with any other Arduino or development platform that uses the popular HopeRF RFM69 or LoRa transceivers, or even the older RFM12B. Moteino also comes with an optional SPI flash memory chip for wireless programming, or data logging. Moteino was designed to be a compact, highly customizable and affordable development platform, suitable for IoT, home automation and long range wireless projects.
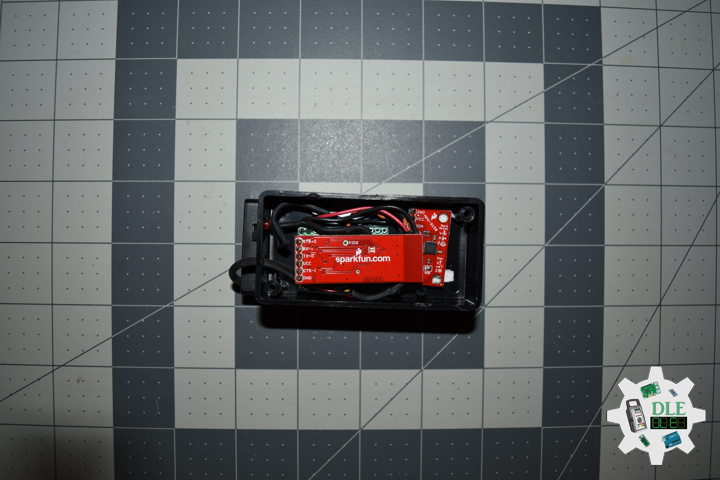
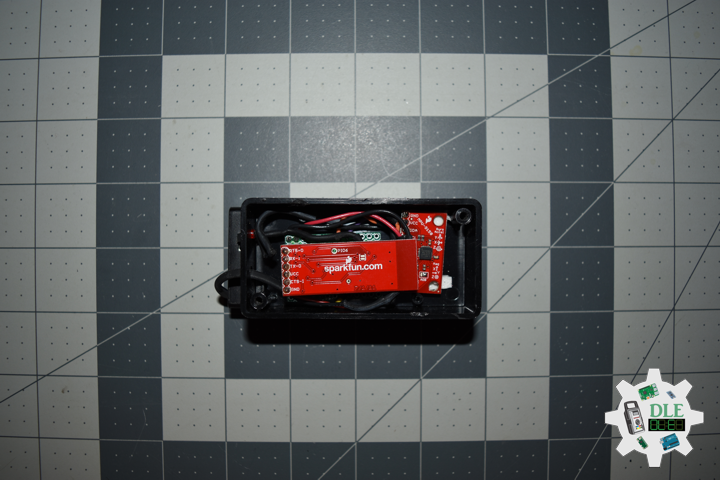
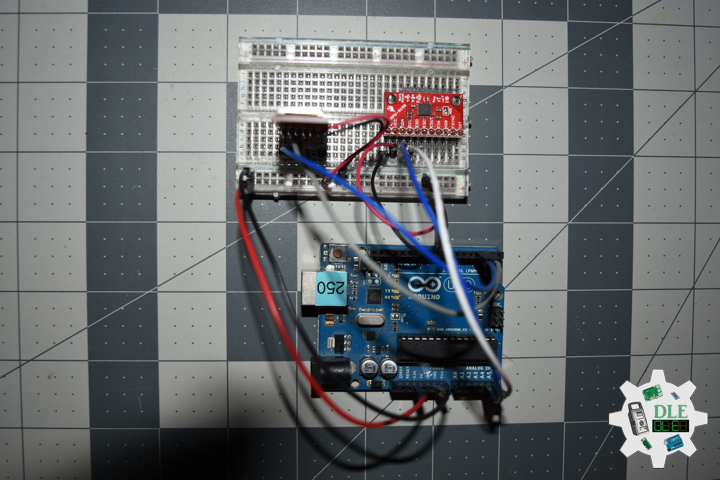
Moteino in RFM12B to rebuild suggests doing as new without completely replacing. I decided to stripped down at RFM12B and rebuild in Bluetooth.
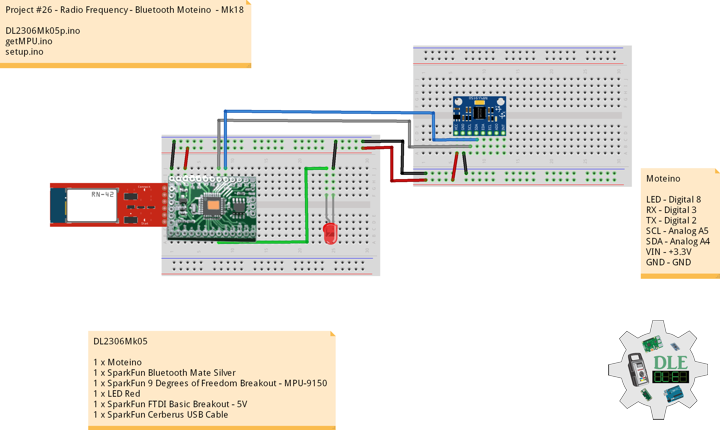
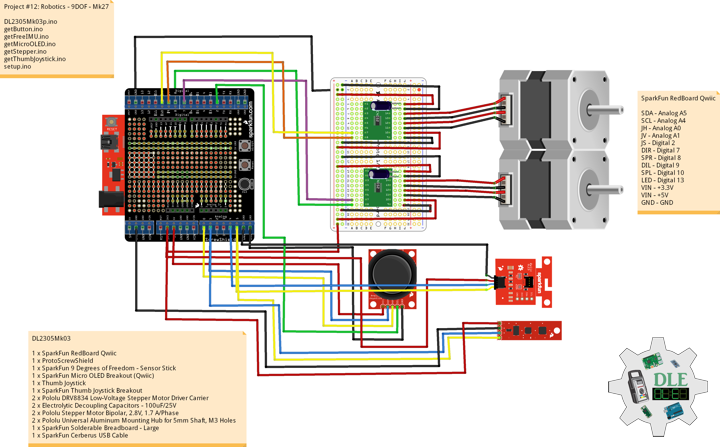
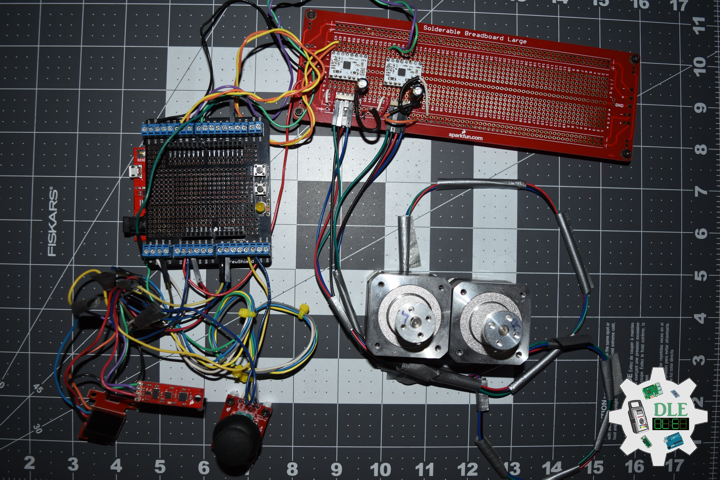
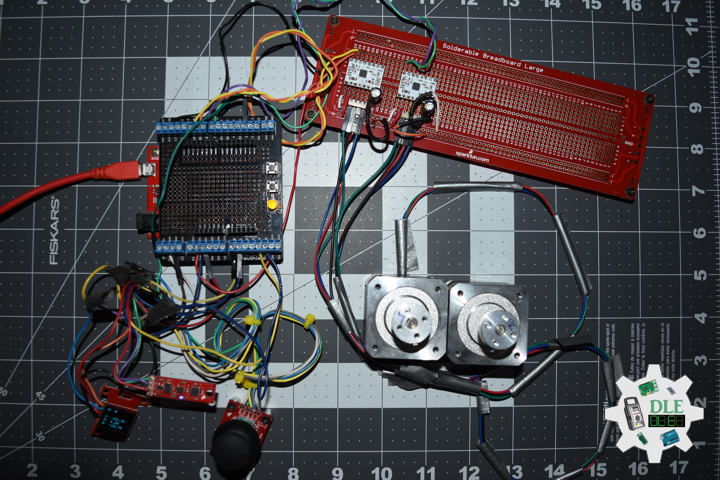
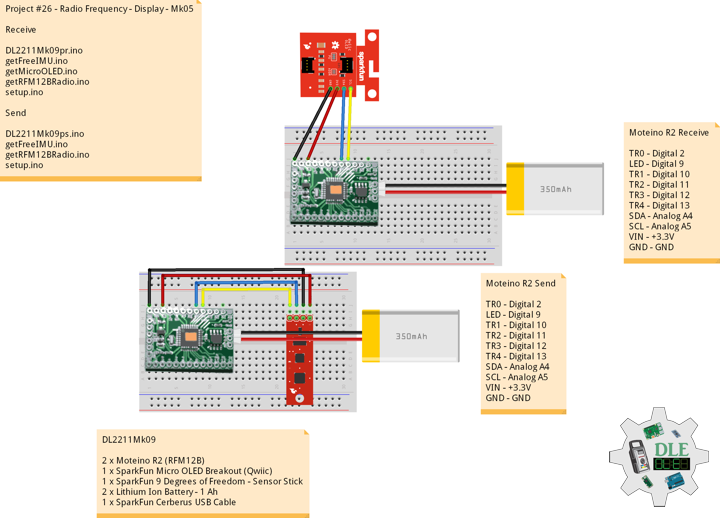
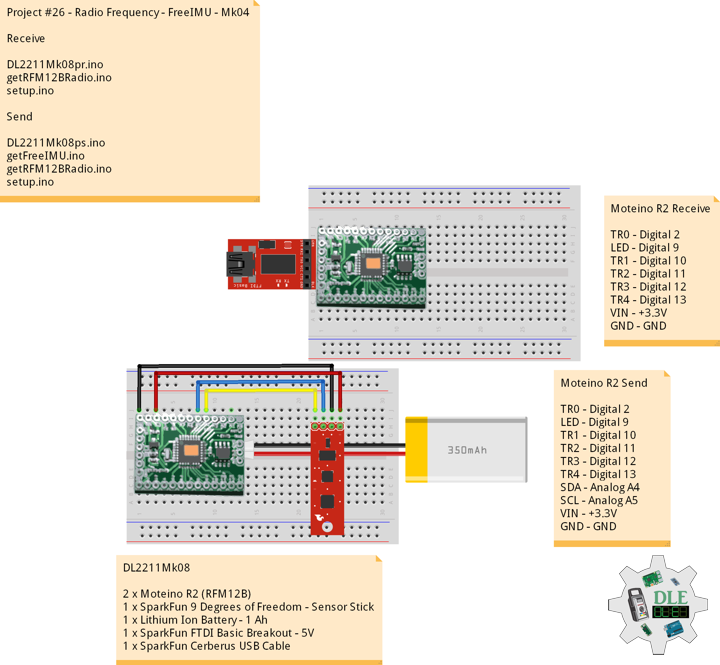
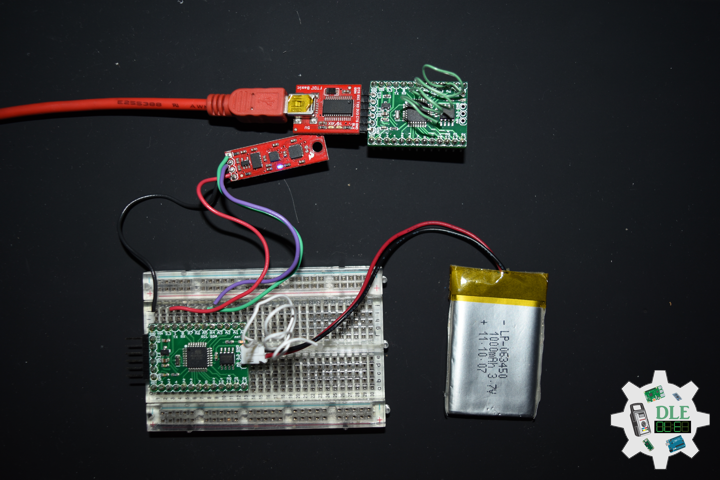
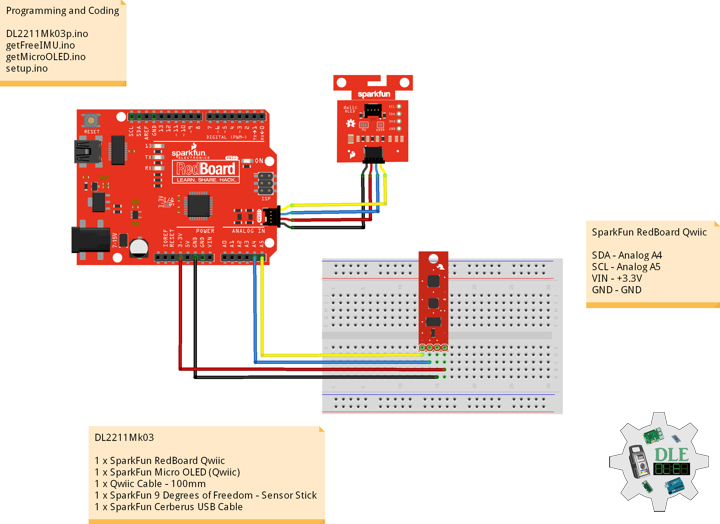
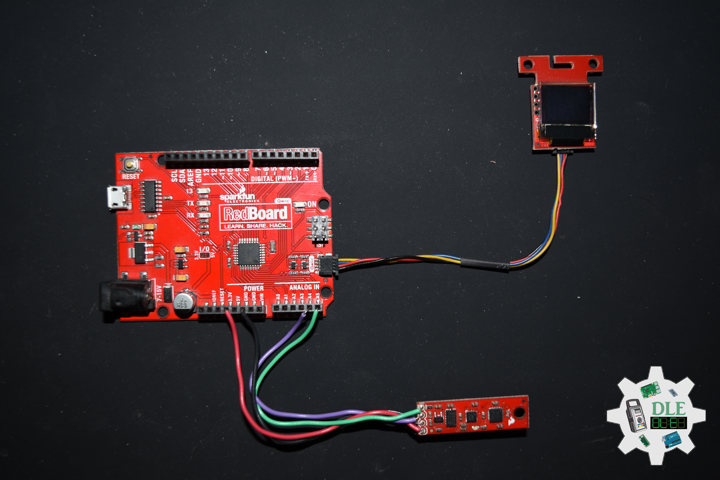
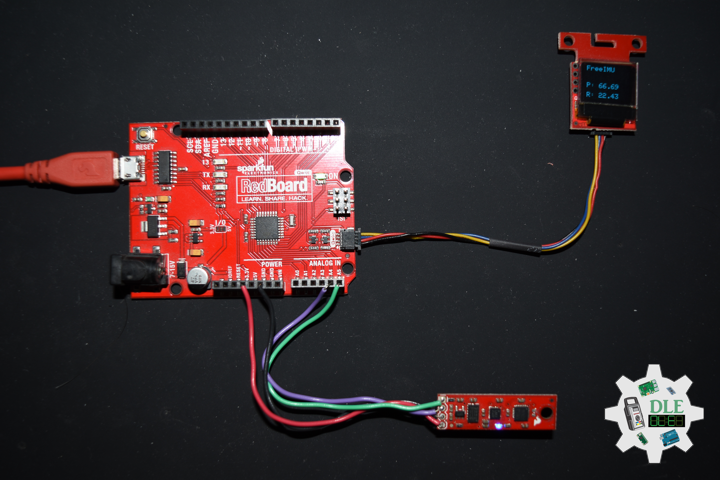
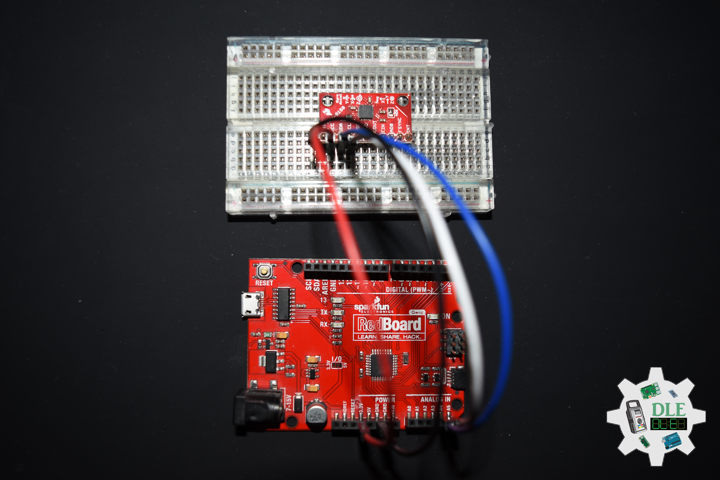
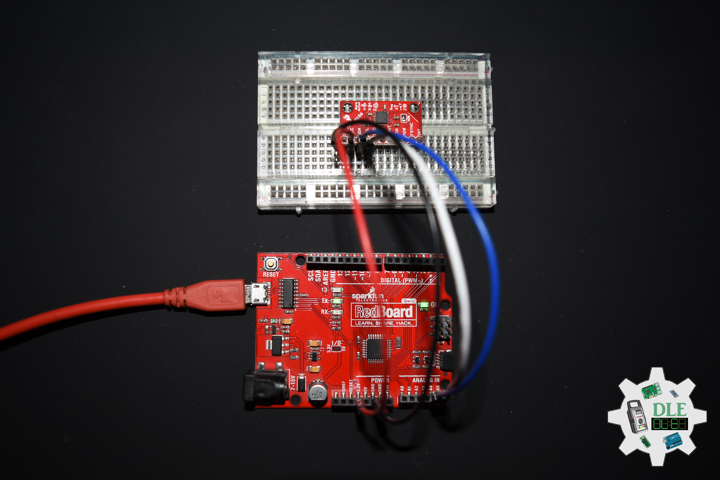
DL2306Mk05
1 x Moteino
1 x SparkFun Bluetooth Mate Silver
1 x SparkFun 9 Degrees of Freedom Breakout – MPU-9150
1 x LED Red
1 x SparkFun FTDI Basic Breakout – 5V
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
Moteino
LED – Digital 8
RX – Digital 3
TX – Digital 2
SDA – Analog A4
SCL – Analog A5
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
——
DL2306Mk05p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
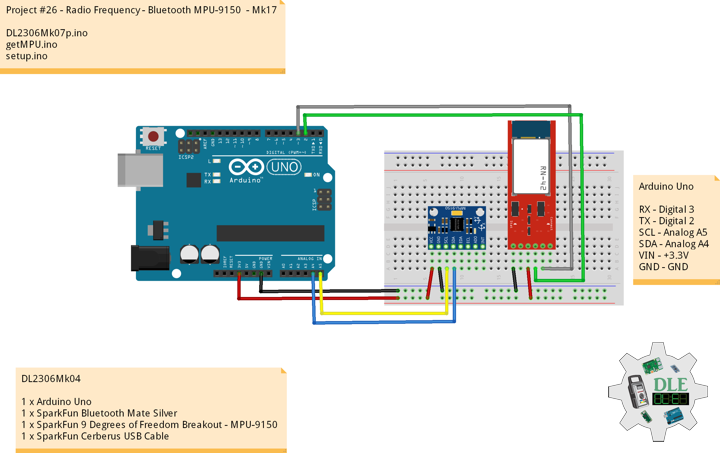
Project #26 - Radio Frequency - Bluetooth Moteino - Mk18
26-18
DL2306Mk05p.ino
1 x Moteino
1 x SparkFun Bluetooth Mate Silver
1 x SparkFun 9 Degrees of Freedom Breakout - MPU-9150
1 x LED Red
1 x SparkFun FTDI Basic Breakout - 5V
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// Software Serial
#include <SoftwareSerial.h>
// Two Wire Interface (TWI/I2C)
#include <Wire.h>
// I2CDev I2C utilities
#include "I2Cdev.h"
// MPU9150Lib 9-axis fusion
#include "MPU9150Lib.h"
// CalLib magnetometer and accelerometer calibration
#include "CalLib.h"
// Motion Driver InvenSense Embedded SDK v5.1
#include <dmpKey.h>
#include <dmpmap.h>
#include <inv_mpu.h>
#include <inv_mpu_dmp_motion_driver.h>
// EEPROM Magnetometer and Accelerometer data is stored
#include <EEPROM.h>
// the MPU object
MPU9150Lib MPU;
// MPU_UPDATE_RATE defines the rate (in Hz)
// at which the MPU updates the sensor data and DMP output
#define MPU_UPDATE_RATE (20)
// MAG_UPDATE_RATE defines the rate (in Hz) at which the
// MPU updates the magnetometer data
// MAG_UPDATE_RATE should be less than or equal to the MPU_UPDATE_RATE
#define MAG_UPDATE_RATE (10)
// MPU_MAG_MIX defines the influence that the magnetometer has on the yaw output.
// The magnetometer itself is quite noisy so some mixing with the gyro yaw can help
// significantly. Some example values are defined below:
// Just use gyro yaw
#define MPU_MAG_MIX_GYRO_ONLY 0
// Just use magnetometer and no gyro yaw
#define MPU_MAG_MIX_MAG_ONLY 1
// A good mix value
#define MPU_MAG_MIX_GYRO_AND_MAG 10
// mainly gyros with a bit of mag correction
#define MPU_MAG_MIX_GYRO_AND_SOME_MAG 50
// MPU_LPF_RATE is the low pas filter rate and can be between 5 and 188Hz
#define MPU_LPF_RATE 5
// This is our earth frame gravity vector - quaternions and vectors
MPUQuaternion gravity;
// Quaternion Result
float Quaternion_X = 0.0;
float Quaternion_Y = 0.0;
float Quaternion_Z = 0.0;
// SERIAL_PORT_SPEED defines the speed to use for the debug serial port
#define SERIAL_PORT_SPEED 115200
// Software Serial
// TX-O pin of bluetooth mate, Arduino D2
int bluetoothTx = 2;
// RX-I pin of bluetooth mate, Arduino D3
int bluetoothRx = 3;
// Bluetooth
SoftwareSerial bluetooth(bluetoothTx, bluetoothRx);
// BTA
String BTA = "0006664FAE18";
// LED Red
int iLedRed = 8;
// Variable to calculate frequency
unsigned long curr = 0;
unsigned long last = 0;
unsigned long freq;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "26-18";
void loop() {
// MPU
isMPU();
}
getMPU.ino
// MPU
// Setup MPU
void isSetupMPU() {
// MPU
MPU.init(MPU_UPDATE_RATE, MPU_MAG_MIX_GYRO_AND_MAG, MAG_UPDATE_RATE, MPU_LPF_RATE); // start the MPU
// Set up the initial gravity vector for quaternion rotation
// Max value down the z axis
gravity[QUAT_W] = 0;
gravity[QUAT_X] = 0;
gravity[QUAT_Y] = 0;
gravity[QUAT_Z] = SENSOR_RANGE;
}
// MPU
void isMPU() {
// Quaternion
// This is our body frame gravity vector
MPUQuaternion rotatedGravity;
// This is the conjugate of the fused quaternion
MPUQuaternion fusedConjugate;
// Used in the rotation
MPUQuaternion qTemp;
// The accelerations
MPUVector3 result;
// Get the latest data
if (MPU.read()) {
// Need this for the rotation
MPUQuaternionConjugate(MPU.m_fusedQuaternion, fusedConjugate);
// Rotate the gravity vector into the body frame
MPUQuaternionMultiply(gravity, MPU.m_fusedQuaternion, qTemp);
MPUQuaternionMultiply(fusedConjugate, qTemp, rotatedGravity);
// Now subtract rotated gravity from the body accels to get real accelerations.
// Note that signs are reversed to get +ve acceleration results
// in the conventional axes.
// Quaternion Result
Quaternion_X = -(MPU.m_calAccel[VEC3_X] - rotatedGravity[QUAT_X]);
Quaternion_Y = -(MPU.m_calAccel[VEC3_Y] - rotatedGravity[QUAT_Y]);
Quaternion_Z = -(MPU.m_calAccel[VEC3_Z] - rotatedGravity[QUAT_Z]);
// Variable to calculate frequency
curr = micros();
freq = curr - last;
last = curr;
// Bluetooth
Serial.print( "Blue|" + BTA + "|" );
Serial.print( Quaternion_X );
Serial.print( "|" );
Serial.print( Quaternion_Y );
Serial.print( "|" );
Serial.print( Quaternion_Z );
Serial.print( "|" );
Serial.print( freq );
Serial.println( "|*" );
// Send any characters the Serial monitor prints to the bluetooth
bluetooth.print((char)Serial.read());
}
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// Serial
Serial.begin(SERIAL_PORT_SPEED);
// Bluetooth
// The Bluetooth Mate defaults to 115200bps
bluetooth.begin(115200);
// LED Red
pinMode(iLedRed, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(iLedRed, HIGH);
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Wire communicate with I2C / TWI devices
Wire.begin();
// Pause
delay(50);
// Setup MPU
isSetupMPU();
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Programming Language
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- RTOS
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor, E-Mentor, STEAM, and Arts-Based Training
- Programming Language
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2023
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/@thesass2063
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc