Fritzing
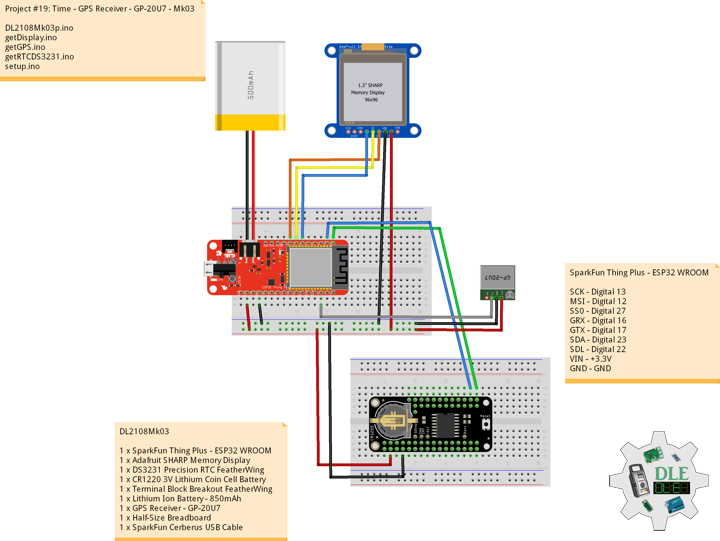
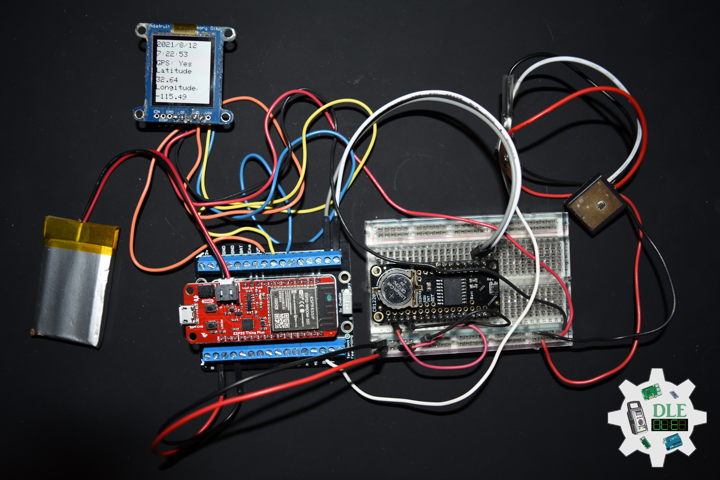
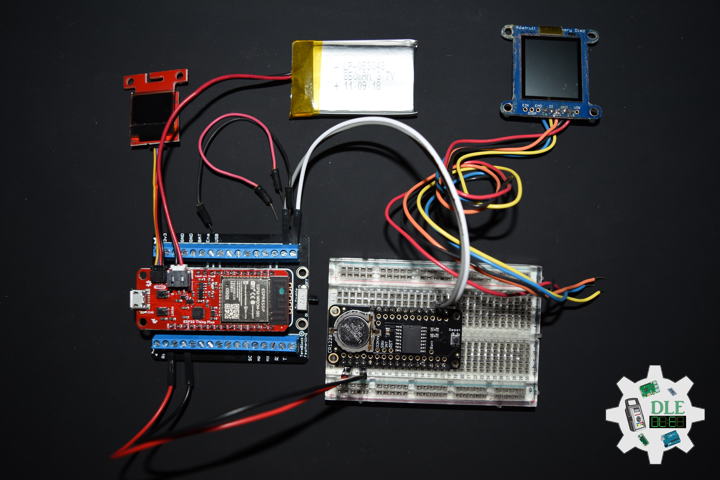
Project #19: Time – GPS Receiver – GP-20U7 – Mk03
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Time #DS3231PrecisionRTC #SHARPMemoryDisplay #GPSReceiver #Arduino #ESP32 #SparkFunThingPlusESP32WROOM #Project #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant #VideoBlog
——
——
——
——
——
——
GPS Receiver – GP-20U7
The GP-20U7 is a compact GPS receiver with a built-in high performances all-in-one GPS chipset. The GP-20U7 accurately provides position, velocity, and time readings as well possessing high sensitivity and tracking capabilities. Thanks to the low power consumption this receiver requires, the GP-20U7 is ideal for portable applications such as tablet PCs, smart phones, and other devices requiring positioning capability.
This 56-channel GPS module, that supports a standard NMEA-0183 and uBlox 7 protocol, has low power consumption of 40mA@3.3V (max), an antenna on board, and -162dBm tracking sensitivity. With 56 channels in search mode and 22 channels “all-in-view” tracking, the GP-20U7 is quite the work horse for its size.
This one is unused and doesnt have a conection TX pin.
NMEA V3.01 Protocol
- Its output signal level is TTL: 9600bps (default), 8 bit data, 1 stop bit and no parity
- It supports the following NMEA-0183
- Messages: GGA, GLL, GSA, GSV, RMC and VTG
NMEA-0183 Output Messages
- NMEA: Record Description
- GGA: Global positoning system fixed data
- GLL: Geogrphic position – latitude / longitude
- GSA: GNSS DOP and active satellites
- GSV: GNSS satellites in view
- RMC: Recommended minimum specific GNSS data
- VTG: Course over ground and ground speed
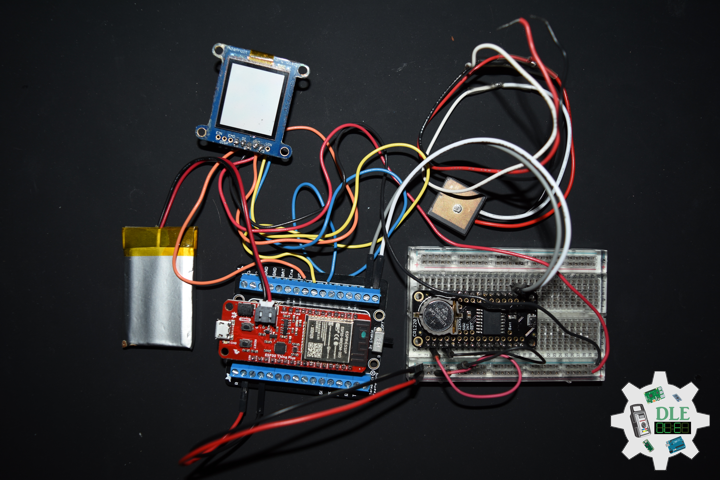
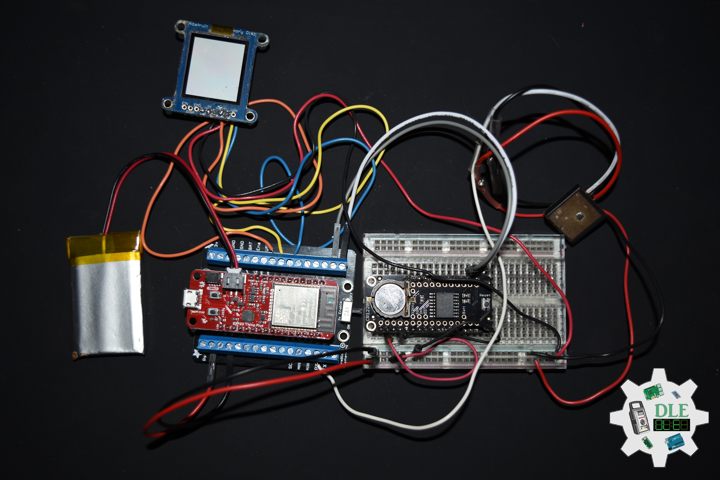
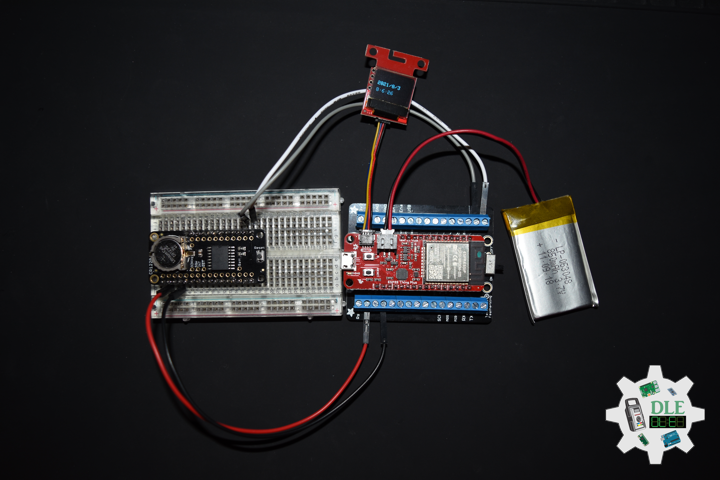
DL2108Mk03
1 x SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
1 x Adafruit SHARP Memory Display
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x Terminal Block Breakout FeatherWing
1 x Lithium Ion Battery – 850mAh
1 x GPS Receiver – GP-20U7
1 x Half-Size Breadboard
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
SCK – Digital 13
MSI – Digital 12
SS0 – Digital 27
GRX – Digital 16
GTX – Digital 17
SDA – Digital 23
SDL – Digital 22
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
DL2108Mk03p.ino
/*
***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #19: Time -GPS Receiver - GP-20U7 - Mk03
08-03
DL2108Mk03p.ino
1 x SparkFun Thing Plus - ESP32 WROOM
1 x Adafruit SHARP Memory Display
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x Terminal Block Breakout FeatherWing
1 x Lithium Ion Battery - 850mAh
1 x GPS Receiver - GP-20U7
1 x Half-Size Breadboard
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// Wire
// #include <Wire.h>
// SHARP Memory Display
#include <Adafruit_SharpMem.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
// Date and time DS3231 RTC
#include <RTClib.h>
// GPS Receiver
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
// ESP32 Hardware Serial
#include <HardwareSerial.h>
// SHARP Memory Display
#define SHARP_SCK 13
#define SHARP_MOSI 12
#define SHARP_SS 27
// Set the size of the display here, e.g. 144x168!
Adafruit_SharpMem display(SHARP_SCK, SHARP_MOSI, SHARP_SS, 144, 168);
// The currently-available SHARP Memory Display (144x168 pixels)
// requires > 4K of microcontroller RAM; it WILL NOT WORK on Arduino Uno
// or other <4K "classic" devices.
#define BLACK 0
#define WHITE 1
// Date and time functions using a DS3231 RTC
RTC_DS3231 RTC;
String sDate;
String sTime;
// ESP32 HardwareSerial
HardwareSerial tGPS(2);
// GPS Receiver
#define gpsRXPIN 16
// This one is unused and doesnt have a conection
#define gpsTXPIN 17
// The TinyGPS++ object
TinyGPSPlus gps;
float TargetLat;
float TargetLon;
int GPSStatus = 0;
String GPSSt = "";
// Software Version Information
// Version
String sver = "19-03";
void loop()
{
// Dates and Time
timeRTC();
// isGPS
isGPS();
// Display Date, Time, GPS
isDisplayDate();
delay( 1000 );
}
getDisplay.ino
// SHARP Memory Display
// SHARP Memory Display - UID
void isDisplayUID() {
// Text Display
// Clear Display
display.clearDisplay();
display.setRotation(4);
display.setTextSize(3);
display.setTextColor(BLACK);
// Don Luc Electronics
display.setCursor(0,10);
display.println( "Don Luc" );
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setCursor(0,40);
display.println( "Electronics" );
// Version
display.setTextSize(3);
display.setCursor(0,70);
display.println( "Version" );
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setCursor(0,100);
display.println( sver );
// Refresh
display.refresh();
delay( 100 );
}
// Display Date
void isDisplayDate() {
// Text Display Date
// Clear Display
display.clearDisplay();
display.setRotation(4);
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setTextColor(BLACK);
// Date
display.setCursor(0,5);
display.println( sDate );
// Time
display.setCursor(0,30);
display.println( sTime );
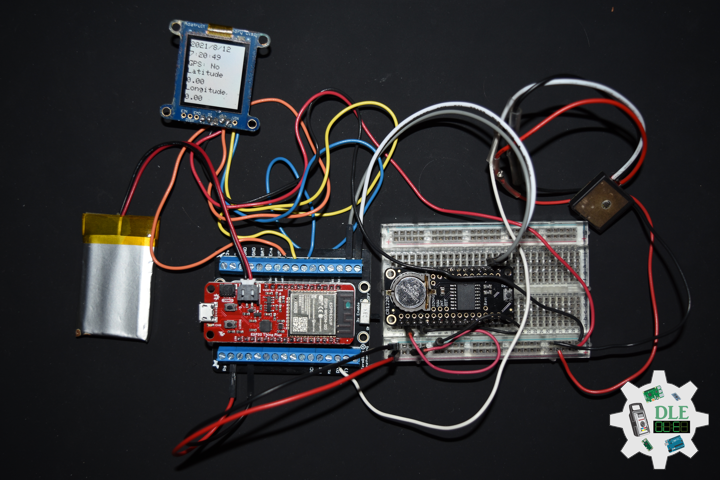
// GPS Status
display.setCursor(0,55);
display.print( "GPS: " );
display.println( GPSSt );
// Target Latitude
display.setCursor(0,75);
display.println( "Latitude" );
display.setCursor(0,100);
display.println( TargetLat );
// Target Longitude
display.setCursor(0,120);
display.println( "Longitude" );
display.setCursor(0,145);
display.println( TargetLon );
// Refresh
display.refresh();
delay( 100 );
}
getGPS.ino
// GPS Receiver
// Setup GPS
void setupGPS() {
// Setup GPS
tGPS.begin( 9600 , SERIAL_8N1 , gpsRXPIN , gpsTXPIN );
}
// isGPS
void isGPS(){
// Receives NEMA data from GPS receiver
// This sketch displays information every time a new sentence is correctly encoded
while ( tGPS.available() > 0)
if (gps.encode( tGPS.read() ))
{
// GPS Vector Pointer Target
displayInfo();
}
if (millis() > 5000 && gps.charsProcessed() < 10)
{
while(true);
}
}
// GPS Vector Pointer Target
void displayInfo(){
// Location
if (gps.location.isValid())
{
// Latitude
TargetLat = gps.location.lat();
// Longitude
TargetLon = gps.location.lng();
// GPS Status 2
GPSStatus = 2;
GPSSt = "Yes";
}
else
{
// GPS Status 0
GPSStatus = 0;
GPSSt = "No";
}
}
getRTCDS3231.ino
// DS3231 Precision RTC
// Setup RTC
void setupRTC() {
// DS3231 Precision RTC
RTC.begin();
if (! RTC.begin()) {
while (1);
}
// Date Time
DateTime now = RTC.now();
if (RTC.lostPower()) {
// Following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled
RTC.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
// This line sets the RTC with an explicit date & time, for example to set
// August 2, 2021 at 13:53:0 you would call:
// RTC.adjust(DateTime(2021, 8, 2, 14, 11, 0));
}
}
// timeRTC
void timeRTC() {
// DS3231 Precision RTC
sDate = "";
sTime = "";
// Date Time
DateTime now = RTC.now();
// sData
sDate += String(now.year(), DEC);
sDate += "/";
sDate += String(now.month(), DEC);
sDate += "/";
sDate += String(now.day(), DEC);
// sTime
sTime += String(now.hour(), DEC);
sTime += ":";
sTime += String(now.minute(), DEC);
sTime += ":";
sTime += String(now.second(), DEC);
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// GPS Receiver
// Setup GPS
setupGPS();
// Set up I2C bus
// Wire.begin();
// SHARP Display Start & Clear the Display
display.begin();
// Clear Display
display.clearDisplay();
// Display UID
isDisplayUID();
// Setup RTC
setupRTC();
delay( 5000 );
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Robotics
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Desktop Applications (Windows, OSX, Linux, Multi-OS, Multi-Tier, etc…)
- Mobile Applications (Android, iOS, Blackberry, Windows Mobile, Windows CE, etc…)
- Web Applications (LAMP, Scripting, Java, ASP, ASP.NET, RoR, Wakanda, etc…)
- Social Media Programming & Integration (Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Pinterest, etc…)
- Content Management Systems (WordPress, Drupal, Joomla, Moodle, etc…)
- Bulletin Boards (phpBB, SMF, Vanilla, jobberBase, etc…)
- eCommerce (WooCommerce, OSCommerce, ZenCart, PayPal Shopping Cart, etc…)
Instructor
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
- DOS, Windows, OSX, Linux, iOS, Android, Multi-OS
- Linux-Apache-PHP-MySQL
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2021 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEngMk2021c.pdf
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEspMk2021c.pdf
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: https://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLE/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLHackster/
Web: https://www.hackster.io/neosteam-labs
Web: https://zoom.us/
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/DonLucElectronics
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
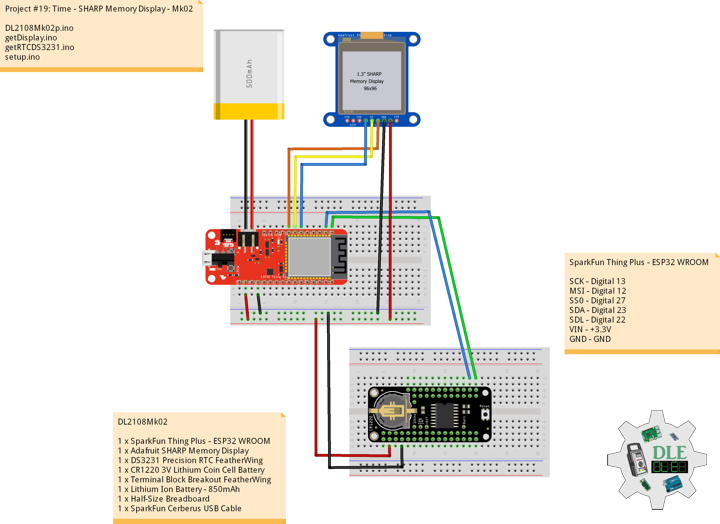
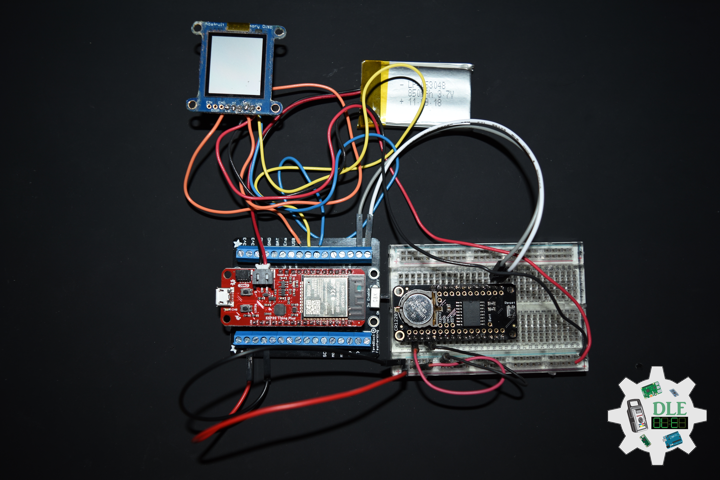
Project #19: Time – SHARP Memory Display – Mk02
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Time #DS3231PrecisionRTC #SHARPMemoryDisplay #Arduino #ESP32 #SparkFunThingPlusESP32WROOM #Project #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant #VideoBlog
——
——
——
——
——
Adafruit SHARP Memory Display Breakout – 1.3 Inches – 168 Pixels x 144 Pixels Monochrome
The 1.3 inches 168 pixels x 144 pixels SHARP Memory LCD display is a cross between an eInk display and an LCD. It has the ultra-low power usage of eInk and the fast-refresh rates of an LCD. This model has a gray background, and pixels show up as black-on-gray for a nice e-reader type display. It does not have a backlight, but it is daylight readable. For dark/night reading you may need to illuminate the LCD area with external LEDs.
The display is write only which means that it only needs 3 pins to send data. However, the downside of a write-only display is that the entire 168×144 bits must be buffered by the microcontroller driver. That means you cannot use this with an ATmega328 or ATmega32u4. You must use a high-RAM chip such as ATSAMD21, Teensy 3, ESP8266, ESP32, etc. On those chips, this display works great and looks wonderful.
DL2108Mk02
1 x SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
1 x Adafruit SHARP Memory Display
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x Terminal Block Breakout FeatherWing
1 x Lithium Ion Battery – 850mAh
1 x Half-Size Breadboard
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
SCK – Digital 13
MSI – Digital 12
SS0 – Digital 27
SDA – Digital 23
SDL – Digital 22
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
DL2108Mk02p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #19: Time -SHARP Memory Display - Mk02
08-02
DL2108Mk02p.ino
1 x SparkFun Thing Plus - ESP32 WROOM
1 x Adafruit SHARP Memory Display
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x Terminal Block Breakout FeatherWing
1 x Qwiic Cable - 50mm
1 x Lithium Ion Battery - 850mAh
1 x Half-Size Breadboard
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
#include <Wire.h>
// SHARP Memory Display
#include <Adafruit_SharpMem.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
// Date and time DS3231 RTC
#include <RTClib.h>
// SHARP Memory Display
#define SHARP_SCK 13
#define SHARP_MOSI 12
#define SHARP_SS 27
// Set the size of the display here, e.g. 144x168!
Adafruit_SharpMem display(SHARP_SCK, SHARP_MOSI, SHARP_SS, 144, 168);
// The currently-available SHARP Memory Display (144x168 pixels)
// requires > 4K of microcontroller RAM; it WILL NOT WORK on Arduino Uno
// or other <4K "classic" devices.
#define BLACK 0
#define WHITE 1
// Set this to 1000 to get _about_ 1 second timing
const int CLOCK_SPEED = 1000;
// Last Draw
unsigned long lastDraw = 0;
// Date and time functions using a DS3231 RTC
RTC_DS3231 RTC;
String sDate;
String sTime;
// Software Version Information
// Version
String sver = "19-02";
void loop()
{
// Check if we need to update date, time
if (lastDraw + CLOCK_SPEED < millis())
{
// Last Draw
lastDraw = millis();
// Dates and Time
timeRTC();
// is OLED
//isOLED();
isDisplayDate();
}
}
getDisplay.ino
// SHARP Memory Display
// SHARP Memory Display - UID
void isDisplayUID() {
// Text Display
// Clear Display
display.clearDisplay();
display.setRotation(4);
display.setTextSize(3);
display.setTextColor(BLACK);
// Don Luc Electronics
display.setCursor(0,10);
display.println( "Don Luc" );
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setCursor(0,40);
display.println( "Electronics" );
// Version
display.setTextSize(3);
display.setCursor(0,70);
display.println( "Version" );
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setCursor(0,100);
display.println( sver );
// Refresh
display.refresh();
delay( 100 );
}
// Display Date
void isDisplayDate() {
// Text Display Date
// Clear Display
display.clearDisplay();
display.setRotation(4);
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setTextColor(BLACK);
// Date
display.setCursor(0,5);
display.println( sDate );
// Time
display.setCursor(0,30);
display.println( sTime );
// Refresh
display.refresh();
delay( 100 );
}
getRTCDS3231.ino
// DS3231 Precision RTC
// Setup RTC
void setupRTC() {
// DS3231 Precision RTC
RTC.begin();
if (! RTC.begin()) {
while (1);
}
DateTime now = RTC.now();
if (RTC.lostPower()) {
// Following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled
RTC.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
// This line sets the RTC with an explicit date & time, for example to set
// August 2, 2021 at 13:53:0 you would call:
// RTC.adjust(DateTime(2021, 8, 2, 14, 11, 0));
}
}
// timeRTC
void timeRTC() {
// DS3231 Precision RTC
sDate = "";
sTime = "";
// Date Time
DateTime now = RTC.now();
// sData
sDate += String(now.year(), DEC);
sDate += "/";
sDate += String(now.month(), DEC);
sDate += "/";
sDate += String(now.day(), DEC);
// sTime
sTime += String(now.hour(), DEC);
sTime += ":";
sTime += String(now.minute(), DEC);
sTime += ":";
sTime += String(now.second(), DEC);
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Set up I2C bus
Wire.begin();
// SHARP Display Start & Clear the Display
display.begin();
// Clear Display
display.clearDisplay();
// Display UID
isDisplayUID();
// Setup RTC
setupRTC();
delay( 5000 );
}
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Robotics
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Desktop Applications (Windows, OSX, Linux, Multi-OS, Multi-Tier, etc…)
- Mobile Applications (Android, iOS, Blackberry, Windows Mobile, Windows CE, etc…)
- Web Applications (LAMP, Scripting, Java, ASP, ASP.NET, RoR, Wakanda, etc…)
- Social Media Programming & Integration (Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Pinterest, etc…)
- Content Management Systems (WordPress, Drupal, Joomla, Moodle, etc…)
- Bulletin Boards (phpBB, SMF, Vanilla, jobberBase, etc…)
- eCommerce (WooCommerce, OSCommerce, ZenCart, PayPal Shopping Cart, etc…)
Instructor
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
- DOS, Windows, OSX, Linux, iOS, Android, Multi-OS
- Linux-Apache-PHP-MySQL
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2021 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEngMk2021c.pdf
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEspMk2021c.pdf
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: https://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLE/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLHackster/
Web: https://www.hackster.io/neosteam-labs
Web: https://zoom.us/
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/DonLucElectronics
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
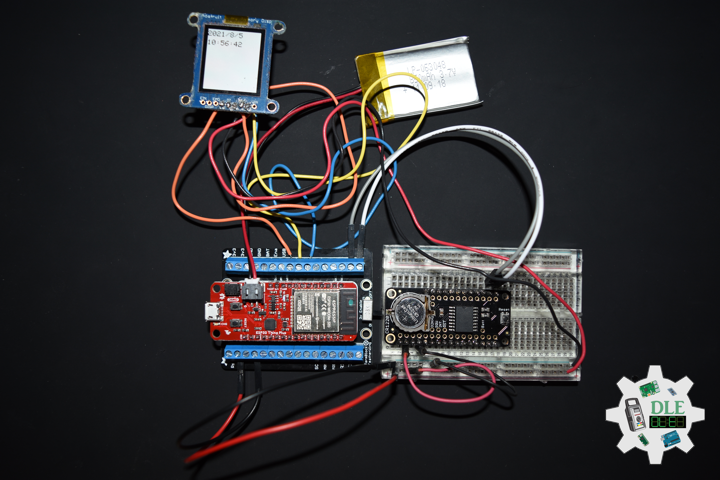
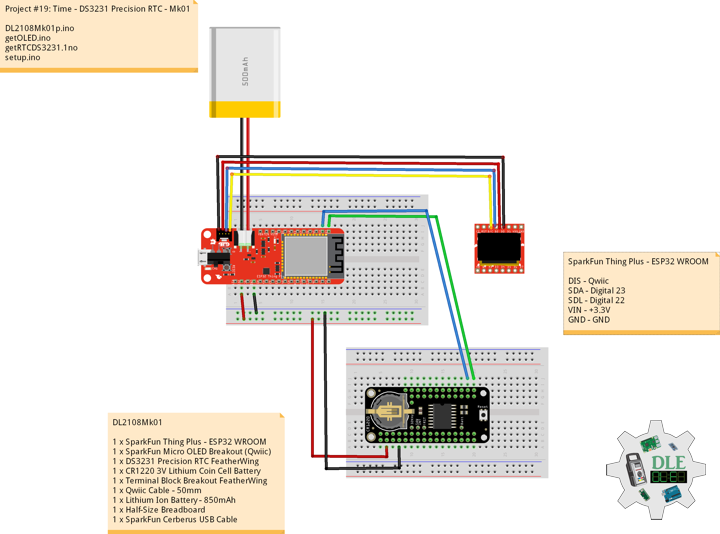
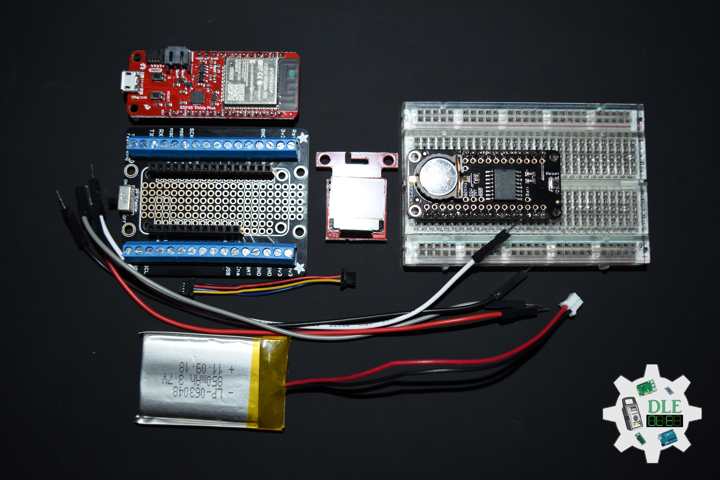
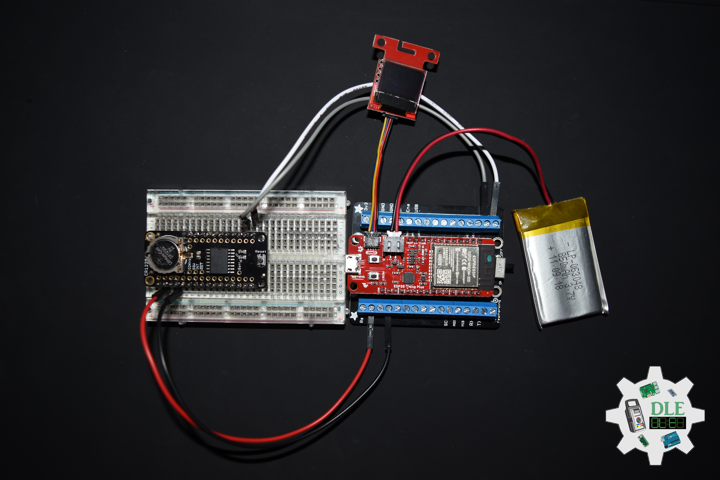
Project #19: Time – DS3231 Precision RTC – Mk01
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Time #DS3231PrecisionRTC #Arduino #ESP32 #SparkFunThingPlusESP32WROOM #Project #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant #VideoBlog
——
——
——
——
——
DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
A Feather board without ambition is a Feather board without FeatherWings. This is the DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing: it adds an extremely accurate I2C-integrated Real Time Clock (RTC) with a Temperature Compensated Crystal Oscillator (TCXO) to any Feather main board. This RTC is the most precise you can get in a small, low power package. Most RTCs use an external 32kHz timing crystal that is used to keep time with low current draw. And that’s all well and good, but those crystals have slight drift, particularly when the temperature changes. This RTC is in a beefy package because the crystal is inside the chip. And right next to the integrated crystal is a temperature sensor. That sensor compensates for the frequency changes by adding or removing clock ticks so that the timekeeping stays on schedule.
SparkFun Micro OLED Breakout (Qwiic)
The SparkFun Qwiic Micro OLED Breakout is a Qwiic-enabled version of our popular Micro OLED display. The small monochrome, blue-on-black OLED screen presents incredibly clear images for your viewing pleasure. The OLED display is crisp, and you can fit a deceivingly large amount of graphics on there. This breakout is perfect for adding graphics to your next project and displaying diagnostic information without resorting to a serial output, all with the ease of use of our own Qwiic Connect System.
DL2108Mk01
1 x SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
1 x SparkFun Micro OLED Breakout (Qwiic)
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x Terminal Block Breakout FeatherWing
1 x Qwiic Cable – 50mm
1 x Lithium Ion Battery – 850mAh
1 x Half-Size Breadboard
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
DIS – Qwiic
SDA – Digital 23
SDL – Digital 22
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
DL2108Mk01p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #19: Time - DS3231 Precision RTC - Mk01
08-01
DL2108Mk01p.ino
1 x SparkFun Thing Plus - ESP32 WROOM
1 x SparkFun Micro OLED Breakout (Qwiic)
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x CR1220 3V Lithium Coin Cell Battery
1 x Terminal Block Breakout FeatherWing
1 x Qwiic Cable - 50mm
1 x Lithium Ion Battery - 850mAh
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
#include <Wire.h>
// OLED
#include <SFE_MicroOLED.h>
// Date and time DS3231 RTC
#include <RTClib.h>
// OLED
// DC Jumper
#define DC_JUMPER 1
// Optional - Connect RST on display to pin 9 on Arduino
#define PIN_RESET 9
MicroOLED oled(PIN_RESET, DC_JUMPER);
// Set this to 1000 to get _about_ 1 second timing
const int CLOCK_SPEED = 1000;
// Last Draw
unsigned long lastDraw = 0;
// Date and time functions using a DS3231 RTC
RTC_DS3231 RTC;
String sDate;
String sTime;
// Software Version Information
// Version
String sver = "19-01";
void loop()
{
// Check if we need to update date, time
if (lastDraw + CLOCK_SPEED < millis())
{
// Last Draw
lastDraw = millis();
// Dates and Time
timeRTC();
// is OLED
isOLED();
}
}
getOLED.ino
// OLED
// Setup OLED
void setupOLED(){
// Initialize the OLED
oled.begin();
// Clear the display's internal memory
oled.clear(PAGE);
// Clear the library's display buffer
oled.clear(ALL);
// Display what's in the buffer
oled.display();
}
// isOLED
void isOLED(){
// Clear the buffer
oled.clear(PAGE);
// Set font to type 0
oled.setFontType(0);
// Date
// Set cursor to top-left
oled.setCursor(0, 18);
oled.print( sDate );
// Time
// Set cursor to top-left
oled.setCursor(0, 32);
oled.print( sTime );
// Draw the memory buffer
oled.display();
}
getRTCDS3231.ino
// DS3231 Precision RTC
// Setup RTC
void setupRTC() {
// DS3231 Precision RTC
RTC.begin();
if (! RTC.begin()) {
while (1);
}
DateTime now = RTC.now();
if (RTC.lostPower()) {
// Following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled
RTC.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
// This line sets the RTC with an explicit date & time, for example to set
// August 2, 2021 at 13:53:0 you would call:
// RTC.adjust(DateTime(2021, 8, 2, 14, 11, 0));
}
}
// timeRTC
void timeRTC() {
// DS3231 Precision RTC
sDate = "";
sTime = "";
// Date Time
DateTime now = RTC.now();
// sData
sDate += String(now.year(), DEC);
sDate += "/";
sDate += String(now.month(), DEC);
sDate += "/";
sDate += String(now.day(), DEC);
// sTime
sTime += String(now.hour(), DEC);
sTime += ":";
sTime += String(now.minute(), DEC);
sTime += ":";
sTime += String(now.second(), DEC);
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Set up I2C bus
Wire.begin();
// Initialize the OLED
setupOLED();
// Setup RTC
setupRTC();
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Robotics
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Desktop Applications (Windows, OSX, Linux, Multi-OS, Multi-Tier, etc…)
- Mobile Applications (Android, iOS, Blackberry, Windows Mobile, Windows CE, etc…)
- Web Applications (LAMP, Scripting, Java, ASP, ASP.NET, RoR, Wakanda, etc…)
- Social Media Programming & Integration (Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Pinterest, etc…)
- Content Management Systems (WordPress, Drupal, Joomla, Moodle, etc…)
- Bulletin Boards (phpBB, SMF, Vanilla, jobberBase, etc…)
- eCommerce (WooCommerce, OSCommerce, ZenCart, PayPal Shopping Cart, etc…)
Instructor
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
- DOS, Windows, OSX, Linux, iOS, Android, Multi-OS
- Linux-Apache-PHP-MySQL
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2021 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEngMk2021c.pdf
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEspMk2021c.pdf
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: https://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLE/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLHackster/
Web: https://www.hackster.io/neosteam-labs
Web: https://zoom.us/
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/DonLucElectronics
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
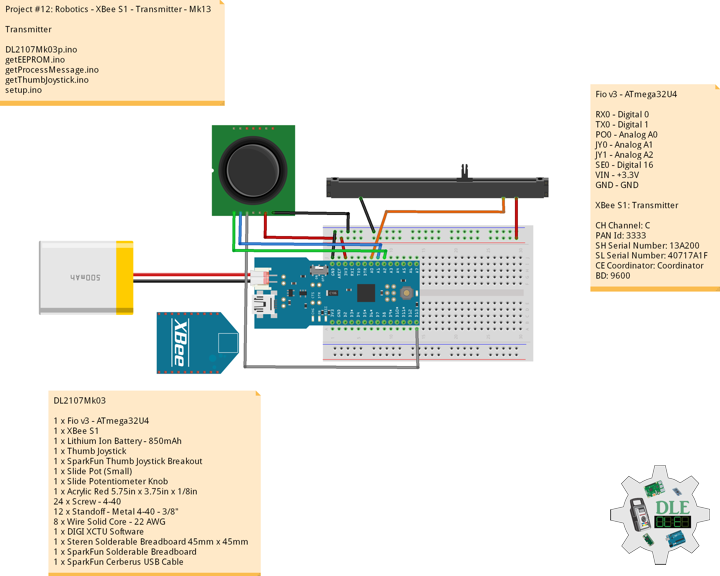
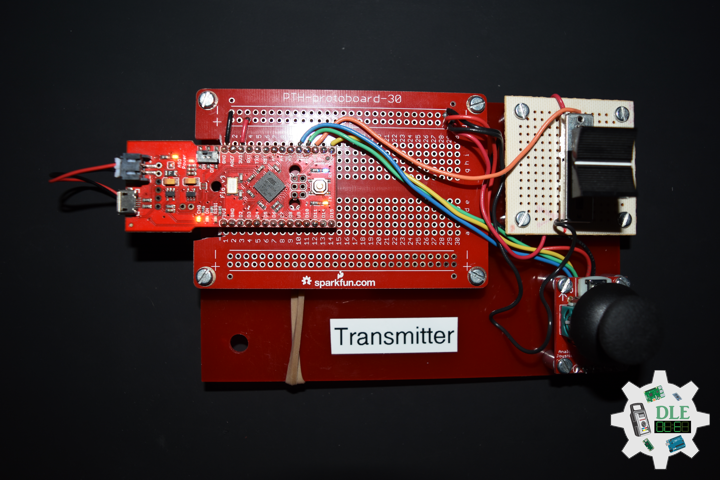
Project #12: Robotics – XBee S1 – Transmitter – Mk13
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Robotics #Arduino #Fio #FioV3ATmega32U4 #XBeeS1 #Transmitter #ThumbJoystick #SlidePot #Project #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant #VideoBlog
——
——
——
——
——
Fio v3 – ATmega32U4
The Fio v3 is a new spin on the Arduino Fio hardware powered by the ATmega32U4.Not only is it small and LiPo-ready, it’s a very capable XBee-ready development board. The JST-connector and 3.3v system voltage make this a great development tool for portable devices, simply plug in a Li-Poly battery and you’re ready to go. Wireless sensor networks and communication are made easy by the on-board XBee socket.
The ATmega32U4, running at 8MHz, makes it possible for you to use the on-board USB jack not only to charge a connected Li-Poly battery but to actually program the device. Because this board uses a similar bootloader to the one on the Pro Micro, you will need to download and install the special software driver below. There’s also a board definition add-on for the Arduino IDE which will add support for this board.
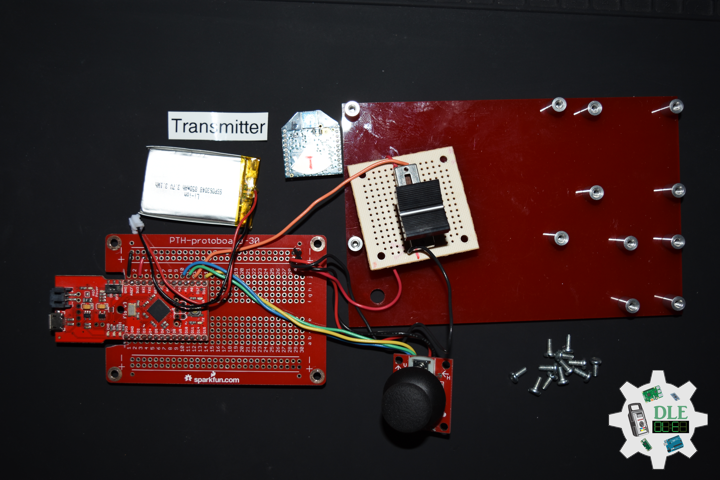
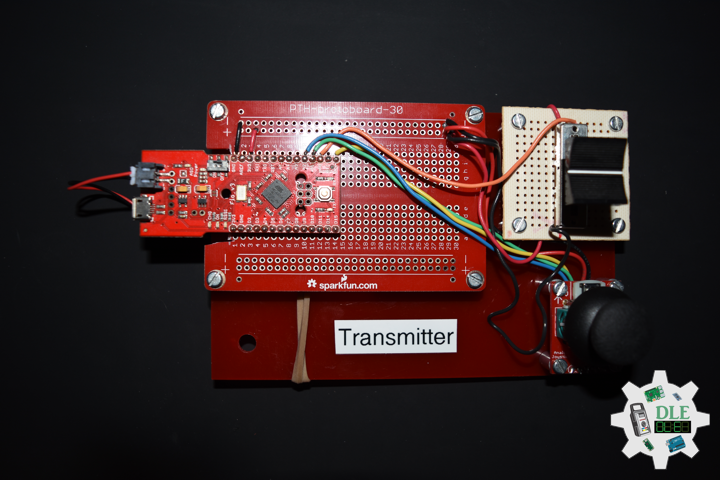
Transmitter
XBee S1: Transmitter
CH Channel: C
PAN Id: 3333
SH Serial Number: 13A200
SL Serial Number: 40717A1F
CE Coordinator: Coordinator
BD: 9600
DL2107Mk03
1 x Fio v3 – ATmega32U4
1 x XBee S1
1 x Lithium Ion Battery – 850mAh
1 x Thumb Joystick
1 x SparkFun Thumb Joystick Breakout
1 x Slide Pot (Small)
1 x Slide Potentiometer Knob
1 x Acrylic Red 5.75in x 3.75in x 1/8in
24 x Screw – 4-40
12 x Standoff – Metal 4-40 – 3/8″
8 x Wire Solid Core – 22 AWG
1 x DIGI XCTU Software
1 x Steren Solderable Breadboard 45mm x 45mm
1 x SparkFun Solderable Breadboard
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
Fio v3 – ATmega32U4
RX0 – Digital 0
TX0 – Digital 1
PO0 – Analog A0
JY0 – Analog A1
JY1 – Analog A2
SE0 – Digital 16
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
DL2107Mk03p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #12: Robotics - XBee S1 - Transmitter - Mk13
07-03
DL2107Mk03p.ino
1 x Fio v3 - ATmega32U4
1 x XBee S1
1 x Lithium Ion Battery - 850mAh
1 x Thumb Joystick
1 x SparkFun Thumb Joystick Breakout
1 x Slide Pot (Small)
1 x Slide Potentiometer Knob
1 x Acrylic Red 5.75in x 3.75in x 1/8in
24 x Screw - 4-40
12 x Standoff - Metal 4-40 - 3/8"
8 x Wire Solid Core - 22 AWG
1 x DIGI XCTU Software
1 x Steren Solderable Breadboard 45mm x 45mm
1 x SparkFun Solderable Breadboard
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// EEPROM library to read and write EEPROM with unique ID for unit
#include <EEPROM.h>
// Communication
unsigned long dTime = 50;
// Slide Pot (Small)
// Select the input pin for the slide pot
// Power
const int iSP1 = A0;
// Power to store the value
int iPower = 0;
// Connections to joystick
// Vertical
const int VERT = A1;
// Horizontal
const int HORIZ = A2;
// Pushbutton
const int SEL = 16;
// Initialize variables for analog and digital values
int vertical;
int horizontal;
int select;
// Software Version Information
// Version
String sver = "12-13";
// Unit ID Information
// UID
String uid = "";
void loop()
{
// Thumb Joystick
isThumbJoystick();
// Process Message
isProcessMessage();
delay( dTime );
}
getEEPROM.ino
// EEPROM
// is UID
void isUID()
{
// Is Unit ID
// UID
uid = "";
for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++)
{
uid = uid + char(EEPROM.read(x));
}
}
getProcessMessage.ino
// Process Message
// isProcessMessage
void isProcessMessage() {
// Loop through serial buffer
while ( Serial.available() )
{
// Print = "<" + vertical + "|" + horizontal + "|" + select + "|" + iValue + "|" + sver + "|" + uid + "*"
Serial.print( '<' );
Serial.print( vertical );
Serial.print( '|' );
Serial.print( horizontal );
Serial.print( '|' );
Serial.print( select );
Serial.print( '|' );
Serial.print( iPower );
Serial.print( '|' );
Serial.print( sver );
Serial.print( '|' );
Serial.print( uid );
Serial.println( '*' );
}
}
getThumbJoystick.ino
// Thumb Joystick
void isThumbJoystick() {
// Read all values from the joystick
// Joystick was sitting around 520 for the vertical and horizontal values
// Will be 0-1023
vertical = analogRead(VERT);
// Will be 0-1023
horizontal = analogRead(HORIZ);
// Will be HIGH (1) if not pressed, and LOW (0) if pressed
select = digitalRead(SEL);
// Read the value
// Power be 0-1023
iPower = analogRead( iSP1 );
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// EEPROM Unit ID
isUID();
// Pause
delay(5);
// Make the SEL line an input
pinMode(SEL, INPUT_PULLUP);
// Open serial port at 9600 baud
Serial.begin( 9600 );
// Pause
delay(5);
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- Robotics
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Desktop Applications (Windows, OSX, Linux, Multi-OS, Multi-Tier, etc…)
- Mobile Applications (Android, iOS, Blackberry, Windows Mobile, Windows CE, etc…)
- Web Applications (LAMP, Scripting, Java, ASP, ASP.NET, RoR, Wakanda, etc…)
- Social Media Programming & Integration (Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Pinterest, etc…)
- Content Management Systems (WordPress, Drupal, Joomla, Moodle, etc…)
- Bulletin Boards (phpBB, SMF, Vanilla, jobberBase, etc…)
- eCommerce (WooCommerce, OSCommerce, ZenCart, PayPal Shopping Cart, etc…)
Instructor
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
- DOS, Windows, OSX, Linux, iOS, Android, Multi-OS
- Linux-Apache-PHP-MySQL
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2021 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEngMk2021c.pdf
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEspMk2021c.pdf
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: https://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLE/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLHackster/
Web: https://www.hackster.io/neosteam-labs
Web: https://zoom.us/
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/DonLucElectronics
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
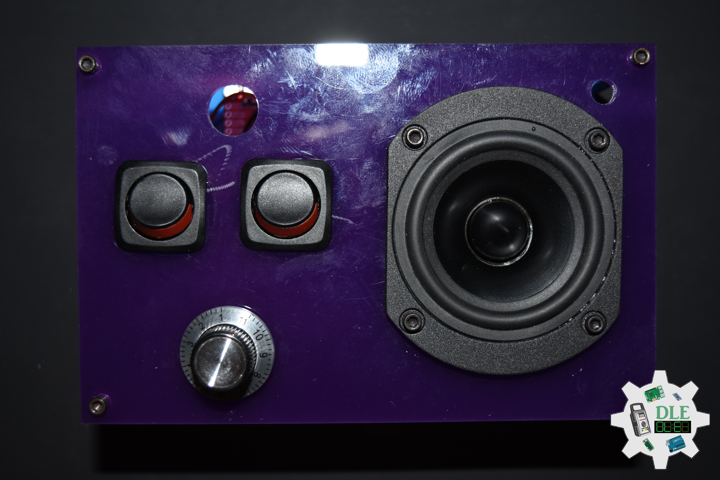
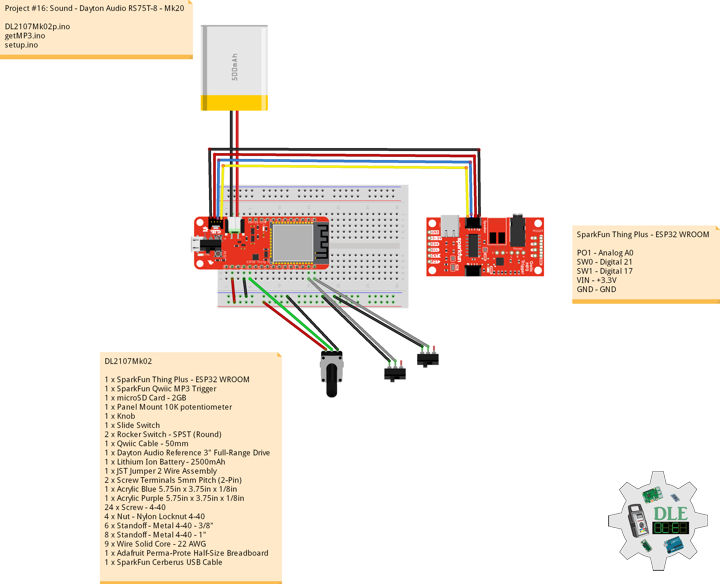
Project #16: Sound – Dayton Audio RS75T-8 – Mk20
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Sound #Arduino #ESP32 #SparkFunThingPlusESP32WROOM #SparkFunQwiicMP3 #DaytonAudioRS75T #Project #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant #VideoBlog
——
——
——
——
——
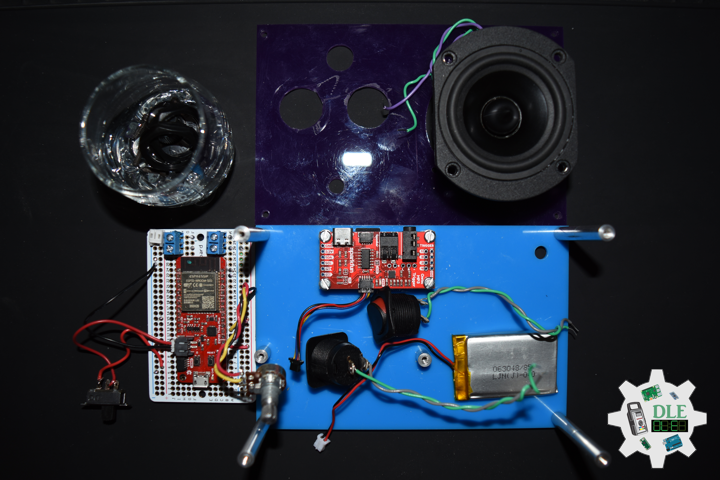
Dayton Audio RS75T-8 3″ Reference Full-Range Driver Truncated Frame
The Dayton Audio Reference Series sets a new standard of value in high-performance loudspeaker drivers. Incorporating a low-distortion motor system with a copper ring, a copper cap, and an aluminum phase plug, the RS75T-8 can outperform “boutique” drivers that cost several times the price. The driver’s truncated frame makes it ideal for line arrays and ultra-compact MTM designs requiring minimal driver-to-driver spacing. Its low-distortion characteristics and smooth response provide exceptional clarity, detail, and dynamics. Features a black anodized cone, heavy-duty 4-hole cast frame, low-loss rubber surround, and gold terminals.
DL2107Mk02
1 x SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
1 x SparkFun Qwiic MP3 Trigger
1 x microSD Card – 2GB
1 x Panel Mount 10K potentiometer
1 x Knob
1 x Slide Switch
2 x Rocker Switch – SPST (Round)
1 x Qwiic Cable – 50mm
1 x Dayton Audio Reference 3″ Full-Range Drive
1 x Lithium Ion Battery – 850mAh
1 x JST Jumper 2 Wire Assembly
2 x Screw Terminals 5mm Pitch (2-Pin)
1 x Acrylic Blue 5.75in x 3.75in x 1/8in
1 x Acrylic Purple 5.75in x 3.75in x 1/8in
24 x Screw – 4-40
4 x Nut – Nylon Locknut 4-40
6 x Standoff – Metal 4-40 – 3/8″
8 x Standoff – Metal 4-40 – 1″
18 x Wire Solid Core – 22 AWG
1 x Adafruit Perma-Prote Half-Size Breadboard
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
PO1 – Analog A0
SW0 – Digital 21
SW1 – Digital 17
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
DL2107Mk02p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
#16 - Sound - Dayton Audio RS75T-8 - Mk20
07-02
DL2107Mk02p.ino
1 x SparkFun Thing Plus - ESP32 WROOM
1 x SparkFun Qwiic MP3 Trigger
1 x microSD Card - 2GB
1 x Panel Mount 10K potentiometer
1 x Knob
1 x Slide Switch
2 x Rocker Switch - SPST (Round)
1 x Qwiic Cable - 50mm
1 x Dayton Audio Reference 3" Full-Range Drive
1 x Lithium Ion Battery - 850mAh
1 x JST Jumper 2 Wire Assembly
2 x Screw Terminals 5mm Pitch (2-Pin)
1 x Acrylic Blue 5.75in x 3.75in x 1/8in
1 x Acrylic Purple 5.75in x 3.75in x 1/8in
24 x Screw - 4-40
4 x Nut - Nylon Locknut 4-40
6 x Standoff - Metal 4-40 - 3/8"
8 x Standoff - Metal 4-40 - 1"
18 x Wire Solid Core - 22 AWG
1 x Adafruit Perma-Prote Half-Size Breadboard
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// Wire communicate with I2C / TWI devices
#include <Wire.h>
// SparkFun MP3 Trigger
#include "SparkFun_Qwiic_MP3_Trigger_Arduino_Library.h"
// SparkFun MP3 Trigger
MP3TRIGGER mp3;
int iSongCount = 0;
int x = 0;
// Volume
int iVolume = A0;
int iVolumeLevel = 0;
// EQ Setting Normal
byte bEQSetting = 0;
// Play Next
const int iPlayNext = 21;
// Variable for reading the iPlayNext status
int iPlayNextState = 0;
// Play Previous
const int iPlayPrevious = 17;
// Variable for reading the iPlayPrevious status
int iPlayPreviousState = 0;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "16-20";
void loop()
{
if (mp3.isPlaying() == false) {
if ( x > iSongCount ) {
x = 0;
} else {
x = x + 1;
}
// Play Track
mp3.playTrack( x );
} else {
// Volume
isVolume();
// Play Next
isPlayNext();
// Play Previous
isPlayPrevious();
}
}
getMP3.ino
// MP3
// Setup MP3
void isSetupMP3(){
// Check to see if Qwiic MP3 is present on the bus
if (mp3.begin() == false)
{
// Qwiic MP3 failed to respond. Please check wiring and possibly the I2C address. Freezing...
while (1);
}
if (mp3.hasCard() == false)
{
// Qwiic MP3 is missing its SD card. Freezing...
while (1);
}
// Song Count
iSongCount = mp3.getSongCount();
// EQ Setting Classic
bEQSetting = mp3.getEQ();
// Initialize the iPlayNext
pinMode( iPlayNext, INPUT);
// Initialize the iPlayPrevious
pinMode( iPlayPrevious, INPUT);
}
// Volume
void isVolume() {
// Volume
iVolumeLevel = analogRead( iVolume );
// (0-1023 for 10 bits or 0-4095 for 12 bits)
iVolumeLevel = map(iVolumeLevel, 0, 4095, 0, 31);
// Volume can be 0 (off) to 31 (max)
mp3.setVolume( iVolumeLevel );
}
// Play Next
void isPlayNext() {
// Read the state of the iPlayNext value
iPlayNextState = digitalRead( iPlayNext );
if ( iPlayNextState == HIGH ) {
mp3.stop();
if ( x > iSongCount ) {
x = 0;
} else {
x = x + 1;
}
// Play Track
mp3.playTrack( x );
}
}
// Play Previous
void isPlayPrevious() {
// Read the state of the iPlayPrevious value
iPlayPreviousState = digitalRead( iPlayPrevious );
if ( iPlayPreviousState == HIGH ) {
mp3.stop();
if ( x > iSongCount ) {
x = 0;
} else {
x = x - 1;
}
// Play Track
mp3.playTrack( x );
}
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// Wire communicate with I2C / TWI devices
Wire.begin();
// SparkFun MP3 Trigger Setup
isSetupMP3();
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- Robotics
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Desktop Applications (Windows, OSX, Linux, Multi-OS, Multi-Tier, etc…)
- Mobile Applications (Android, iOS, Blackberry, Windows Mobile, Windows CE, etc…)
- Web Applications (LAMP, Scripting, Java, ASP, ASP.NET, RoR, Wakanda, etc…)
- Social Media Programming & Integration (Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Pinterest, etc…)
- Content Management Systems (WordPress, Drupal, Joomla, Moodle, etc…)
- Bulletin Boards (phpBB, SMF, Vanilla, jobberBase, etc…)
- eCommerce (WooCommerce, OSCommerce, ZenCart, PayPal Shopping Cart, etc…)
Instructor
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
- DOS, Windows, OSX, Linux, iOS, Android, Multi-OS
- Linux-Apache-PHP-MySQL
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2021 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEngMk2021c.pdf
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEspMk2021c.pdf
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: http://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLE/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLHackster/
Web: https://www.hackster.io/neosteam-labs
Web: https://zoom.us/
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/DonLucElectronics
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
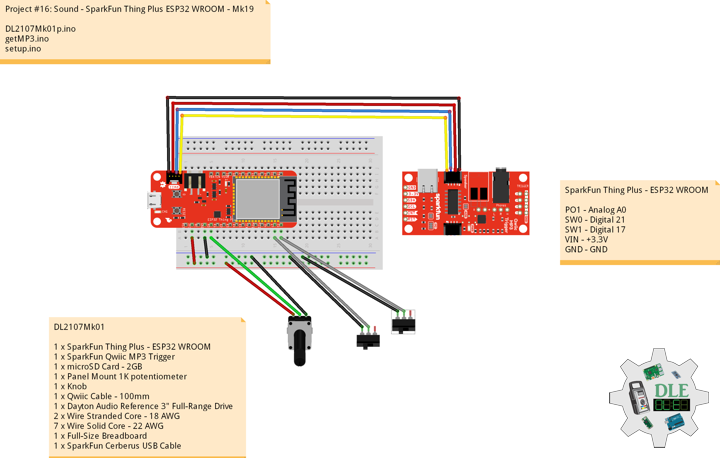
Project #16: Sound – SparkFun Thing Plus ESP32 WROOM – Mk19
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Sound #Arduino #ESP32 #SparkFunThingPlusESP32WROOM #SparkFunQwiicMP3 #Project #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant #VideoBlog
——
——
——
——
——-
SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
The SparkFun ESP32 Thing Plus is the next step to get started with Espressif IoT ideations while still enjoying all the amenities of the original ESP32 Thing. Espressif’s ESP32 WROOM is a powerful WiFi and Bluetooth MCU module that targets a wide variety of applications. At the core of this module is the ESP32-D0WDQ6 chip which is designed to be both scalable and adaptive. To make the Thing Plus even easier to use, we’ve moved a few pins around to make the board Feather compatible and it utilizes our handy Qwiic Connect System which means no soldering or shields are required to connect it to the rest of your system. A JST connector to plug in a LiPo battery.
SparkFun Qwiic MP3 Trigger
Sometimes you just need an MP3 to play. The SparkFun Qwiic MP3 Trigger takes care of all the necessary requirements, all you need to do is send a simple I2C command and listen to whatever is on your micro SD card. The contents of the microSD card appears as a jump drive. Simply plug in the Qwiic MP3 Trigger and you’ll be transferring MP3s, no need for drivers and no need for WAV or Vorbis conversion. Your supplied speaker is boosted by a Class-D mono amplifier capable of outputting up to 1.4W making it capable of being incredibly loud. Volume is software selectable between 32 levels.
DL2107Mk01
1 x SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
1 x SparkFun Qwiic MP3 Trigger
1 x microSD Card – 2GB
1 x Panel Mount 1K potentiometer
1 x Knob
1 x Qwiic Cable – 100mm
1 x Dayton Audio Reference 3″ Full-Range Drive
2 x Wire Stranded Core – 18 AWG
7 x Wire Solid Core – 22 AWG
1 x Full-Size Breadboard
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM
PO1 – Analog A0
SW0 – Digital 21
SW1 – Digital 17
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
DL2107Mk01p.ino
// ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
// Software Version Information
// #16 - Sound - SparkFun Thing Plus ESP32 WROOM - Mk19
// 07-01
// DL2107Mk01p.ino
// 1 x SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
// 1 x SparkFun Qwiic MP3 Trigger
// 1 x microSD Card - 2GB
// 1 x Panel Mount 1K potentiometer
// 1 x Knob
// 1 x Qwiic Cable - 100mm
// 1 x Dayton Audio Reference 3" Full-Range Drive
// 2 x Wire Stranded Core - 18 AWG
// 7 x Wire Solid Core - 22 AWG
// 1 x Full-Size Breadboard
// 1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
// Include the Library Code
// Wire communicate with I2C / TWI devices
#include <Wire.h>
// SparkFun MP3 Trigger
#include "SparkFun_Qwiic_MP3_Trigger_Arduino_Library.h"
// SparkFun MP3 Trigger
MP3TRIGGER mp3;
int iSongCount = 0;
int x = 0;
// Volume
int iVolume = A0;
int iVolumeLevel = 0;
// EQ Setting Normal
byte bEQSetting = 0;
// Play Next
const int iPlayNext = 21;
// Variable for reading the iPlayNext status
int iPlayNextState = 0;
// Play Previous
const int iPlayPrevious = 17;
// Variable for reading the iPlayPrevious status
int iPlayPreviousState = 0;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "16-19";
void loop()
{
if (mp3.isPlaying() == false) {
if ( x > iSongCount ) {
x = 0;
} else {
x = x + 1;
}
// Play Track
mp3.playTrack( x );
} else {
// Volume
isVolume();
// Play Next
isPlayNext();
// Play Previous
isPlayPrevious();
}
}
getMP3.ino
// MP3
// Setup MP3
void isSetupMP3(){
// Check to see if Qwiic MP3 is present on the bus
if (mp3.begin() == false)
{
// Qwiic MP3 failed to respond. Please check wiring and possibly the I2C address. Freezing...
while (1);
}
if (mp3.hasCard() == false)
{
// Qwiic MP3 is missing its SD card. Freezing...
while (1);
}
// Song Count
iSongCount = mp3.getSongCount();
// EQ Setting Classic
bEQSetting = mp3.getEQ();
// Initialize the iPlayNext
pinMode( iPlayNext, INPUT);
// Initialize the iPlayPrevious
pinMode( iPlayPrevious, INPUT);
}
// Volume
void isVolume() {
// Volume
iVolumeLevel = analogRead( iVolume );
// (0-1023 for 10 bits or 0-4095 for 12 bits)
iVolumeLevel = map(iVolumeLevel, 0, 4095, 0, 31);
// Volume can be 0 (off) to 31 (max)
mp3.setVolume( iVolumeLevel );
}
// Play Next
void isPlayNext() {
// Read the state of the iPlayNext value
iPlayNextState = digitalRead( iPlayNext );
if ( iPlayNextState == HIGH ) {
mp3.stop();
if ( x > iSongCount ) {
x = 0;
} else {
x = x + 1;
}
// Play Track
mp3.playTrack( x );
}
}
// Play Previous
void isPlayPrevious() {
// Read the state of the iPlayPrevious value
iPlayPreviousState = digitalRead( iPlayPrevious );
if ( iPlayPreviousState == HIGH ) {
mp3.stop();
if ( x > iSongCount ) {
x = 0;
} else {
x = x - 1;
}
// Play Track
mp3.playTrack( x );
}
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// Wire communicate with I2C / TWI devices
Wire.begin();
// SparkFun MP3 Trigger Setup
isSetupMP3();
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- Robotics
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Desktop Applications (Windows, OSX, Linux, Multi-OS, Multi-Tier, etc…)
- Mobile Applications (Android, iOS, Blackberry, Windows Mobile, Windows CE, etc…)
- Web Applications (LAMP, Scripting, Java, ASP, ASP.NET, RoR, Wakanda, etc…)
- Social Media Programming & Integration (Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Pinterest, etc…)
- Content Management Systems (WordPress, Drupal, Joomla, Moodle, etc…)
- Bulletin Boards (phpBB, SMF, Vanilla, jobberBase, etc…)
- eCommerce (WooCommerce, OSCommerce, ZenCart, PayPal Shopping Cart, etc…)
Instructor
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
- DOS, Windows, OSX, Linux, iOS, Android, Multi-OS
- Linux-Apache-PHP-MySQL
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2021 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEngMk2021c.pdf
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEspMk2021c.pdf
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: http://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLE/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLHackster/
Web: https://www.hackster.io/neosteam-labs
Web: https://zoom.us/
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/DonLucElectronics
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
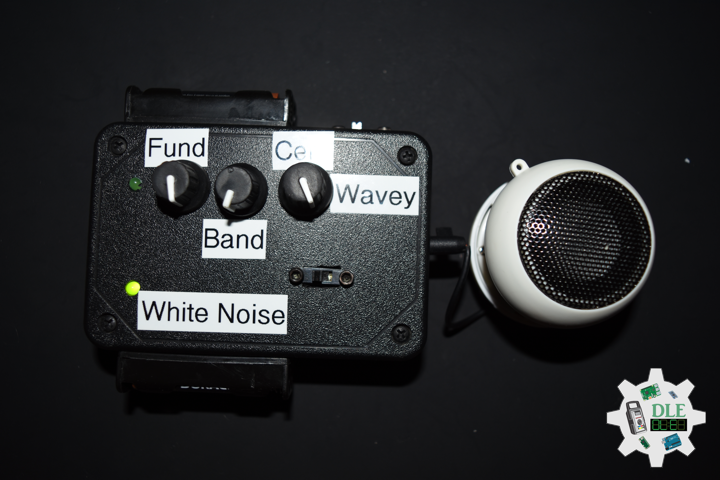
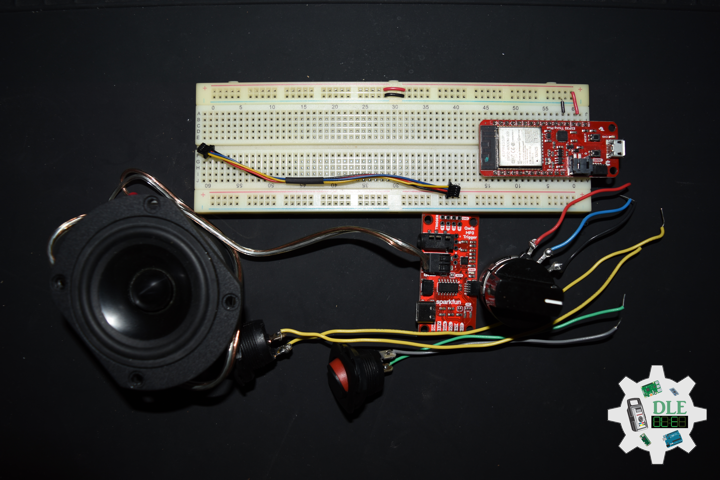
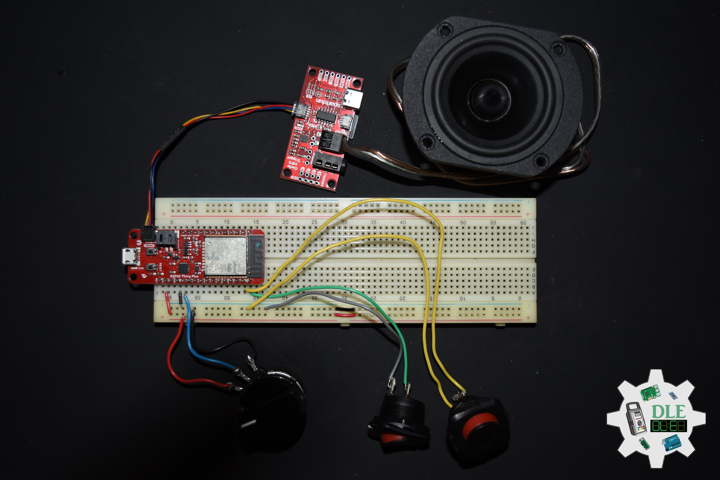
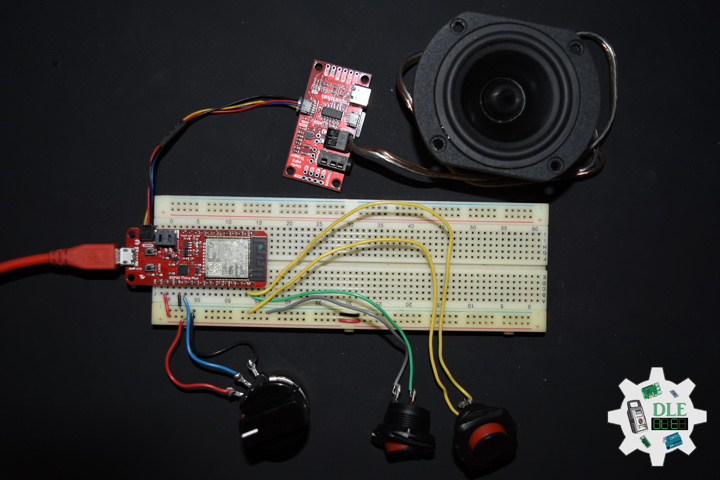
Project #16: Sound – Music Acoustics – Mk18
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Sound #WhiteNoise #Mozzi #WavePacket #Arduino #Project #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant #VideoBlog
——
——
——
——
——
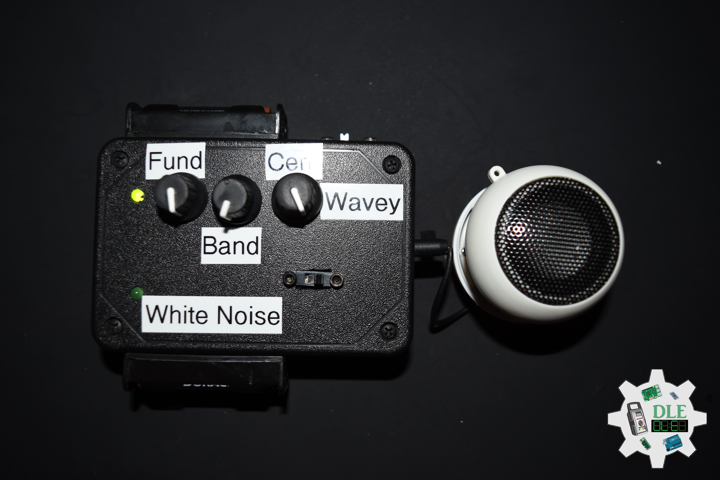
Music Acoustics
Music acoustics is a multidisciplinary field that combines knowledge from physics, psychophysics, physiology, and signal processing among other disciplines. As a branch of acoustics, it is concerned with researching and describing the physics of music, how sounds are employed to make music. Examples of areas of study are the function human voice (the physics of speech), computer analysis, and in the clinical.
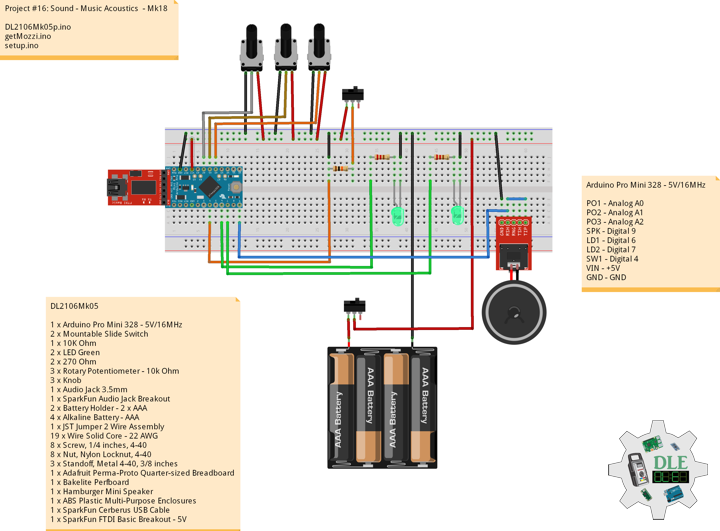
DL2106Mk05
1 x Arduino Pro Mini 328 – 5V/16MHz
2 x Mountable Slide Switch
1 x 10K Ohm
2 x LED Green
2 x 270 Ohm
3 x Rotary Potentiometer – 10k Ohm
3 x Knob
1 x Audio Jack 3.5mm
1 x SparkFun Audio Jack Breakout
2 x Battery Holder – 2 x AAA
4 x Alkaline Battery – AAA
1 x JST Jumper 2 Wire Assembly
19 x Wire Solid Core – 22 AWG
8 x Screw, 1/4 inches, 4-40
8 x Nut, Nylon Locknut, 4-40
3 x Standoff, Metal 4-40, 3/8 inches
1 x Adafruit Perma-Proto Quarter-sized Breadboard PCB
1 x Bakelite Perfboard
1 x Hamburger Mini Speaker
1 x ABS Plastic Multi-Purpose Enclosures
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
1 x SparkFun FTDI Basic Breakout – 5V
Arduino Pro Mini 328 – 5V/16MHz
PO1 – Analog A0
PO2 – Analog A1
PO3 – Analog A2
SPK – Digital 9
LD1 – Digital 6
LD2 – Digital 7
SW1 – Digital 4
VIN – +5V
GND – GND
DL2106Mk05p.ino
// ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
// Software Version Information
// Project #16: Sound - Music Acoustics - Mk18
// 06-05
// DL2106Mk05.ino 16-18
// 1 x Arduino Pro Mini 328 - 5V/16MHz
// 2 x Mountable Slide Switch
// 1 x 10K Ohm
// 2 x LED Green
// 2 x 270 Ohm
// 3 x Rotary Potentiometer - 10k Ohm
// 3 x Knob
// 1 x Audio Jack 3.5mm
// 1 x SparkFun Audio Jack Breakout
// 2 x Battery Holder - 2 x AAA
// 4 x Alkaline Battery - AAA
// 1 x JST Jumper 2 Wire Assembly
// 19 x Wire Solid Core - 22 AWG
// 8 x Screw, 1/4 inches, 4-40
// 8 x Nut, Nylon Locknut, 4-40
// 3 x Standoff, Metal 4-40, 3/8 inches
// 1 x Adafruit Perma-Proto Quarter-sized Breadboard PCB
// 1 x Bakelite Perfboard
// 1 x Hamburger Mini Speaker
// 1 x ABS Plastic Multi-Purpose Enclosures
// 1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
// 1 x SparkFun FTDI Basic Breakout - 5V
// Include the Library Code
// Mozzi
#include <MozziGuts.h>
// Mozzi Random
#include <mozzi_rand.h>
// Oscillator template
#include <Oscil.h>
// Mozzi Analog
#include <mozzi_analog.h>
// WavePacket Sample
#include <WavePacket.h>
// Rolling Average
#include <RollingAverage.h>
// Sine table for oscillator whitenoise
#include <tables/whitenoise8192_int8.h>
// Set the input for the knob
#define FUNDAMENTAL_PIN A0
#define BANDWIDTH_PIN A1
#define CENTREFREQ_PIN A2
// for smoothing the control signals
// Rolling Average
RollingAverage <int, 32> kAverageF;
RollingAverage <int, 32> kAverageBw;
RollingAverage <int, 32> kAverageCf;
// SINGLE selects 1 non-overlapping stream
WavePacket <SINGLE> wavey;
// Oscil <table_size, update_rate> oscilName (wavetable)
Oscil <WHITENOISE8192_NUM_CELLS, AUDIO_RATE> aSin(WHITENOISE8192_DATA);
// Mini Speaker
int SPK = 9;
// Mountable Slide Switch
int iSS1 = 4;
// State
int iSS1State = 0;
// LED Green
int iLEDG1 = 6;
int iLEDG2 = 7;
// Set the input for the volume
// Volume level from updateControl() to updateAudio()
byte vol;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "16-18";
void loop() {
// Slide Switch
// Read the state of the iSS1 value
iSS1State = digitalRead(iSS1);
// Audio Hook
audioHook();
}
getMozzi.ino
// Mozzi
// Update Control
void updateControl(){
// If it is the Slide Switch State is HIGH
if (iSS1State == HIGH) {
// White Noise
vol = 255;
} else {
// Wavey Set
wavey.set(kAverageF.next(mozziAnalogRead(FUNDAMENTAL_PIN))+1,
kAverageBw.next(mozziAnalogRead(BANDWIDTH_PIN)),
kAverageCf.next(2*mozziAnalogRead(CENTREFREQ_PIN)));
}
}
// Update Audio
int updateAudio()
{
// If it is the Slide Switch State is HIGH
if (iSS1State == HIGH) {
// LED Green
digitalWrite(iLEDG1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(iLEDG2, LOW);
// White Noise
char whitenoise = rand((byte)255) - 128;
return (((whitenoise * aSin.next())) * vol)>>8;
} else {
// LED Green
digitalWrite(iLEDG1, LOW);
digitalWrite(iLEDG2, HIGH);
// AUDIO_MODE STANDARD
// Wavey Next
return wavey.next()>>8;
}
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// Slide Switch
pinMode(iSS1, INPUT);
// LED Green
pinMode(iLEDG1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(iLEDG2, OUTPUT);
// Mozzi Start
startMozzi();
// Set the frequency
aSin.setFreq(0.05f);
}
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- Robotics
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Desktop Applications (Windows, OSX, Linux, Multi-OS, Multi-Tier, etc…)
- Mobile Applications (Android, iOS, Blackberry, Windows Mobile, Windows CE, etc…)
- Web Applications (LAMP, Scripting, Java, ASP, ASP.NET, RoR, Wakanda, etc…)
- Social Media Programming & Integration (Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Pinterest, etc…)
- Content Management Systems (WordPress, Drupal, Joomla, Moodle, etc…)
- Bulletin Boards (phpBB, SMF, Vanilla, jobberBase, etc…)
- eCommerce (WooCommerce, OSCommerce, ZenCart, PayPal Shopping Cart, etc…)
Instructor
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
- DOS, Windows, OSX, Linux, iOS, Android, Multi-OS
- Linux-Apache-PHP-MySQL
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2021 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEngMk2021c.pdf
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEspMk2021c.pdf
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: http://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLE/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLHackster/
Web: https://www.hackster.io/neosteam-labs
Web: https://zoom.us/
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/DonLucElectronics
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
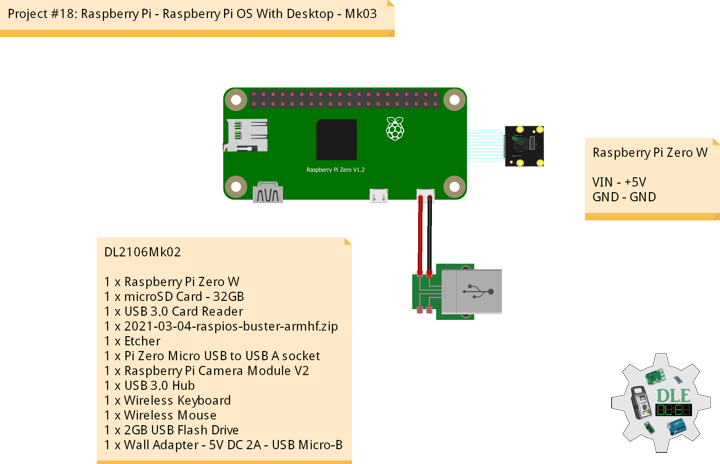
Project #18: Raspberry Pi – Raspberry Pi OS With Desktop – Mk03
——
#donluc #project #RaspberryPiZeroW #RaspberryPi #RaspberryPiCamera #Camera #programming #electronics #microcontrollers #consultant #zoom #patreon #videoblog
——
——
——
——
——
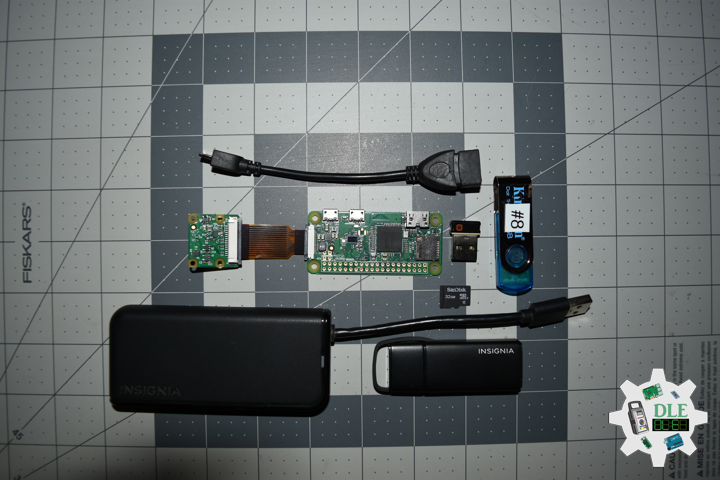
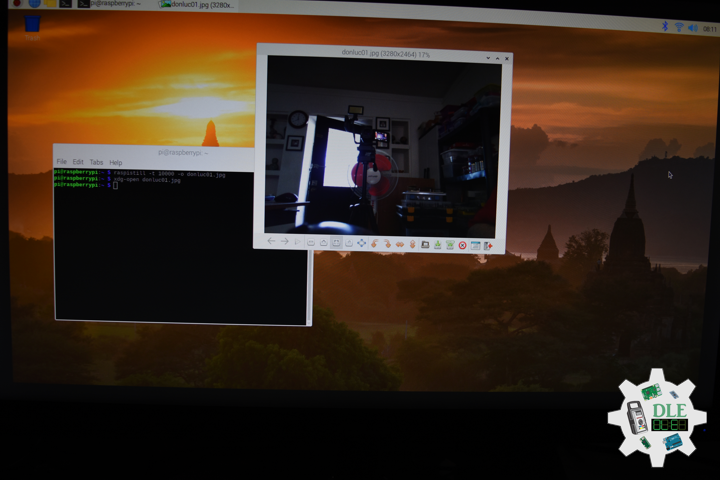
Raspberry Pi OS With Desktop
Raspberry PI OS Desktop versions come with a default Graphical User Interface. Based on Pixel, it aims to be light and to run fast in your Raspberry Pi. The desktop version includes all the scripts to display the icons. It also includes all the tools to configure your environment and utilities to interface other programs/applications. Command Line interface is still available using terminal window. Like all Desktop environments, even if optimized it requires anyway addicting packages and software, RAM and CPU usage will result increased if compared to Lite version. Raspberry PI OS Desktop requires keyboard, mouse and monitor, at least until you will configure remote desktop service.
DL2106Mk02
1 x Raspberry Pi Zero W
1 x microSD Card – 32GB
1 x USB 3.0 Card Reader
1 x 2021-03-04-raspios-buster-armhf.zip
1 x Etcher
1 x Pi Zero Micro USB to USB A socket
1 x Raspberry Pi Camera Module V2
1 x USB 3.0 Hub
1 x Wireless Keyboard
1 x Wireless Mouse
1 x 2GB USB Flash Drive
1 x Wall Adapter – 5V DC 2A – USB Micro-B
Raspberry Pi Zero W
VIN – +5V
GND – GND
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- Robotics
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Desktop Applications (Windows, OSX, Linux, Multi-OS, Multi-Tier, etc…)
- Mobile Applications (Android, iOS, Blackberry, Windows Mobile, Windows CE, etc…)
- Web Applications (LAMP, Scripting, Java, ASP, ASP.NET, RoR, Wakanda, etc…)
- Social Media Programming & Integration (Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Pinterest, etc…)
- Content Management Systems (WordPress, Drupal, Joomla, Moodle, etc…)
- Bulletin Boards (phpBB, SMF, Vanilla, jobberBase, etc…)
- eCommerce (WooCommerce, OSCommerce, ZenCart, PayPal Shopping Cart, etc…)
Instructor
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
- DOS, Windows, OSX, Linux, iOS, Android, Multi-OS
- Linux-Apache-PHP-MySQL
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2021 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEngMk2021c.pdf
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEspMk2021c.pdf
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: http://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLE/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLHackster/
Web: https://www.hackster.io/neosteam-labs
Web: https://zoom.us/
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/DonLucElectronics
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
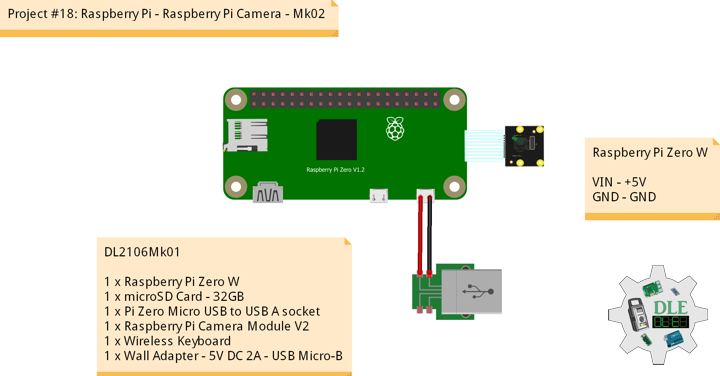
Project #18: Raspberry Pi – Raspberry Pi Camera – Mk02
——
#donluc #project #RaspberryPiZeroW #RaspberryPi #RaspberryPiCamera #Camera #programming #electronics #microcontrollers #consultant #zoom #patreon #videoblog
——
——
——
——
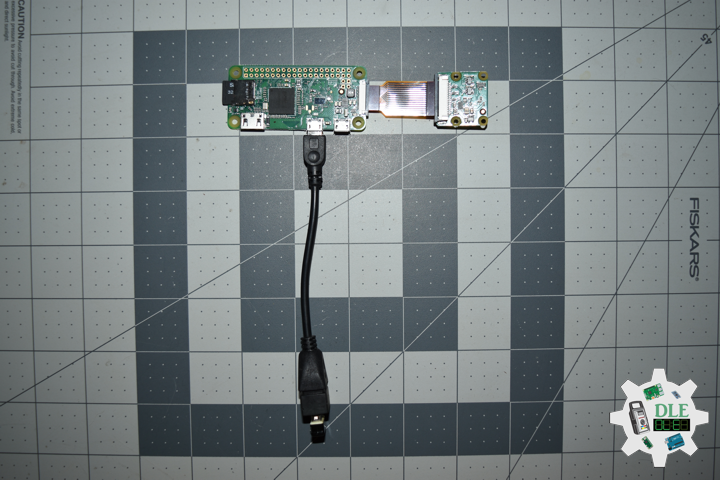
Raspberry Pi Camera
This 8mp camera module is capable of 1080p video and still images that connect directly to your Raspberry Pi. This is the plug-and-play-compatible latest version of the Raspbian operating system, making it perfect for time-lapse photography, recording video, motion detection and security applications. Connect the included ribbon cable to the CSI (Camera Serial Interface) port on your Raspberry Pi, and you are good to go.
The board itself is tiny, at around 25mm x 23mm x 9mm and weighing in at just over 3g, making it perfect for mobile or other applications where size and weight are important. The sensor has a native resolution of 8 megapixel, and has a fixed focus lens on board. In terms of still images, the camera is capable of 3280 x 2464 pixel static images, and also supports 1080p30, 720p60 and 640x480p90 video.
DL2106Mk01
1 x Raspberry Pi Zero W
1 x microSD Card – 32GB
1 x Pi Zero Micro USB to USB A socket
1 x Raspberry Pi Camera Module V2
1 x Wireless Keyboard
1 x Wall Adapter – 5V DC 2A – USB Micro-B
Raspberry Pi Zero W
VIN – +5V
GND – GND
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- Robotics
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Desktop Applications (Windows, OSX, Linux, Multi-OS, Multi-Tier, etc…)
- Mobile Applications (Android, iOS, Blackberry, Windows Mobile, Windows CE, etc…)
- Web Applications (LAMP, Scripting, Java, ASP, ASP.NET, RoR, Wakanda, etc…)
- Social Media Programming & Integration (Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Pinterest, etc…)
- Content Management Systems (WordPress, Drupal, Joomla, Moodle, etc…)
- Bulletin Boards (phpBB, SMF, Vanilla, jobberBase, etc…)
- eCommerce (WooCommerce, OSCommerce, ZenCart, PayPal Shopping Cart, etc…)
Instructor
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
- DOS, Windows, OSX, Linux, iOS, Android, Multi-OS
- Linux-Apache-PHP-MySQL
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2021 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEngMk2021c.pdf
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEspMk2021c.pdf
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: http://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLE/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLHackster/
Web: https://www.hackster.io/neosteam-labs
Web: https://zoom.us/
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/DonLucElectronics
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
Project #18: Raspberry Pi – Raspberry Pi Zero W – Mk01
——
#donluc #project #RaspberryPiZeroW #RaspberryPi #PuTTY #Etcher #programming #electronics #microcontrollers #consultant #zoom #patreon #videoblog
——
——
——
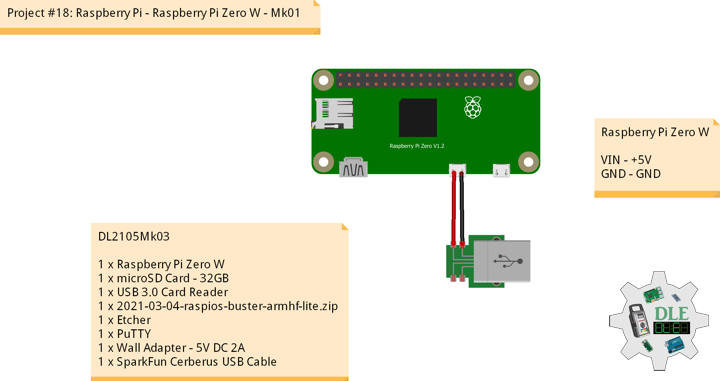
Raspberry Pi Zero W
The Raspberry Pi is a popular Single Board Computer in that it is a full computer packed into a single board. Many may already familiar with the Raspberry Pi 4 and its predecessors, which comes in a form factor that has become as highly recognizable. The Raspberry Pi comes in an even smaller form factor. The introduction of the Raspberry Pi Zero allowed one to embed an entire computer in even smaller projects. While these directions should work for most any version and form factor of the Raspberry Pi Zero W.
The credit-card-sized computer has become even smaller. The Raspberry Pi Zero W is still the Pi you know and love, but at a largely reduced size of only 65mm long by 30mm wide. With the addition of wireless LAN and Bluetooth, the Raspberry Pi Zero W is ideal for making embedded IoT projects. The Pi Zero W has been designed to be as flexible and compact as possible with mini connectors and an unpopulated 40-pin GPIO, allowing you to use only what your project requires.
At the heart of the Raspberry Pi Zero W is a 1GHz BCM2835 single-core processor with 512MB RAM. The setup for the Raspberry Pi Zero W is a little more complicated than on other Pis.
Etcher
balenaEtcher is a free and open-source utility used for writing image files such as .iso and .img files, as well as zipped folders onto storage media to create live SD cards and USB flash drives.
DL2105Mk03
1 x Raspberry Pi Zero W
1 x microSD Card – 32GB
1 x USB 3.0 Card Reader
1 x 2021-03-04-raspios-buster-armhf-lite.zip
1 x Etcher
1 x PuTTY
1 x Wall Adapter – 5V DC 2A
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
Raspberry Pi Zero W
VIN – +5V
GND – GND
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- Robotics
- Research & Development (R & D)
- Desktop Applications (Windows, OSX, Linux, Multi-OS, Multi-Tier, etc…)
- Mobile Applications (Android, iOS, Blackberry, Windows Mobile, Windows CE, etc…)
- Web Applications (LAMP, Scripting, Java, ASP, ASP.NET, RoR, Wakanda, etc…)
- Social Media Programming & Integration (Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Pinterest, etc…)
- Content Management Systems (WordPress, Drupal, Joomla, Moodle, etc…)
- Bulletin Boards (phpBB, SMF, Vanilla, jobberBase, etc…)
- eCommerce (WooCommerce, OSCommerce, ZenCart, PayPal Shopping Cart, etc…)
Instructor
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
- DOS, Windows, OSX, Linux, iOS, Android, Multi-OS
- Linux-Apache-PHP-MySQL
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2021 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEngMk2021c.pdf
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/CV/LucPaquinCVEspMk2021c.pdf
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: http://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLE/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/DLHackster/
Web: https://www.hackster.io/neosteam-labs
Web: https://zoom.us/
Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/DonLucElectronics
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc