Consultant
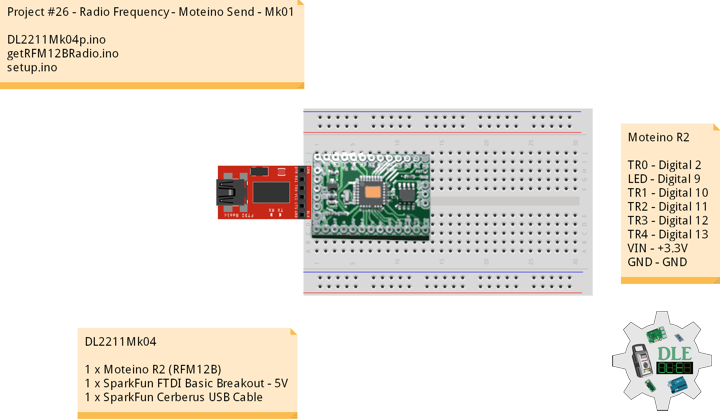
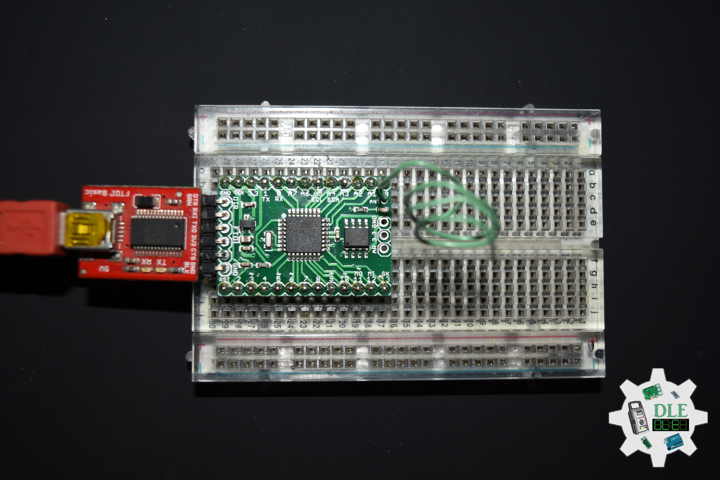
Project #26 – Radio Frequency – Moteino Send – Mk01
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #RadioFrequency #Moteino #Send #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
Radio Frequency
Radio Frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around 20 kHz to around 300 GHz. This is roughly between the upper limit of audio frequencies and the lower limit of infrared frequencies, these are the frequencies at which energy from an oscillating current can radiate off a conductor into space as radio waves. Different sources specify different upper and lower bounds for the frequency range. Energy from RF currents in conductors can radiate into space as radio waves. This is the basis of radio technology.
Duplex Telecommunications
A duplex communication system is a point-to-point system composed of two or more connected parties or devices that can communicate with one another in both directions. Duplex systems are employed in many communications networks, either to allow for simultaneous communication in both directions between two connected parties or to provide a reverse path for the monitoring and remote adjustment of equipment in the field. There are two types of duplex communication systems: full-duplex (FDX) and half-duplex (HDX).
ISM Radio Band
The ISM radio bands are portions of the radio spectrum reserved internationally for industrial, scientific and medical (ISM) purposes, excluding applications in telecommunications. Examples of applications for the use of radio frequency (RF) energy in these bands include radio-frequency process heating, microwave ovens, and medical diathermy machines. The powerful emissions of these devices can create electromagnetic interference and disrupt radio communication using the same frequency, so these devices are limited to certain bands of frequencies. In general, communications equipment operating in ISM bands must tolerate any interference generated by ISM applications, and users have no regulatory protection from ISM device operation in these bands.
RFM12B Universal ISM Band FSK Transceiver
Hoperf is RFM12B is a single chip, low power, multi-channel FSK transceiver designed for use in applications requiring FCC or ETSI conformance for unlicensed use in the 433, 868 and 915 MHz bands. The RFM12B transceiver is a part of Hoperf EZRadio product line, which produces a flexible, low cost, and highly integrated solution that does not require production alignments. All required RF functions are integrated. Only an external crystal and bypass filtering are needed for operation.
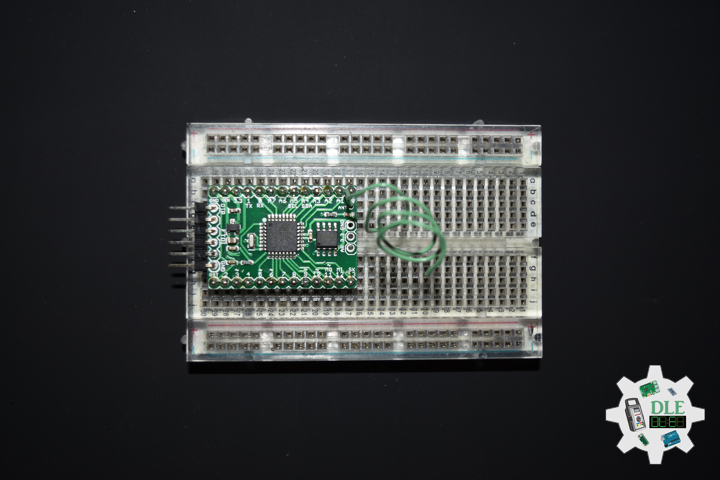
Moteino
Moteino began as a low power wireless Arduino compatible development platform based on the popular ATmega328p chip used in the Arduino UNO. Moteinos are compatible and can communicate with any other Arduino or development platform that uses the popular HopeRF RFM69 or LoRa transceivers, or even the older RFM12B. Moteino also comes with an optional SPI flash memory chip for wireless programming, or data logging. Moteino was designed to be a compact, highly customizable and affordable development platform, suitable for IoT, home automation and long range wireless projects.
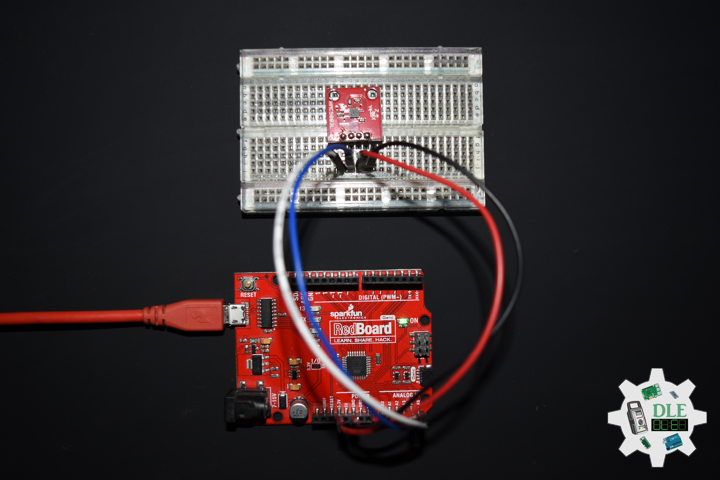
Moteino R2 (RFM12B)
- Frequency Band: 433 MHz
- Flash Memory: With 4Mbit Flash Chip
DL2211Mk04
1 x Moteino R2 (RFM12B)
1 x SparkFun FTDI Basic Breakout – 5V
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
——
Moteino R2
TR0 – Digital 2
LED – Digital 9
TR1 – Digital 10
TR2 – Digital 11
TR3 – Digital 12
TR4 – Digital 13
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
——
DL2211Mk04p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #26 - Radio Frequency - Moteino Send - Mk01
26-01
DL2211Mk04p.ino
1 x Moteino R2 (RFM12B)
1 x SparkFun FTDI Basic Breakout - 5V
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// RFM12B Radio
#include <RFM12B.h>
// Sleep
#include <avr/sleep.h>
// You will need to initialize the radio by telling it what ID
// it has and what network it's on
// The NodeID takes values from 1-127, 0 is reserved for sending
// broadcast messages (send to all nodes)
// The Network ID takes values from 0-255
// By default the SPI-SS line used is D10 on Atmega328.
// You can change it by calling .SetCS(pin) where pin can be {8,9,10}
// Network ID used for this unit
#define NODEID 2
// The network ID we are on
#define NETWORKID 99
// The node ID we're sending to
#define GATEWAYID 1
// # of ms to wait for an ack
#define ACK_TIME 50
// Serial
#define SERIAL_BAUD 115200
// Encryption is OPTIONAL
// to enable encryption you will need to:
// - provide a 16-byte encryption KEY (same on all nodes that talk encrypted)
// - to call .Encrypt(KEY) to start encrypting
// - to stop encrypting call .Encrypt(NULL)
uint8_t KEY[] = "ABCDABCDABCDABCD";
// Wait this many ms between sending packets
int interPacketDelay = 1000;
// Input
char input = 0;
// Need an instance of the RFM12B Radio Module
RFM12B radio;
// Send Size
byte sendSize = 0;
// Payload
char payload[] = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ1234567890~!@#$%^&*(){}[]`|<>?+=:;,.";
// Request ACK
bool requestACK = false;
// LED
int iLED = 9;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "26-01";
void loop()
{
// is RFM12B Radio
isRFM12BRadio();
// Inter Packet Delay
delay(interPacketDelay);
}
getRFM12BRadio.ino
// RFM12B Radio
void isSetupRFM12BRadio(){
// RFM12B Radio
radio.Initialize(NODEID, RF12_433MHZ, NETWORKID);
// Encryption
radio.Encrypt(KEY);
// Sleep right away to save power
radio.Sleep();
// Transmitting
Serial.println("Transmitting...\n\n");
}
// is RFM12 BRadio
void isRFM12BRadio(){
// Serial input of [0-9] will change the transmit delay between 100-1000ms
if (Serial.available() > 0)
{
// Input
input = Serial.read();
// [1..9] = {100..900}ms; [0]=1000ms
if (input >= 48 && input <= 57)
{
// Inter Packet Delay
interPacketDelay = 100 * (input-48);
if (interPacketDelay == 0) interPacketDelay = 1000;
Serial.print("\nChanging delay to ");
Serial.print(interPacketDelay);
Serial.println("ms\n");
}
}
// Serial
Serial.print("Sending[");
Serial.print(sendSize+1);
Serial.print("]:");
for(byte i = 0; i < sendSize+1; i++)
Serial.print((char)payload[i]);
// Request ACK every 3rd xmission
requestACK = !(sendSize % 3);
// Wakeup
radio.Wakeup();
// Turn the LED on HIGH
digitalWrite( iLED , HIGH);
// Send
radio.Send(GATEWAYID, payload, sendSize+1, requestACK);
// Request ACK
if (requestACK)
{
Serial.print(" - waiting for ACK...");
if (waitForAck()) Serial.print("ok!");
else Serial.print("nothing...");
}
// Turn the LED on LOW
digitalWrite( iLED , LOW);
// Sleep
radio.Sleep();
// Send Size
sendSize = (sendSize + 1) % 88;
// Serial
Serial.println();
}
// Wait a few milliseconds for proper ACK, return true if received
static bool waitForAck(){
// Now
long now = millis();
// ACK
while (millis() - now <= ACK_TIME){
if (radio.ACKReceived(GATEWAYID)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup(){
// Serial
Serial.begin(SERIAL_BAUD);
// LED
pinMode( iLED , OUTPUT);
// RFM12B Radio
isSetupRFM12BRadio();
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- RTOS
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor, E-Mentor, STEAM, and Arts-Based Training
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2023
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
Instructor, E-Mentor, STEAM, and Arts-Based Training
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Instructor #E-Mentor #STEAM #ArtsBasedTraining #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
——
What do remote controllers, routers, and robots all have in common? These beginner-friendly microcontrollers are easy to use and program with just a computers or laptop, a USB cable, and some open-source software. All the projects, here we come. Whether you are looking to build some cool electronic projects, learn programming, or wanting to teach others about electronics, this a teaching session will help you figure out what microcontroller is right for your needs, goals, and budgets. Here is some helpful content to start you on your electronics journey. There are different microcontrollers and it can be daunting to get started, especially if you’re just getting into electronics.
- Arduino Uno – R3, SparkFun RedBoard, Arduino Fio, LilyPad Arduino, FLORA, Adafruit METRO 328, Arduino Pro Mini 328, Adafruit Metro Mini 328, Adafruit Pro Trinket, Adafruit Feather 328P, Moteino, etcetera, is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328 (5V/16MHz, 3.3V/8MHz).
- SparkFun Pro Micro, SparkFun Fio V3, Adafruit ItsyBitsy 32u4, Adafruit Feather 32u4, Circuit Playground Classic, etcetera, is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega32U4 (5V/16MHz, 3.3V/8MHz).
- Arduino Mega 2560 R3 is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega2560 (5V/16MHz).
- Arduino Nano Every is a microcontroller board based on the ATMega 4809 (5V/20MHz).
- Arduino Due is a microcontroller board based on the AT91SAM3X8E (3.3V/84MHz).
- SparkFun RedBoard Turbo, SparkFun SAMD21 Mini Breakout, Adafruit METRO M0 Express, LilyPad Simblee BLE, etcetera, is a microcontroller board based on the ATSAMD21G18 ARM Cortex M0+ (3.3V/48MHz).
- SparkFun Thing Plus – SAMD51, Adafruit Metro M4 Express, Adafruit Feather M4 Express, etcetera, is a microcontroller board based on the ATSAMD51 Cortex M4 (3.3V/120MHz).
- SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM, Adafruit HUZZAH32 – ESP32 Feather Board, etcetera, is a microcontroller board based on the Espressif Xtensa® dual-core 32-bit LX6 (3.3V/240MHz).
- Raspberry Pi 4 Model B is a microcontroller board based on the Broadcom BCM2711, quad-core Cortex-A72 (ARM v8) 64-bit SoC (5.1V/1.5GHz).
- Raspberry Pi Zero W is a microcontroller board based on the Broadcom BCM2837B0 64-bit ARM Cortex-A53 Quad Core Processor SoC (5.1V/1GHz). Etcetera…
At Don Luc Electronics I believe that an understanding of electronics is a core literacy that opens up a world of opportunities in the fields of robotics, Internet of Things (IoT), machine learning, engineering, fashion, medical industries, environmental sciences, performing arts and more. This guide is designed to explore the connection between software and hardware, introducing code and parts as they are used in the context of building engaging projects. The circuits in this guide progress in difficulty as new concepts and components are introduced. Completing each circuit means much more than just experimenting you will walk away with a fun project you can use and a sense of accomplishment that is just the beginning of your electronics journey. At the end of each circuit, you’ll find coding challenges that extend your learning and fuel ongoing innovation.
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- RTOS
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor and E-Mentor
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2023
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
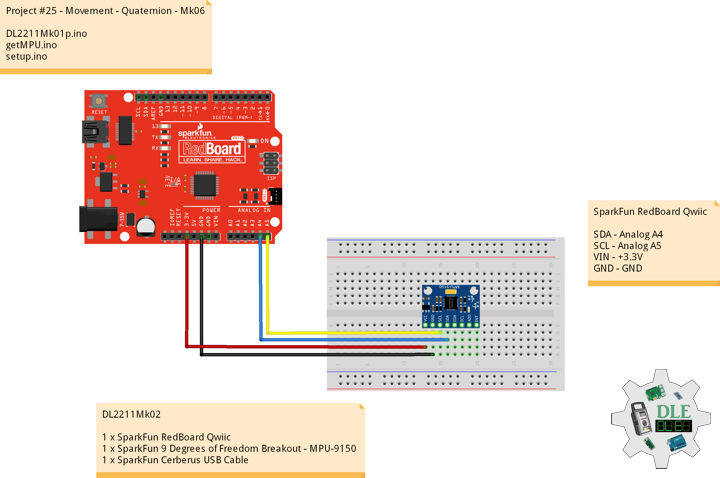
Project #25 – Movement – Quaternion – Mk06
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #SparkFunRedBoard #Movement #MPU9150 #9DOF #Quaternion #Magnetometer #Accelerometer #Gyroscope #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
Quaternion
In mathematics, the quaternion number system extends the complex numbers. Quaternions were first described by the Irish mathematician William Rowan Hamilton in 1843 and applied to mechanics in three-dimensional space. Hamilton defined a quaternion as the quotient of two directed lines in a three-dimensional space, as the quotient of two vectors. Multiplication of quaternions is noncommutative.
Quaternions are used in pure mathematics, but also have practical uses in applied mathematics, particularly for calculations involving three-dimensional rotations, such as in three-dimensional computer graphics, computer vision, and crystallographic texture analysis. They can be used alongside other methods of rotation, such as Euler angles and rotation matrices, or as an alternative to them, depending on the application.
SparkFun 9 Degrees of Freedom Breakout – MPU-9150
The SparkFun 9DOF MPU-9150 is the world’s first 9-axis MotionTracking MEMS device designed for the low power, low cost, and high performance requirements of consumer electronics equipment including smartphones, tablets and wearable sensors. And guess what? You get to play with it.
This breakout board makes it easy to prototype with the InvenSense MPU-9150 by breaking out all the pins you need to standard 0.1″ spaced headers. The board also provides I2C pullup resistors and a solder jumper to switch the I2C address of the device.
The MPU-9150 is a System in Package (SiP) that combines two chips: the MPU-6050, which contains a 3-axis gyroscope, 3-axis accelerometer, and an onboard Digital Motion Processor™ (DMP™) capable of processing complex MotionFusion algorithms; and the AK8975, a 3-axis digital compass. The part’s integrated 6-axis MotionFusion algorithms access all internal sensors to gather a full set of sensor data.
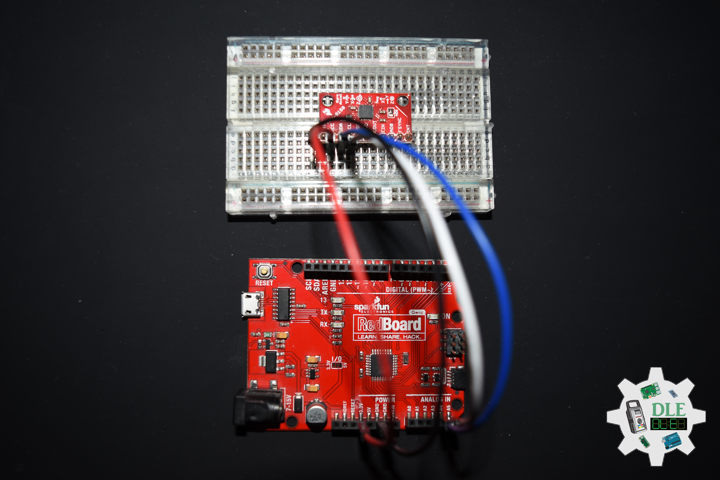
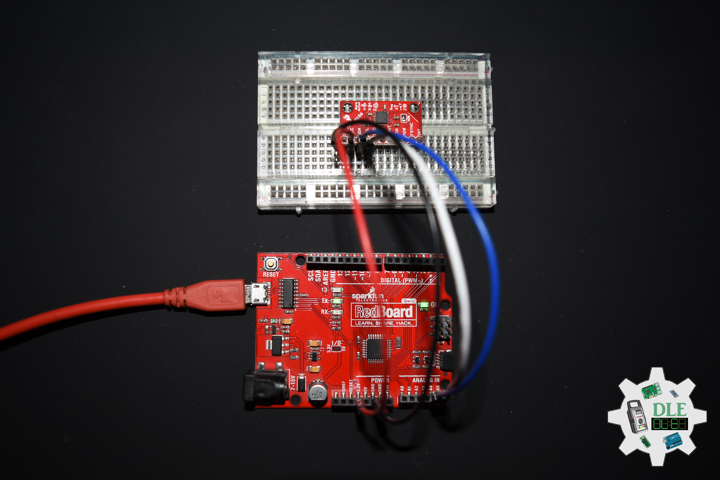
DL2211Mk02
1 x SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
1 x SparkFun 9 Degrees of Freedom Breakout – MPU-9150
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
SDA – Analog A4
SCL – Analog A5
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
——
DL2211Mk02p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #25 - Movement - Quaternion - Mk06
25-06
DL2211Mk02p.ino
1 x SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
1 1 x SparkFun 9 Degrees of Freedom Breakout - MPU-9150
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// Two Wire Interface (TWI/I2C)
#include <Wire.h>
// I2CDev I2C utilities
#include "I2Cdev.h"
// MPU9150Lib 9-axis fusion
#include "MPU9150Lib.h"
// CalLib magnetometer and accelerometer calibration
#include "CalLib.h"
// Motion Driver InvenSense Embedded SDK v5.1
#include <dmpKey.h>
#include <dmpmap.h>
#include <inv_mpu.h>
#include <inv_mpu_dmp_motion_driver.h>
// EEPROM Magnetometer and Accelerometer data is stored
#include <EEPROM.h>
// the MPU object
MPU9150Lib MPU;
// MPU_UPDATE_RATE defines the rate (in Hz)
// at which the MPU updates the sensor data and DMP output
#define MPU_UPDATE_RATE (20)
// MAG_UPDATE_RATE defines the rate (in Hz) at which the
// MPU updates the magnetometer data
// MAG_UPDATE_RATE should be less than or equal to the MPU_UPDATE_RATE
#define MAG_UPDATE_RATE (10)
// MPU_MAG_MIX defines the influence that the magnetometer has on the yaw output.
// The magnetometer itself is quite noisy so some mixing with the gyro yaw can help
// significantly. Some example values are defined below:
// Just use gyro yaw
#define MPU_MAG_MIX_GYRO_ONLY 0
// Just use magnetometer and no gyro yaw
#define MPU_MAG_MIX_MAG_ONLY 1
// A good mix value
#define MPU_MAG_MIX_GYRO_AND_MAG 10
// mainly gyros with a bit of mag correction
#define MPU_MAG_MIX_GYRO_AND_SOME_MAG 50
// MPU_LPF_RATE is the low pas filter rate and can be between 5 and 188Hz
#define MPU_LPF_RATE 5
// This is our earth frame gravity vector - quaternions and vectors
MPUQuaternion gravity;
// SERIAL_PORT_SPEED defines the speed to use for the debug serial port
#define SERIAL_PORT_SPEED 115200
// Software Version Information
String sver = "25-06";
void loop() {
// MPU
isMPU();
}
getMPU.ino
// MPU
// Setup MPU
void isSetupMPU() {
// MPU
MPU.init(MPU_UPDATE_RATE, MPU_MAG_MIX_GYRO_AND_MAG, MAG_UPDATE_RATE, MPU_LPF_RATE); // start the MPU
// Set up the initial gravity vector for quaternion rotation
// Max value down the z axis
gravity[QUAT_W] = 0;
gravity[QUAT_X] = 0;
gravity[QUAT_Y] = 0;
gravity[QUAT_Z] = SENSOR_RANGE;
}
// MPU
void isMPU() {
// Quaternion
// This is our body frame gravity vector
MPUQuaternion rotatedGravity;
// This is the conjugate of the fused quaternion
MPUQuaternion fusedConjugate;
// Used in the rotation
MPUQuaternion qTemp;
// The accelerations
MPUVector3 result;
// Get the latest data
if (MPU.read()) {
// Need this for the rotation
MPUQuaternionConjugate(MPU.m_fusedQuaternion, fusedConjugate);
// Rotate the gravity vector into the body frame
MPUQuaternionMultiply(gravity, MPU.m_fusedQuaternion, qTemp);
MPUQuaternionMultiply(fusedConjugate, qTemp, rotatedGravity);
// Now subtract rotated gravity from the body accels to get real accelerations.
// Note that signs are reversed to get +ve acceleration results
// in the conventional axes.
result[VEC3_X] = -(MPU.m_calAccel[VEC3_X] - rotatedGravity[QUAT_X]);
result[VEC3_Y] = -(MPU.m_calAccel[VEC3_Y] - rotatedGravity[QUAT_Y]);
result[VEC3_Z] = -(MPU.m_calAccel[VEC3_Z] - rotatedGravity[QUAT_Z]);
// print the residual accelerations
MPU.printVector(result);
Serial.println();
}
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// Serial
Serial.begin(SERIAL_PORT_SPEED);
Serial.println("Accel9150 starting");
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Set up I2C bus
Wire.begin();
// Setup MPU
isSetupMPU();
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- RTOS
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor and E-Mentor
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2023
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
Project #25 – Movement – IMU – Mk05
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #SparkFunRedBoard #Movement #Magnetometer #Accelerometer #Gyroscope #9DOF #Barometer #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
Inertial Measurement Unit
An inertial measurement unit (IMU) is an electronic device that measures and reports a body’s specific force, angular rate, and sometimes the orientation of the body, using a combination of accelerometers, gyroscopes, and sometimes magnetometers. When the magnetometer is included, IMUs are referred to as IMMUs. IMUs are typically used to maneuver modern vehicles including motorcycles, missiles, aircraft, including unmanned aerial vehicles, among many others, and spacecraft, including satellites and landers. Recent developments allow for the production of IMU-enabled GPS devices. An IMU allows a GPS receiver to work when GPS-signals are unavailable, such as in tunnels, inside buildings, or when electronic interference is present.
AltIMU-10 v5 Gyro, Accelerometer, Compass, and Altimeter (LSM6DS33, LIS3MDL, and LPS25H Carrier)
The Pololu AltIMU-10 v5 is an inertial measurement unit (IMU) and altimeter that features the same LSM6DS33 gyro and accelerometer and LIS3MDL magnetometer as the MinIMU-9 v5, and adds an LPS25H digital barometer. An I²C interface accesses ten independent pressure, rotation, acceleration, and magnetic measurements that can be used to calculate the sensor’s altitude and absolute orientation. The board operates from 2.5 to 5.5 V and has a 0.1″ pin spacing.
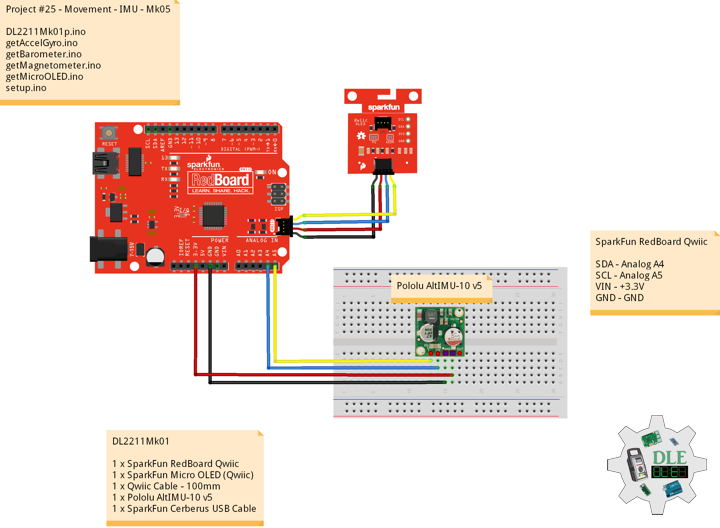
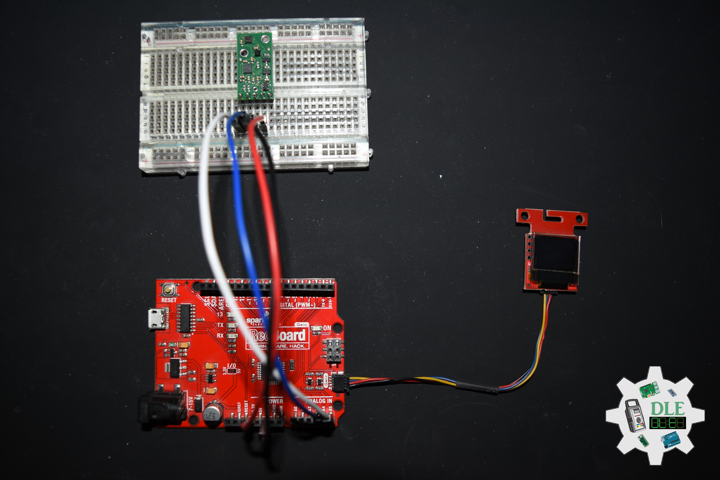
DL2211Mk01
1 x SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
1 x SparkFun Micro OLED (Qwiic)
1 x Qwiic Cable – 100mm
1 x Pololu AltIMU-10 v5
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
SDA – Analog A4
SCL – Analog A5
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
——
DL2211Mk01p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #25 - Movement - IMU - Mk05
25-05
DL2211Mk01p.ino
1 x SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
1 x SparkFun Micro OLED (Qwiic)
1 x Qwiic Cable - 100mm
1 x Pololu AltIMU-10 v5
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// Two Wire Interface (TWI/I2C)
#include <Wire.h>
// SparkFun Micro OLED
#include <SFE_MicroOLED.h>
// Includes and variables for IMU integration
// STMicroelectronics LSM6DS33 gyroscope and accelerometer
#include <LSM6.h>
// STMicroelectronics LIS3MDL magnetometer
#include <LIS3MDL.h>
// STMicroelectronics LPS25H digital barometer
#include <LPS.h>
// 9DoF IMU
// STMicroelectronics LSM6DS33 gyroscope and accelerometer
LSM6 imu;
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
// Accelerometer
int imuAX;
int imuAY;
int imuAZ;
// Gyroscopes
int imuGX;
int imuGY;
int imuGZ;
// STMicroelectronics LIS3MDL magnetometer
LIS3MDL mag;
// Magnetometer
int magX;
int magY;
int magZ;
// STMicroelectronics LPS25H digital barometer
LPS ps;
// Digital Barometer
float pressure;
float altitude;
float temperature;
// SparkFun Micro OLED
#define PIN_RESET 9
#define DC_JUMPER 1
// I2C declaration
MicroOLED oled(PIN_RESET, DC_JUMPER);
// Software Version Information
String sver = "25-05";
void loop() {
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
isIMU();
// Magnetometer
isMag();
// Barometer
isBarometer();
// Micro OLED
isMicroOLED();
}
getAccelGyro.ino
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
// Setup IMU
void setupIMU() {
// Setup IMU
imu.init();
// Default
imu.enableDefault();
}
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
void isIMU() {
// Accelerometer and Gyroscopes
imu.read();
// Accelerometer x, y, z
imuAX = imu.a.x;
imuAY = imu.a.y;
imuAZ = imu.a.z;
// Gyroscopes x, y, z
imuGX = imu.g.x;
imuGY = imu.g.y;
imuGZ = imu.g.z;
}
getBarometer.ino
// STMicroelectronics LPS25H digital barometer
// Setup Barometer
void isSetupBarometer(){
// Setup Barometer
ps.init();
// Default
ps.enableDefault();
}
// Barometer
void isBarometer(){
// Barometer
pressure = ps.readPressureMillibars();
// Altitude Meters
altitude = ps.pressureToAltitudeMeters(pressure);
// Temperature Celsius
temperature = ps.readTemperatureC();
}
getMagnetometer.ino
// Magnetometer
// Setup Magnetometer
void setupMag() {
// Setup Magnetometer
mag.init();
// Default
mag.enableDefault();
}
// Magnetometer
void isMag() {
// Magnetometer
mag.read();
// Magnetometer x, y, z
magX = mag.m.x;
magY = mag.m.y;
magZ = mag.m.z;
}
getMicroOLED.ino
// SparkFun Micro OLED
// Setup Micro OLED
void isSetupMicroOLED() {
// Initialize the OLED
oled.begin();
// Clear the display's internal memory
oled.clear(ALL);
// Display what's in the buffer (splashscreen)
oled.display();
// Delay 1000 ms
delay(1000);
// Clear the buffer.
oled.clear(PAGE);
}
// Micro OLED
void isMicroOLED() {
// Text Display Accelerometer
// Clear the display
oled.clear(PAGE);
// Set cursor to top-left
oled.setCursor(0, 0);
// Set font to type 0
oled.setFontType(0);
// Accelerometer
oled.print("Acceler");
oled.setCursor(0, 12);
// X
oled.print("X: ");
oled.print(imuAX);
oled.setCursor(0, 25);
// Y
oled.print("Y: ");
oled.print(imuAY);
oled.setCursor(0, 39);
// Z
oled.print("Z: ");
oled.print(imuAZ);
oled.display();
// Delay
delay(3000);
// Text Display Gyroscopes
// Clear the display
oled.clear(PAGE);
// Set cursor to top-left
oled.setCursor(0, 0);
// Set font to type 0
oled.setFontType(0);
// Gyroscopes
oled.print("Gyro");
oled.setCursor(0, 12);
// X
oled.print("X: ");
oled.print(imuGX);
oled.setCursor(0, 25);
// Y
oled.print("Y: ");
oled.print(imuGY);
oled.setCursor(0, 39);
// Z
oled.print("Z: ");
oled.print(imuGZ);
oled.display();
// Delay
delay(3000);
// Text Display Magnetometer
// Clear the display
oled.clear(PAGE);
// Set cursor to top-left
oled.setCursor(0, 0);
// Set font to type 0
oled.setFontType(0);
// Magnetometer
oled.print("Mag");
oled.setCursor(0, 12);
// X
oled.print("X: ");
oled.print(magX);
oled.setCursor(0, 25);
// Y
oled.print("Y: ");
oled.print(magY);
oled.setCursor(0, 39);
// Z
oled.print("Z: ");
oled.print(magZ);
oled.display();
// Delay
delay(3000);
// Text Display Barometer
// Clear the display
oled.clear(PAGE);
// Set cursor to top-left
oled.setCursor(0, 0);
// Set font to type 0
oled.setFontType(0);
// Barometer
oled.print("Baro");
oled.setCursor(0, 12);
// Pressure
oled.print("P: ");
oled.print(pressure);
oled.setCursor(0, 25);
// Altitude Meters
oled.print("A: ");
oled.print(altitude);
oled.setCursor(0, 39);
// Temperature Celsius
oled.print("T: ");
oled.print(temperature);
oled.display();
// Delay
delay(3000);
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Set up I2C bus
Wire.begin();
// Setup Micro OLED
isSetupMicroOLED();
// Setup IMU
setupIMU();
// Setup Magnetometer
setupMag();
// Setup Barometer
isSetupBarometer();
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- RTOS
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor and E-Mentor
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2022
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
Project #25 – Movement – 9-DOF – Mk04
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #SparkFunRedBoard #Movement #9DOF #Accelerometer #Magnetometer #Gyroscope #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
Roll, Pitch, and Yaw
How is Controlling an Airplane or Robotic Different than Controlling a Car or Boat?
Stability and control are much more complex for an airplane, which can move freely in three dimensions, than for cars or boats, which only move in two. A change in any one of the three types of motion affects the other two.
Imagine three lines running through an airplane and intersecting at right angles at the airplane’s center of gravity.
- Rotation around the front-to-back axis is called Roll.
- Rotation around the side-to-side axis is called Pitch.
- Rotation around the vertical axis is called Yaw.
SparkFun 9 Degrees of Freedom – Sensor Stick
The SparkFun 9DOF Sensor Stick is a very small sensor board with 9 degrees of freedom. It includes the ADXL345 accelerometer, the HMC5883L magnetometer, and the ITG-3200 MEMS gyro. The “Stick” has a simple I2C interface and a mounting hole for attaching it to your project. Also, the board is a mere allowing it to be easily mounted in just about any application.
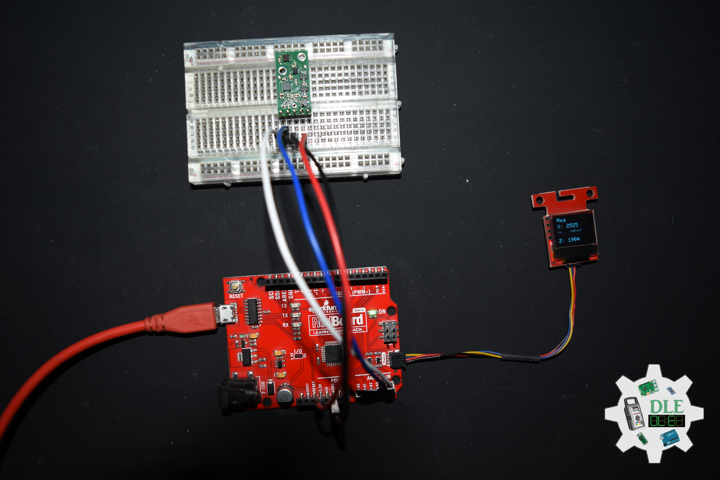
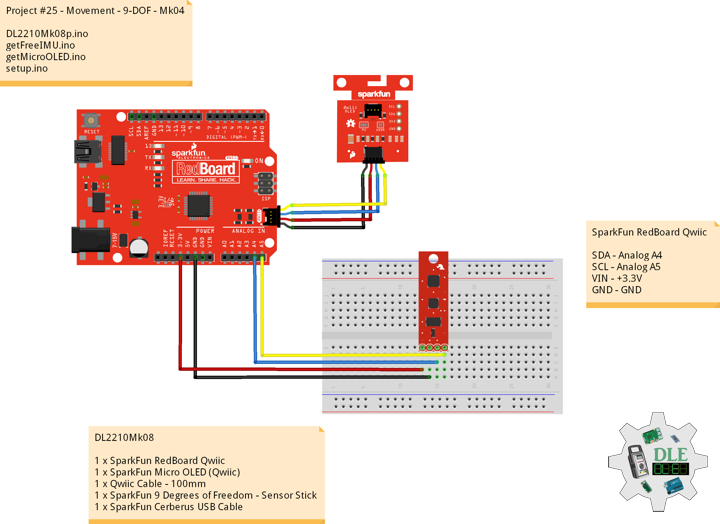
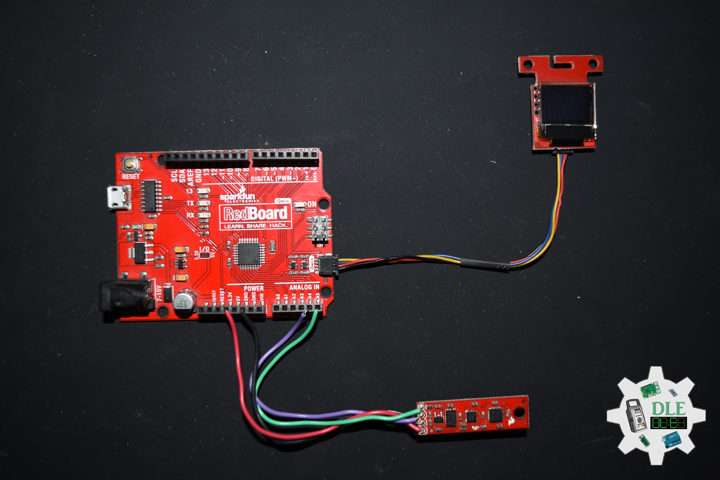
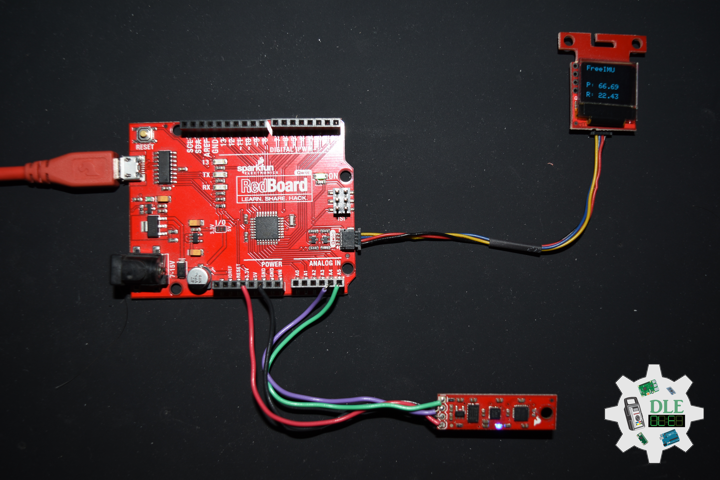
DL2210Mk08
1 x SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
1 x SparkFun Micro OLED (Qwiic)
1 x Qwiic Cable – 100mm
1 x SparkFun 9 Degrees of Freedom – Sensor Stick
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
SDA – Analog A4
SCL – Analog A5
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
——
DL2210Mk08p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #25 - Movement - 9-DOF - Mk04
25-04
DL2210Mk06p.ino
1 x SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
1 x SparkFun Micro OLED (Qwiic)
1 x Qwiic Cable - 100mm
1 x SparkFun 9 Degrees of Freedom - Sensor Stick
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// Two Wire Interface (TWI/I2C)
#include <Wire.h>
// SparkFun Micro OLED
#include <SFE_MicroOLED.h>
// Includes and variables for IMU integration
// Accelerometer
#include <ADXL345.h>
// Magnetometer
#include <HMC58X3.h>
// MEMS Gyroscope
#include <ITG3200.h>
// Debug
#include "DebugUtils.h"
// FreeIMU
#include <CommunicationUtils.h>
#include <FreeIMU.h>
// Set the FreeIMU object
FreeIMU my3IMU = FreeIMU();
// Yaw Pitch Roll
float ypr[3];
float Yaw = 0;
float Pitch = 0;
float Roll = 0;
// SparkFun Micro OLED
#define PIN_RESET 9
#define DC_JUMPER 1
// I2C declaration
MicroOLED oled(PIN_RESET, DC_JUMPER);
// Software Version Information
String sver = "25-04";
void loop() {
// isFreeIMU
isFreeIMU();
// Micro OLED
isMicroOLED();
// One delay in between reads
delay(1000);
}
getFreeIMU.ino
// FreeIMU
// isFreeIMU
void isFreeIMU(){
// FreeIMU
// Yaw Pitch Roll
my3IMU.getYawPitchRoll(ypr);
// Yaw
Yaw = ypr[0];
// Pitch
Pitch = ypr[1];
// Roll
Roll = ypr[2];
}
getMicroOLED.ino
// SparkFun Micro OLED
// Setup Micro OLED
void isSetupMicroOLED() {
// Initialize the OLED
oled.begin();
// Clear the display's internal memory
oled.clear(ALL);
// Display what's in the buffer (splashscreen)
oled.display();
// Delay 1000 ms
delay(1000);
// Clear the buffer.
oled.clear(PAGE);
}
// Micro OLED
void isMicroOLED() {
// Text Display FreeIMU
// Clear the display
oled.clear(PAGE);
// Set cursor to top-left
oled.setCursor(0, 0);
// Set font to type 0
oled.setFontType(0);
// FreeIMU
oled.print("FreeIMU");
oled.setCursor(0, 12);
// Yaw
oled.print("Y: ");
oled.print(Yaw);
oled.setCursor(0, 25);
// Pitch
oled.print("P: ");
oled.print(Pitch);
oled.setCursor(0, 39);
// Roll
oled.print("R: ");
oled.print(Roll);
oled.display();
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Set up I2C bus
Wire.begin();
// Setup Micro OLED
isSetupMicroOLED();
// Pause
delay(5);
// Initialize IMU
my3IMU.init();
// Pause
delay(5);
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- RTOS
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor and E-Mentor
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2022
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
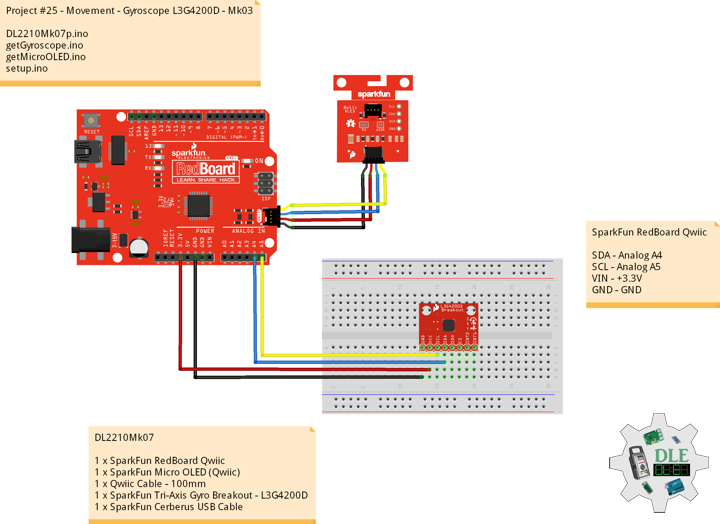
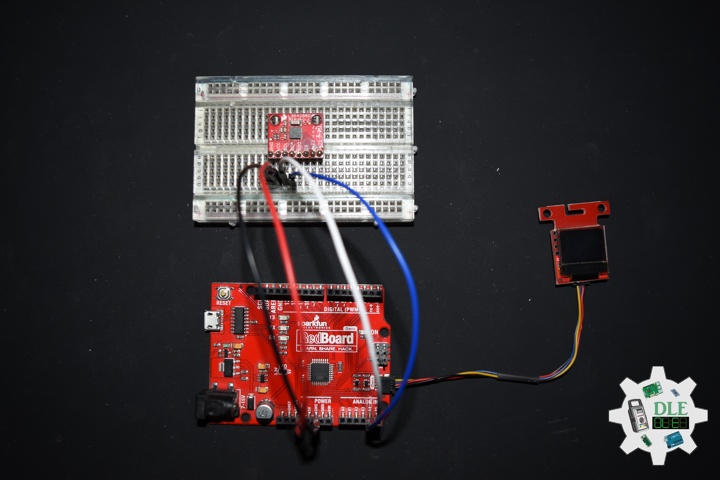
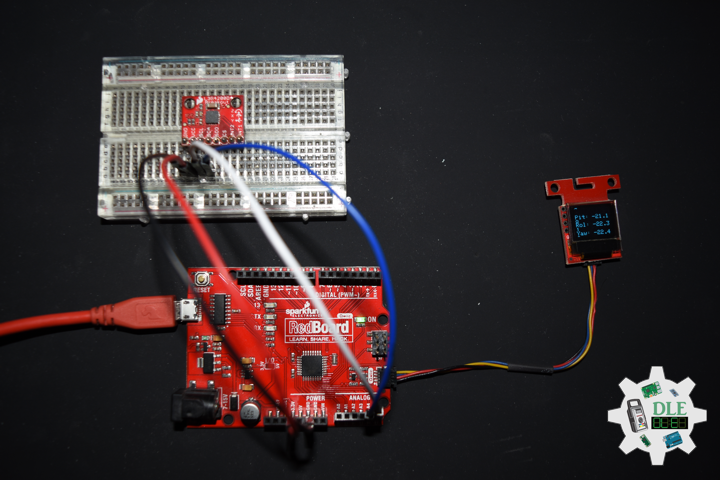
Project #25 – Movement – Gyroscope L3G4200D – Mk03
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #SparkFunRedBoard #Movement #Gyroscope #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
Gyroscope
A gyroscope is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity.It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rotation is free to assume any orientation by itself. When rotating, the orientation of this axis is unaffected by tilting or rotation of the mounting, according to the conservation of angular momentum.
Gyroscopes based on other operating principles also exist, such as the microchip-packaged MEMS gyroscopes found in electronic devices, solid-state ring lasers, fibre optic gyroscopes, and the extremely sensitive quantum gyroscope. MEMS gyroscopes are popular in some consumer electronics, such as smartphones.
SparkFun Tri-Axis Gyro Breakout – L3G4200D
This is a breakout board for the L3G4200D low-power three-axis angular rate sensor. The L3G4200D is a MEMS motion sensor and has a full scale of ±250 or ±500 or ±2000 dps and is capable of measuring rates with a user selectable bandwidth. These work great in gaming and virtual reality input devices, GPS navigation systems and robotics.
DL2210Mk07
1 x SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
1 x SparkFun Micro OLED (Qwiic)
1 x Qwiic Cable – 100mm
1 x SparkFun Tri-Axis Gyro Breakout – L3G4200D
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
SDA – Analog A4
SCL – Analog A5
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
DL2210Mk07p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #25 - Movement - Gyroscope L3G4200D - Mk03
25-02
DL2210Mk06p.ino
1 x SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
1 x SparkFun Micro OLED (Qwiic)
1 x Qwiic Cable - 100mm
1 x SparkFun Tri-Axis Gyro Breakout - L3G4200D
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// Two Wire Interface (TWI/I2C)
#include <Wire.h>
// SparkFun Micro OLED
#include <SFE_MicroOLED.h>
// Gyroscope
#include <L3G4200D.h>
// Gyroscope
L3G4200D gyroscope;
// Timers
unsigned long timer = 0;
float timeStep = 0.01;
// Pitch, Roll and Yaw values
float pitch = 0;
float roll = 0;
float yaw = 0;
// SparkFun Micro OLED
#define PIN_RESET 9
#define DC_JUMPER 1
// I2C declaration
MicroOLED oled(PIN_RESET, DC_JUMPER);
// Software Version Information
String sver = "25-03";
void loop() {
// Gyroscope
isGyroscope(),
// Micro OLED
isMicroOLED();
// Wait to full timeStep period
delay((timeStep*1000) - (millis() - timer));
}
getGyroscope.ino
// L3G4200D Triple Axis Gyroscope
// Setup Gyroscope
void isSetupGyroscope() {
// Setup Gyroscope
// Set scale 2000 dps and 400HZ Output data rate (cut-off 50)
while(!gyroscope.begin(L3G4200D_SCALE_2000DPS, L3G4200D_DATARATE_400HZ_50))
{
// Could not find a valid L3G4200D sensor, check wiring!
delay(500);
}
// Calibrate gyroscope. The calibration must be at rest.
// If you don't want calibrate, comment this line.
gyroscope.calibrate(100);
}
// L3G4200D Gyroscope
void isGyroscope(){
// Timer
timer = millis();
// Read normalized values
Vector norm = gyroscope.readNormalize();
// Calculate Pitch, Roll and Yaw
pitch = pitch + norm.YAxis * timeStep;
roll = roll + norm.XAxis * timeStep;
yaw = yaw + norm.ZAxis * timeStep;
}
getMicroOLED.ino
// SparkFun Micro OLED
// Setup Micro OLED
void isSetupMicroOLED() {
// Initialize the OLED
oled.begin();
// Clear the display's internal memory
oled.clear(ALL);
// Display what's in the buffer (splashscreen)
oled.display();
// Delay 1000 ms
delay(1000);
// Clear the buffer.
oled.clear(PAGE);
}
// Micro OLED
void isMicroOLED() {
// Text Display Gyroscope
// Clear the display
oled.clear(PAGE);
// Set cursor to top-left
oled.setCursor(0, 0);
// Set font to type 0
oled.setFontType(0);
// Gyroscope
oled.print("Gyro");
oled.setCursor(0, 12);
// X
oled.print("Pit: ");
oled.print(pitch);
oled.setCursor(0, 25);
// Y
oled.print("Rol: ");
oled.print(roll);
oled.setCursor(0, 39);
// Z
oled.print("Yaw: ");
oled.print(yaw);
oled.display();
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Set up I2C bus
Wire.begin();
// Setup Micro OLED
isSetupMicroOLED();
// L3G4200D Gyroscope
isSetupGyroscope();
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- RTOS
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor and E-Mentor
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2022
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
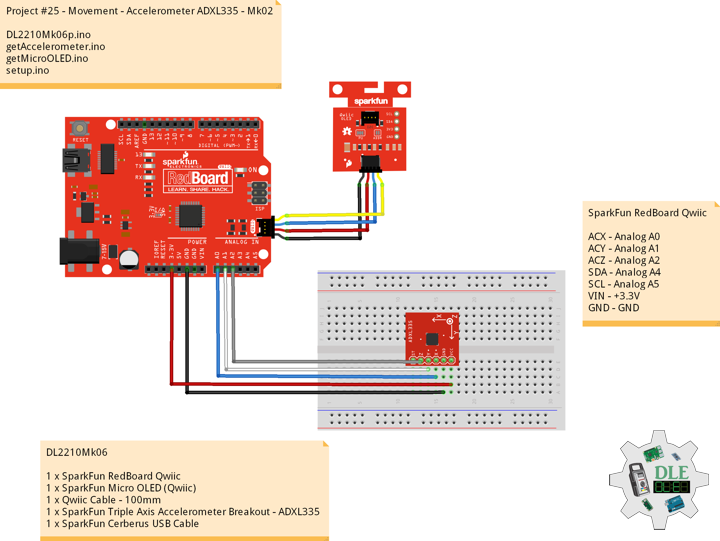
Project #25 – Movement – Accelerometer ADXL335 – Mk02
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #SparkFunRedBoard #Movement #Accelerometer #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame, this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth’s gravity, straight upwards 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall, falling toward the center of the Earth at a rate of about 9.81 m/s2, will measure zero.
Accelerometers have many uses in industry and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. Vibration in rotating machines is monitored by accelerometers. They are used in tablet computers and digital cameras so that images on screens are always displayed upright. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilise flight. Micromachined microelectromechanical systems accelerometers are increasingly present in portable electronic devices and video-game controllers, to detect changes in the positions of these devices.
SparkFun Triple Axis Accelerometer Breakout – ADXL335
Breakout board for the 3 axis ADXL335 from Analog Devices. This is the latest in a long, proven line of analog sensors, the holy grail of accelerometers. The ADXL335 is a triple axis MEMS accelerometer with extremely low noise and power consumption, only 320uA. The sensor has a full sensing range of +/-3g. There is no on-board regulation, provided power should be between 1.8 and 3.6VDC. Board comes fully assembled and tested with external components installed. The included 0.1uF capacitors set the bandwidth of each axis to 50Hz.
DL2210Mk06
1 x SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
1 x SparkFun Micro OLED (Qwiic)
1 x Qwiic Cable – 100mm
1 x SparkFun Triple Axis Accelerometer Breakout – ADXL335
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
ACX – Analog A0
ACY – Analog A1
ACZ – Analog A2
SDA – Analog A4
SCL – Analog A5
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
——
DL2210Mk06p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #25 - Movement - Accelerometer ADXL335 - Mk02
25-02
DL2210Mk06p.ino
1 x SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
1 x SparkFun Micro OLED (Qwiic)
1 x Qwiic Cable - 100mm
1 x SparkFun Triple Axis Accelerometer Breakout - ADXL335
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// Two Wire Interface (TWI/I2C)
#include <Wire.h>
// SparkFun Micro OLED
#include <SFE_MicroOLED.h>
// Accelerometer
int iX = A0;
int iY = A1;
int iZ = A2;
// Accelerometer
int X = 0;
int Y = 0;
int Z = 0;
// SparkFun Micro OLED
#define PIN_RESET 9
#define DC_JUMPER 1
// I2C declaration
MicroOLED oled(PIN_RESET, DC_JUMPER);
// Software Version Information
String sver = "25-02";
void loop() {
// Accelerometer
isAccelerometer(),
// Micro OLED
isMicroOLED();
// One delay in between reads
delay(1000);
}
getAccelerometer.ino
// Accelerometer
// Accelerometer
void isAccelerometer(){
// Accelerometer X, Y, Z
// X
X = analogRead(iX);
// Y
Y = analogRead(iY);
// Z
Z = analogRead(iZ);
}
getMicroOLED.ino
// SparkFun Micro OLED
// Setup Micro OLED
void isSetupMicroOLED() {
// Initialize the OLED
oled.begin();
// Clear the display's internal memory
oled.clear(ALL);
// Display what's in the buffer (splashscreen)
oled.display();
// Delay 1000 ms
delay(1000);
// Clear the buffer.
oled.clear(PAGE);
}
// Micro OLED
void isMicroOLED() {
// Text Display Accelerometer
// Clear the display
oled.clear(PAGE);
// Set cursor to top-left
oled.setCursor(0, 0);
// Set font to type 0
oled.setFontType(0);
// Magnetometer
oled.print("Accel");
oled.setCursor(0, 12);
// X
oled.print("X: ");
oled.print(X);
oled.setCursor(0, 25);
// Y
oled.print("Y: ");
oled.print(Y);
oled.setCursor(0, 39);
// Z
oled.print("Z: ");
oled.print(Z);
oled.display();
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Set up I2C bus
Wire.begin();
// Setup Micro OLED
isSetupMicroOLED();
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- RTOS
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor and E-Mentor
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2022
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
Project #25 – Movement – Sensors – Mk01
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #SparkFunRedBoard #Movement #Magnetometer #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
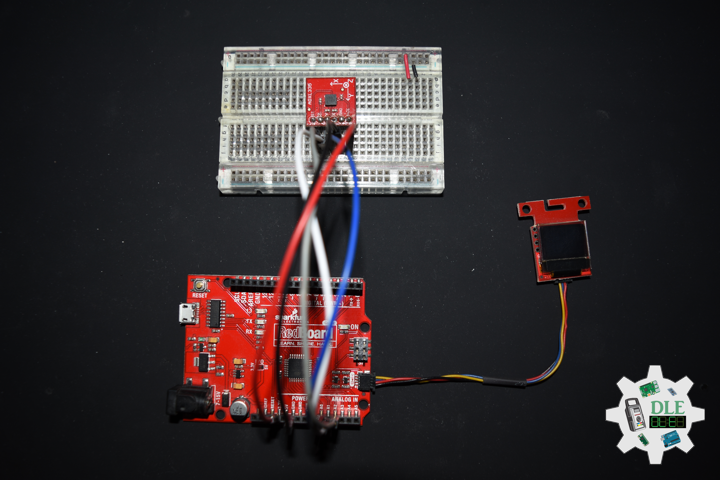
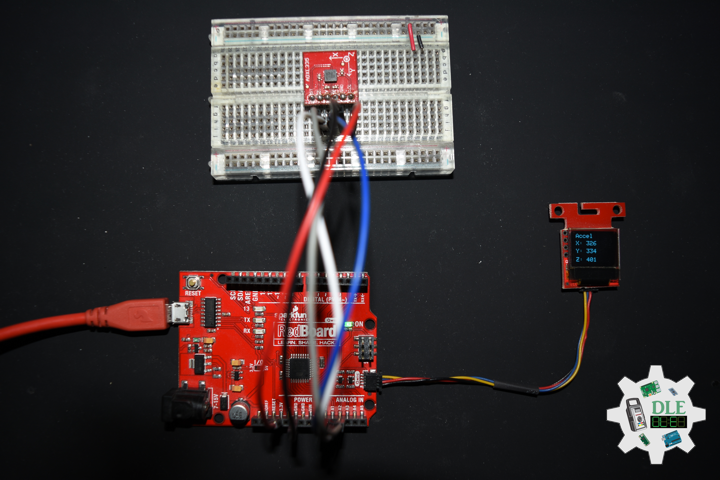
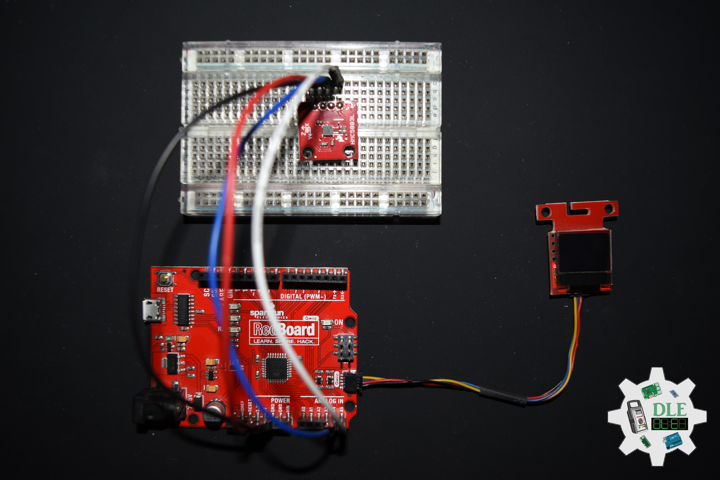
Movement
Accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers are the three main sensors we use for detecting motion and orientation. We can sense motion with an accelerometer.
Accelerometers are used to measure acceleration, that means linear motion in X, Y or Z. They can be used to detect when they are being moved around, detect motion, shock or vibration. They can also be used to detect gravitational pull in order to detect orientation or tilt.
Gyroscopes are used to measure rotational motion in X, Y or Z. They are often paired with accelerometers for inertial guidance systems, 3D motion capture and inverted pendulum type applications.
Magnetometers can sense where the strongest magnetic force is coming from, generally used to detect magnetic north, but can also be used for measuring magnetic fields. When combined with accelerometers and gyroscopes you can stabilize orientation calculations and also determine orientation with respect to the Earth.
Many 6-DoF sensors, which combine accelerometer and gyroscope or compass, accelerometer and magnetometer, and 9-DoF sensors that have 9DoF IMU accelerometers and gyroscopes and magnetometers.
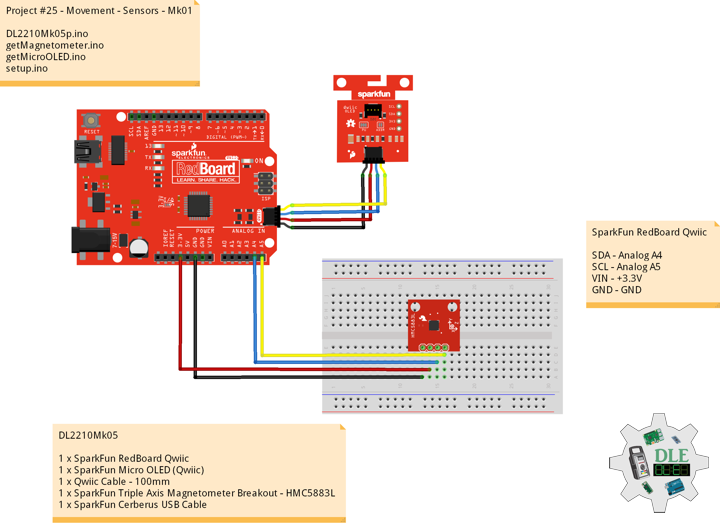
DL2210Mk05
1 x SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
1 x SparkFun Micro OLED (Qwiic)
1 x Qwiic Cable – 100mm
1 x SparkFun Triple Axis Magnetometer Breakout – HMC5883L
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
SDA – Analog A4
SCL – Analog A5
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
DL2210Mk05p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #25 - Movement - Sensors - Mk01
25-01
DL2210Mk05p.ino
1 x SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
1 x SparkFun Micro OLED (Qwiic)
1 x Qwiic Cable - 100mm
1 x SparkFun Triple Axis Magnetometer Breakout - HMC5883L
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// Two Wire Interface (TWI/I2C)
#include <Wire.h>
// Triple Axis Magnetometer
#include <HMC5883L.h>
// SparkFun Micro OLED
#include <SFE_MicroOLED.h>
// Triple Axis Magnetometer
HMC5883L compass;
// SparkFun Micro OLED
#define PIN_RESET 9
#define DC_JUMPER 1
// I2C declaration
MicroOLED oled(PIN_RESET, DC_JUMPER);
// Triple Axis Magnetometer
int X = 0;
int Y = 0;
int Z = 0;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "25-01";
void loop() {
// Triple Axis Magnetometer
isMagnetometer(),
// Micro OLED
isMicroOLED();
// One delay in between reads
delay(1000);
}
getMagnetometer.ino
// Magnetometer
// Setup Magnetometer
void isSetupMagnetometer(){
// Magnetometer Serial
// Initialize HMC5883L
while (!compass.begin())
{
delay(500);
}
// Set measurement range
// +/- 1.30 Ga: HMC5883L_RANGE_1_3GA (default)
compass.setRange(HMC5883L_RANGE_1_3GA);
// Set measurement mode
// Continuous-Measurement: HMC5883L_CONTINOUS (default)
compass.setMeasurementMode(HMC5883L_CONTINOUS);
// Set data rate
// 15.00Hz: HMC5883L_DATARATE_15HZ (default)
compass.setDataRate(HMC5883L_DATARATE_15HZ);
// Set number of samples averaged
// 1 sample: HMC5883L_SAMPLES_1 (default)
compass.setSamples(HMC5883L_SAMPLES_1);
}
// Magnetometer
void isMagnetometer(){
// Vector Norm
Vector norm = compass.readNormalize();
// Vector X, Y, Z
// X Normalize
X = norm.XAxis;
// Y Normalize
Y = norm.YAxis;
// Z Normalize
Z = norm.ZAxis;
}
getMicroOLED.ino
// SparkFun Micro OLED
// Setup Micro OLED
void isSetupMicroOLED() {
// Initialize the OLED
oled.begin();
// Clear the display's internal memory
oled.clear(ALL);
// Display what's in the buffer (splashscreen)
oled.display();
// Delay 1000 ms
delay(1000);
// Clear the buffer.
oled.clear(PAGE);
}
// Micro OLED
void isMicroOLED() {
// Text Display Magnetometer
// Clear the display
oled.clear(PAGE);
// Set cursor to top-left
oled.setCursor(0, 0);
// Set font to type 0
oled.setFontType(0);
// Magnetometer
oled.print("Magneto");
oled.setCursor(0, 12);
// X Normalize
oled.print("X: ");
oled.print(X);
oled.setCursor(0, 25);
// Y Normalize
oled.print("Y: ");
oled.print(Y);
oled.setCursor(0, 39);
// Z Normalize
oled.print("Z: ");
oled.print(Z);
oled.display();
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// Give display time to power on
delay(100);
// Set up I2C bus
Wire.begin();
// Setup Triple Axis Magnetometer
isSetupMagnetometer();
// Setup Micro OLED
isSetupMicroOLED();
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- RTOS
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor and E-Mentor
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2022 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: https://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
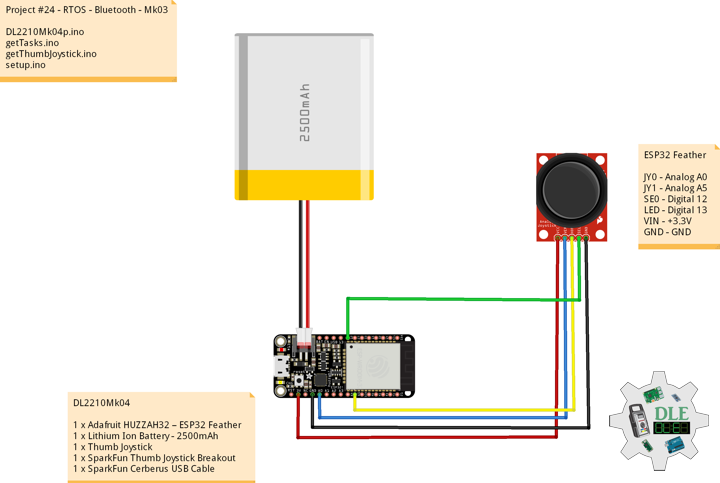
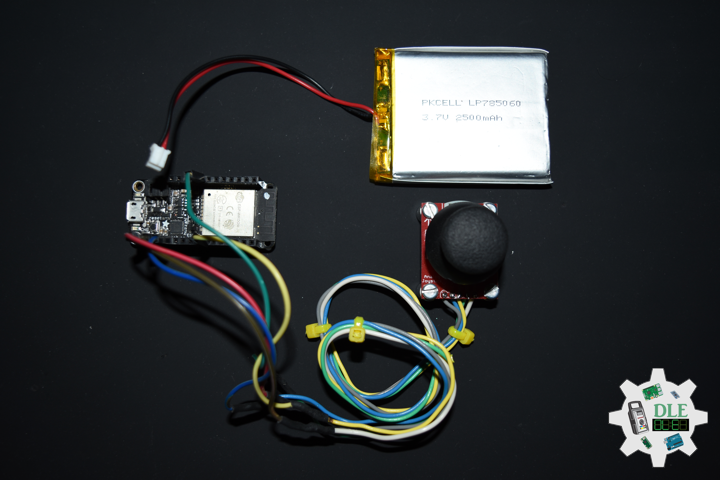
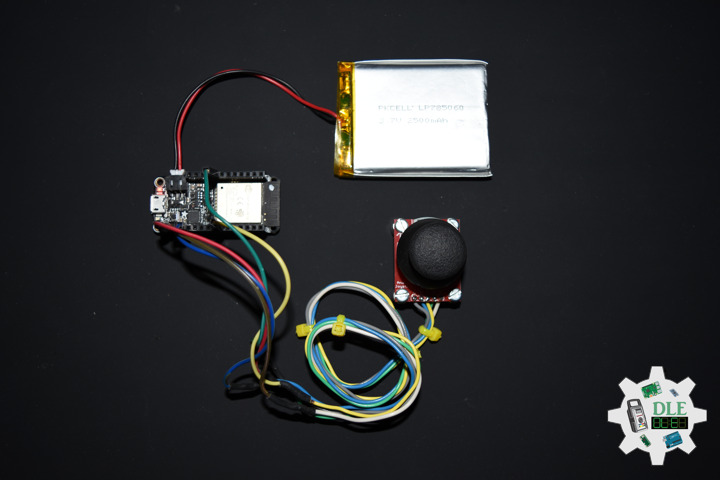
Project #24 – RTOS – Bluetooth – Mk03
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #ESP32 #RTOS #FreeRTOS #Bluetooth #ThumbJoystick #Keyboard #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
Joystick
A joystick is an input device consisting of a stick that pivots on a base and reports its angle or direction to the device it is controlling. Joysticks are often used to control video games, and usually have one or more push-buttons whose state can also be read by the computer. A popular variation of the joystick used on modern video game consoles is the analog stick. Joysticks are also used for controlling machines such as cranes, trucks, underwater unmanned vehicles, wheelchairs, surveillance cameras, and zero turning radius lawn mowers. This is a joystick very similar to the analog joysticks on PS2 controllers. Directional movements are simply two potentiometers, one for each axis. Pots are 10k Ohm each. This joystick also has a select button that is actuated when the joystick is pressed down.
DL2210Mk04
1 x Adafruit HUZZAH32 – ESP32 Feather
1 x Lithium Ion Battery – 2500mAh
1 x Thumb Joystick
1 x SparkFun Thumb Joystick Breakout
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
ESP32 Feather
JY0 – Analog A0
JY1 – Analog A5
SE0 – Digital 12
LED – Digital 13
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
——
DL2210Mk04p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #24 - RTOS - Bluetooth - Mk03
24-03
DL2210Mk04p.ino
1 x Adafruit HUZZAH32 – ESP32 Feather
1 x Lithium Ion Battery - 2500mAh
1 x Thumb Joystick
1 x SparkFun Thumb Joystick Breakout
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// FreeRTOS ESP32
#if CONFIG_FREERTOS_UNICORE
#define ARDUINO_RUNNING_CORE 0
#else
#define ARDUINO_RUNNING_CORE 1
#endif
// ESP32 BLE Keyboard
#include <BleKeyboard.h>
// ESP32 BLE Keyboard
BleKeyboard bleKeyboard;
// Connections to joystick
// Vertical
const int VERT = A0;
// Horizontal
const int HORIZ = A5;
// Pushbutton
const int SEL = 12;
// Initialize variables for analog and digital values
int vertical;
int horizontal;
int selec;
// Led Built In
#ifndef LED_BUILTIN
#define LED_BUILTIN 13
#endif
// Define two tasks for Blink
void isTaskBlink( void *pvParameters );
// Software Version Information
String sver = "24-03";
void loop() {
// ESP32 BLE Keyboard
if(bleKeyboard.isConnected()) {
// Thumb Joystick
isThumbJoystick();
}
// Delay
delay( 1000 );
}
getTasks.ino
// Tasks
// Setup Task
void isSetupTask(){
// Now set up two tasks to run independently
// TaskBlink
xTaskCreatePinnedToCore(
isTaskBlink
, "TaskBlink" // A name just for humans
, 1024 // This stack size can be checked & adjusted by reading.
, NULL
, 2 // Priority, with 2 being the highest, and 0 being the lowest.
, NULL
, ARDUINO_RUNNING_CORE);
// Now the task scheduler, which takes over control of scheduling individual tasks,
// is automatically started.
}
// This is a Task Blink
void isTaskBlink(void *pvParameters)
{
(void) pvParameters;
// Blink
// Turns on an LED on for 2 second, then off for 2 second, repeatedly
// Initialize digital LED_BUILTIN on pin 13 as an output.
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
// A Task shall never return or exit
for (;;)
{
// Turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level)
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH);
// One tick delay in between reads
vTaskDelay(2000);
// Turn the LED off by making the voltage LOW
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW);
// One tick delay in between reads
vTaskDelay(2000);
}
}
getThumbJoystick.ino
// Thumb Joystick
void isThumbJoystick() {
// Read all values from the joystick
// Joystick was sitting around 2047 for the vertical and horizontal values
// Will be 0-4095
// Vertical
vertical = analogRead(VERT);
if (vertical == 4095) {
// Volume Up
bleKeyboard.write(KEY_MEDIA_VOLUME_UP);
} else if (vertical == 0) {
// Volume Down
bleKeyboard.write(KEY_MEDIA_VOLUME_DOWN);
}
// Horizontal
// Will be 0-4095
horizontal = analogRead(HORIZ);
if (horizontal == 4095) {
// Previous Track
bleKeyboard.write(KEY_MEDIA_PREVIOUS_TRACK);
} else if (horizontal == 0) {
// Next Track
bleKeyboard.write(KEY_MEDIA_NEXT_TRACK);
}
// Will be HIGH (1) if not pressed, and LOW (0) if pressed
selec = digitalRead(SEL);
if (selec == 0) {
// Play/Pause media key
bleKeyboard.write(KEY_MEDIA_PLAY_PAUSE);
}
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// Make the SEL line an input
pinMode(SEL, INPUT_PULLUP);
// ESP32 BLE Keyboard
bleKeyboard.begin();
// Setup Task
isSetupTask();
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- RTOS
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor and E-Mentor
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2022 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: https://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
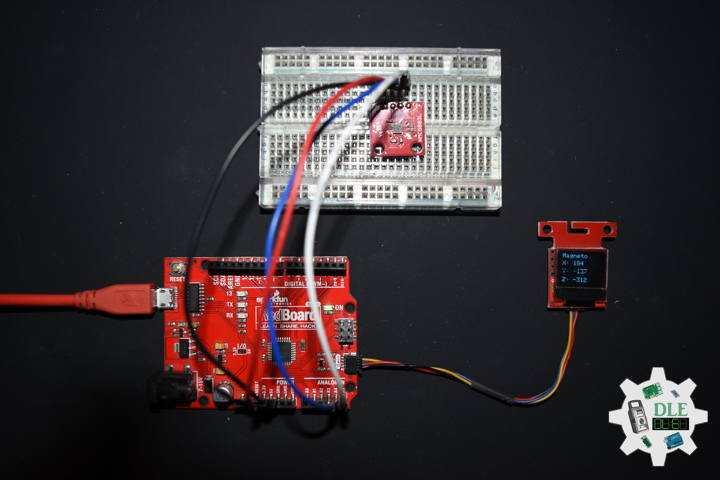
Project #24 – RTOS – Magnetometers HMC5883L – Mk02
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #SparkFunRedBoard #RTOS #FreeRTOS #Magnetometer #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
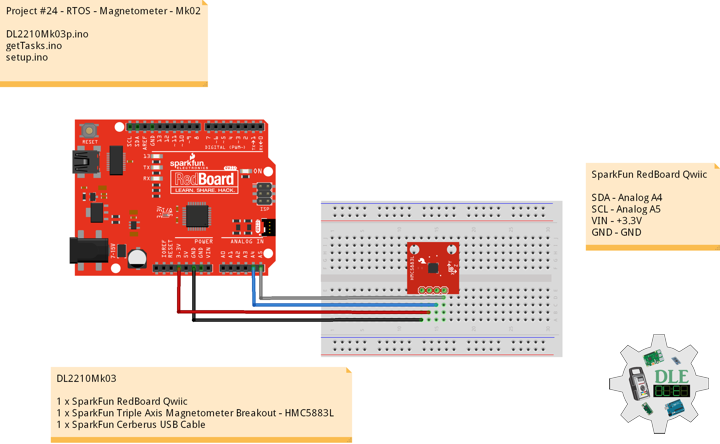
SparkFun Triple Axis Magnetometer Breakout – HMC5883L
This is a breakout board for Honeywell’s HMC5883L, a 3-axis digital compass. Communication with the HMC5883L is simple and all done through an I2C interface. There is no on-board regulator, so a regulated voltage of 2.16-3.6VDC should be supplied. The breakout board includes the HMC5883L sensor and all filtering capacitors as shown. The power and 2-wire interface pins are all broken out to a 0.1″ pitch header.
Magnetometers have a wide range of uses. The most common include using the chip as a digital compass to sense direction or using them to detect ferrous (magnetic) metals. Magnetic fields and current go hand-in-hand. When current flows through a wire, a magnetic field is created. This is the basic principle behind electromagnets. This is also the principle used to measure magnetic fields with a magnetometer. The direction of Earth’s magnetic fields affects the flow of electrons in the sensor, and those changes in current can be measured and calculated to derive a compass heading or other useful information.
DL2210Mk03
1 x SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
1 x SparkFun Triple Axis Magnetometer Breakout – HMC5883L
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
SDA – Analog A4
SCL – Analog A5
VIN – +3.3V
GND – GND
DL2210Mk03p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #24 - RTOS - Magnetometer - Mk02
24-02
DL2210Mk03p.ino
1 x SparkFun RedBoard Qwiic
1 x SparkFun Triple Axis Magnetometer Breakout - HMC5883L
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// FreeRTOS
#include <Arduino_FreeRTOS.h>
// Two Wire Interface (TWI/I2C)
#include <Wire.h>
// Triple Axis Magnetometer
#include <HMC5883L.h>
// Define two tasks for Triple Axis Magnetometer
void isTaskMagnetometer( void *pvParameters );
// Software Version Information
String sver = "24-02";
void loop() {
// Empty. Things are done in Tasks.
}
getTasks.ino
// Tasks
// Setup Task
void isSetupTask(){
// Now set up one tasks to run independently
// Magnetometer
//xTaskCreatePinnedToCore(
xTaskCreate(
isTaskMagnetometer
, "Magnetometer"
, 128 // Stack size
, NULL
, 1 // Priority
, NULL);
// Now the task scheduler, which takes over control of scheduling individual tasks,
// is automatically started.
}
// This is a Task Magnetometer Serial
void isTaskMagnetometer(void *pvParameters)
{
(void) pvParameters;
// Triple Axis Magnetometer
HMC5883L compass;
// Magnetometer Serial
// Initialize HMC5883L
Serial.println("Initialize HMC5883L");
while (!compass.begin())
{
Serial.println("Could not find a valid HMC5883L sensor, check wiring!");
delay(500);
}
// Set measurement range
// +/- 1.30 Ga: HMC5883L_RANGE_1_3GA (default)
compass.setRange(HMC5883L_RANGE_1_3GA);
// Set measurement mode
// Continuous-Measurement: HMC5883L_CONTINOUS (default)
compass.setMeasurementMode(HMC5883L_CONTINOUS);
// Set data rate
// 15.00Hz: HMC5883L_DATARATE_15HZ (default)
compass.setDataRate(HMC5883L_DATARATE_15HZ);
// Set number of samples averaged
// 1 sample: HMC5883L_SAMPLES_1 (default)
compass.setSamples(HMC5883L_SAMPLES_1);
for (;;)
{
// Vector Norm
Vector norm = compass.readNormalize();
// Vector X, Y, Z
Serial.print("Xnorm = ");
Serial.print(norm.XAxis);
Serial.print(" Ynorm = ");
Serial.print(norm.YAxis);
Serial.print(" ZNorm = ");
Serial.print(norm.ZAxis);
Serial.println();
// One tick delay in between reads
vTaskDelay(500);
}
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// Initialize serial communication
// at 9600 bits per second:
Serial.begin(9600);
// Setup Task
isSetupTask();
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor and E-Mentor
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2022 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: https://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc