ESP8266
Instructor, E-Mentor, STEAM, and Arts-Based Training
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Instructor #E-Mentor #STEAM #ArtsBasedTraining #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
——
What do remote controllers, routers, and robots all have in common? These beginner-friendly microcontrollers are easy to use and program with just a computers or laptop, a USB cable, and some open-source software. All the projects, here we come. Whether you are looking to build some cool electronic projects, learn programming, or wanting to teach others about electronics, this a teaching session will help you figure out what microcontroller is right for your needs, goals, and budgets. Here is some helpful content to start you on your electronics journey. There are different microcontrollers and it can be daunting to get started, especially if you’re just getting into electronics.
- Arduino Uno – R3, SparkFun RedBoard, Arduino Fio, LilyPad Arduino, FLORA, Adafruit METRO 328, Arduino Pro Mini 328, Adafruit Metro Mini 328, Adafruit Pro Trinket, Adafruit Feather 328P, Moteino, etcetera, is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328 (5V/16MHz, 3.3V/8MHz).
- SparkFun Pro Micro, SparkFun Fio V3, Adafruit ItsyBitsy 32u4, Adafruit Feather 32u4, Circuit Playground Classic, etcetera, is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega32U4 (5V/16MHz, 3.3V/8MHz).
- Arduino Mega 2560 R3 is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega2560 (5V/16MHz).
- Arduino Nano Every is a microcontroller board based on the ATMega 4809 (5V/20MHz).
- Arduino Due is a microcontroller board based on the AT91SAM3X8E (3.3V/84MHz).
- SparkFun RedBoard Turbo, SparkFun SAMD21 Mini Breakout, Adafruit METRO M0 Express, LilyPad Simblee BLE, etcetera, is a microcontroller board based on the ATSAMD21G18 ARM Cortex M0+ (3.3V/48MHz).
- SparkFun Thing Plus – SAMD51, Adafruit Metro M4 Express, Adafruit Feather M4 Express, etcetera, is a microcontroller board based on the ATSAMD51 Cortex M4 (3.3V/120MHz).
- SparkFun Thing Plus – ESP32 WROOM, Adafruit HUZZAH32 – ESP32 Feather Board, etcetera, is a microcontroller board based on the Espressif Xtensa® dual-core 32-bit LX6 (3.3V/240MHz).
- Raspberry Pi 4 Model B is a microcontroller board based on the Broadcom BCM2711, quad-core Cortex-A72 (ARM v8) 64-bit SoC (5.1V/1.5GHz).
- Raspberry Pi Zero W is a microcontroller board based on the Broadcom BCM2837B0 64-bit ARM Cortex-A53 Quad Core Processor SoC (5.1V/1GHz). Etcetera…
At Don Luc Electronics I believe that an understanding of electronics is a core literacy that opens up a world of opportunities in the fields of robotics, Internet of Things (IoT), machine learning, engineering, fashion, medical industries, environmental sciences, performing arts and more. This guide is designed to explore the connection between software and hardware, introducing code and parts as they are used in the context of building engaging projects. The circuits in this guide progress in difficulty as new concepts and components are introduced. Completing each circuit means much more than just experimenting you will walk away with a fun project you can use and a sense of accomplishment that is just the beginning of your electronics journey. At the end of each circuit, you’ll find coding challenges that extend your learning and fuel ongoing innovation.
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Wireless (Radio Frequency, Bluetooth, WiFi, Etc…)
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Machine Learning
- RTOS
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor and E-Mentor
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2023
https://www.donluc.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
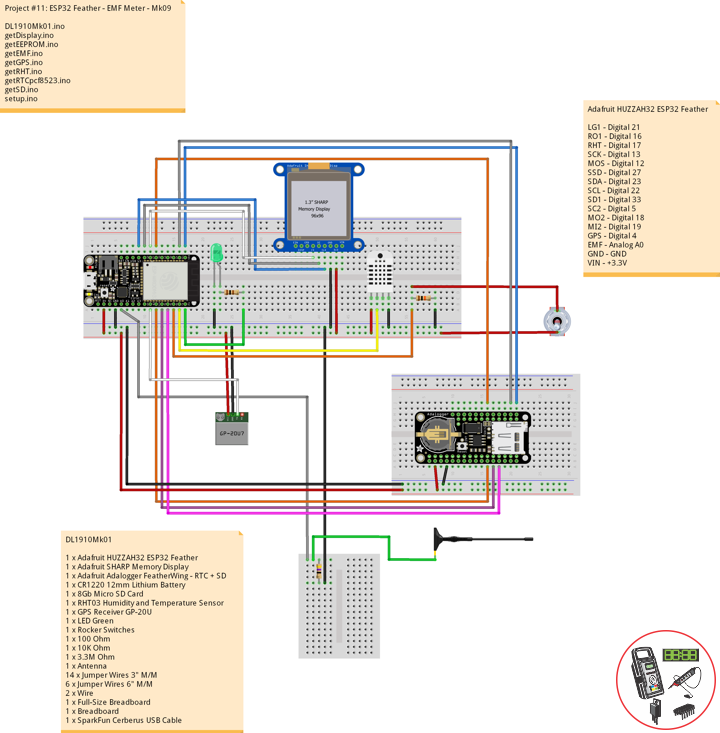
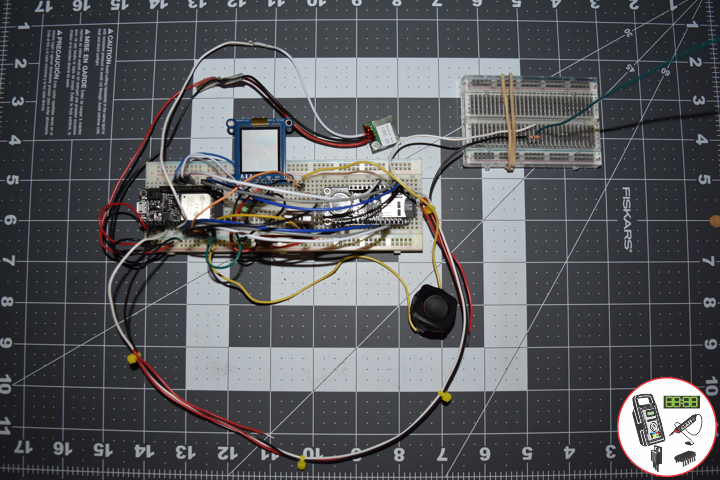
Project #11: ESP32 Feather – EMF Meter – Mk09
——
——
——
——
EMF Meter
EMF measurements are measurements of ambient electromagnetic fields that are performed using particular sensors or probes, such as EMF meters. These probes can be generally considered as antennas although with different characteristics. In fact probes should not perturb the electromagnetic field and must prevent coupling and reflection as much as possible in order to obtain precise results.
EMF probes may respond to fields only on one axis. Amplified, active, probes can improve measurement precision and sensitivity but their active components may limit their speed of response.
DL1910Mk01
1 x Adafruit HUZZAH32 ESP32 Feather
1 x Adafruit SHARP Memory Display
1 x Adafruit Adalogger FeatherWing – RTC + SD
1 x CR1220 12mm Lithium Battery
1 x 8Gb Micro SD Card
1 x RHT03 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
1 x GPS Receiver GP-20U
1 x LED Green
1 x Rocker Switches
1 x 100 Ohm
1 x 10K Ohm
1 x 3.3M Ohm
1 x Antenna
14 x Jumper Wires 3″ M/M
6 x Jumper Wires 6″ M/M
2 x Wire
1 x Full-Size Breadboard
1 x Breadboard
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
Adafruit HUZZAH32 ESP32 Feather
LG1 – Digital 21
RO1 – Digital 16
RHT – Digital 17
SCK – Digital 13
MOS – Digital 12
SSD – Digital 27
SDA – Digital 23
SCL – Digital 22
SD1 – Digital 33
SC2 – Digital 5
MO2 – Digital 18
MI2 – Digital 19
GPS – Digital 4
EMF – Analog A0
GND – GND
VIN – +3.3V
DL1910Mk01.ino
// ***** Don Luc Electronics *****
// Software Version Information
// Project #11: HUZZAH32 ESP32 Feather - EMF - Mk09
// 10-01
// DL1910Mk01p.ino 11-09
// Adafruit HUZZAH32 ESP32 Feather Board
// SHARP Display
// LED Green
// Adalogger FeatherWing - RTC + SD
// EEPROM
// RHT03 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
// Rocker Switches
// GPS Receiver
// EMF Meter (Single Axis)
// include Library Code
// SHARP Memory Display
#include <Adafruit_SharpMem.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
// Date and Time
#include "RTClib.h"
// EEPROM library to read EEPROM with unique ID for unit
#include "EEPROM.h"
// RHT Humidity and Temperature Sensor
#include <SparkFun_RHT03.h>
// SD Card
#include "FS.h"
#include "SD.h"
#include "SPI.h"
// GPS Receiver
#include <TinyGPS++.h>
#include <HardwareSerial.h>
// SHARP Memory Display
// any pins can be used
#define SHARP_SCK 13
#define SHARP_MOSI 12
#define SHARP_SS 27
// Set the size of the display here, e.g. 144x168!
Adafruit_SharpMem display(SHARP_SCK, SHARP_MOSI, SHARP_SS, 144, 168);
// The currently-available SHARP Memory Display (144x168 pixels)
// requires > 4K of microcontroller RAM; it WILL NOT WORK on Arduino Uno
// or other <4K "classic" devices!
#define BLACK 0
#define WHITE 1
int minorHalfSize; // 1/2 of lesser of display width or height
// LED Green
int iLEDGreen = 21; // LED Green
// PCF8523 Precision RTC
RTC_PCF8523 rtc;
String dateRTC = "";
String timeRTC = "";
// RHT Humidity and Temperature Sensor
const int RHT03_DATA_PIN = 17; // RHT03 data pin Digital 17
RHT03 rht; // This creates a RTH03 object, which we'll use to interact with the sensor
float latestHumidity;
float latestTempC;
float latestTempF;
// SD Card
const int chipSelect = 33; // SD Card
String zzzzzz = "";
// Rocker Switches
int iRow1 = 16; // Rocker Switches Digital 16
int iRow1State = 0; // Variable for reading the pushbutton status
// ESP32 HardwareSerial
HardwareSerial tGPS(2);
// GPS Receiver
#define gpsRXPIN 4
#define gpsTXPIN 36 // This one is unused and doesnt have a conection
// The TinyGPS++ object
TinyGPSPlus gps;
float TargetLat;
float TargetLon;
int Status = 0;
// EMF Meter (Single Axis)
#define NUMREADINGS 15 // Raise this number to increase data smoothing
int senseLimit = 15; // Raise this number to decrease sensitivity (up to 1023 max)
int val = 0; // Val
int iEMF = A0; // EMF Meter
int readings[ NUMREADINGS ]; // Readings from the analog input
int ind = 0; // Index of the current reading
int total = 0; // Running total
int average = 0; // Final average of the probe reading
int iEMFDis = 0;
int iEMFRect = 0;
// The current address in the EEPROM (i.e. which byte
// we're going to read to next)
#define EEPROM_SIZE 64
String sver = "10-1.p";
// Unit ID information
String uid = "";
void loop() {
// Receives NEMA data from GPS receiver
// This sketch displays information every time a new sentence is correctly encoded.
while ( tGPS.available() > 0)
if (gps.encode( tGPS.read() ))
{
displayInfo();
}
if (millis() > 5000 && gps.charsProcessed() < 10)
{
while(true);
}
// Date and Time
isRTC();
// RHT03 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
isRHT03();
// SHARP Memory Display On
isDisplayOn();
// Rocker Switched
// Read the state of the iRow1 value
iRow1State = digitalRead(iRow1);
// EMF Meter (Single Axis)
isEMF();
// Check if the pushbutton is pressed. If it is, the buttonState is HIGH:
if (iRow1State == HIGH) {
// iLEDGreen
digitalWrite(iLEDGreen, HIGH );
// SD Card
isSD();
} else {
// iLEDGreen
digitalWrite(iLEDGreen, LOW );
}
// Delay
delay( 1000 );
}
getDisplay.ino
// SHARP Memory Display On
void isDisplayOn() {
// Clear Display
display.clearDisplay();
// text display date, time, LED on
display.setRotation(4);
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setTextColor(BLACK);
display.setCursor(0,1);
display.println( dateRTC );
display.setCursor(0,17);
display.println( timeRTC );
//display.setTextSize(2);
display.setCursor(0,35);
display.print("Lon: ");
display.println( TargetLon );
display.setCursor(0,55);
display.print("Lat: ");
display.println( TargetLat );
display.setCursor(0,74);
display.print("Hum: ");
display.print( latestHumidity );
display.println("%");
display.setCursor(0,94);
display.print("Cel: ");
display.print( latestTempC );
display.println("*C");
display.setCursor(0,114);
display.print("EMF: ");
display.println( iEMFDis );
display.setCursor(0,134);
display.setTextSize(1);
display.println( "0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10" );
display.setCursor(0,144);
display.drawRect(0, 144, iEMFRect , display.height(), BLACK);
display.fillRect(0, 144, iEMFRect , display.height(), BLACK);
display.refresh();
}
// SHARP Memory Display - UID
void isDisplayUID() {
// text display EEPROM
display.setRotation(4);
display.setTextSize(2);
display.setTextColor(BLACK);
display.setCursor(0,20);
display.print( "UID: " );
display.println( uid );
// display.setTextSize();
display.setTextColor(BLACK);
display.setCursor(0,45);
display.print( "VER: ");
display.println( sver );
display.refresh();
delay( 100 );
}
getEEPROM.ino
// EEPROM
void GetUID()
{
// Get unit ID
uid = "";
for (int x = 0; x < 5; x++)
{
uid = uid + char(EEPROM.read(x));
}
}
getEMF.ino
// EMF Meter (Single Axis)
// setupEMF
void setupEMF() {
// EMF Meter (Single Axis)
pinMode( iEMF, OUTPUT ); // EMF Meter
for (int i = 0; i < NUMREADINGS; i++){
readings[ i ] = 0; // Initialize all the readings to 0
}
}
// isEMF
void isEMF(){
// Probe
val = analogRead( iEMF ); // Take a reading from the probe
if( val >= 1 ){ // If the reading isn't zero, proceed
val = constrain( val, 1, senseLimit ); // Turn any reading higher than the senseLimit value into the senseLimit value
val = map( val, 1, senseLimit, 1, 1023 ); // Remap the constrained value within a 1 to 1023 range
total -= readings[ ind ]; // Subtract the last reading
readings[ ind ] = val; // Read from the sensor
total += readings[ ind ]; // Add the reading to the total
ind = ( ind + 1 ); // Advance to the next index
if ( ind >= NUMREADINGS ) { // If we're at the end of the array...
ind = 0; // ...wrap around to the beginning
}
average = total / NUMREADINGS; // Calculate the average
}
else
{
iEMFRect = 0;
val = 0;
average = 0;
}
iEMFDis = average;
iEMFRect = map( average, 1, 1023, 1, 144 );
}
getGPS.ino
// GPS Receiver
void setupGPS() {
// Setup GPS
tGPS.begin( 9600 , SERIAL_8N1, gpsRXPIN, gpsTXPIN );
}
// GPS Vector Pointer Target
void displayInfo()
{
// Location
if (gps.location.isValid())
{
TargetLat = gps.location.lat();
TargetLon = gps.location.lng();
Status = 2;
}
else
{
Status = 0;
}
}
getRHT.ino
// RHT03 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
void isRHT03(){
// Call rht.update() to get new humidity and temperature values from the sensor.
int updateRet = rht.update();
// The humidity(), tempC(), and tempF() functions can be called -- after
// a successful update() -- to get the last humidity and temperature value
latestHumidity = rht.humidity();
latestTempC = rht.tempC();
latestTempF = rht.tempF();
}
getRTCpcf8523.ino
// PCF8523 Precision RTC
void setupRTC() {
// pcf8523 Precision RTC
if (! rtc.begin()) {
while (1);
}
if (! rtc.initialized()) {
// Following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled
rtc.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
// This line sets the RTC with an explicit date & time, for example to set
// January 21, 2014 at 3am you would call:
// rtc.adjust(DateTime(2018, 9, 29, 12, 17, 0));
}
}
// Date and Time RTC
void isRTC () {
// Date and Time
DateTime now = rtc.now();
// Date
dateRTC = now.year(), DEC;
dateRTC = dateRTC + "/";
dateRTC = dateRTC + now.month(), DEC;
dateRTC = dateRTC + "/";
dateRTC = dateRTC + now.day(), DEC;
// Time
timeRTC = now.hour(), DEC;
timeRTC = timeRTC + ":";
timeRTC = timeRTC + now.minute(), DEC;
timeRTC = timeRTC + ":";
timeRTC = timeRTC + now.second(), DEC;
}
getSD.ino
// SD Card
void setupSD() {
// SD Card
pinMode( chipSelect , OUTPUT );
if(!SD.begin( chipSelect )){
;
return;
}
uint8_t cardType = SD.cardType();
if(cardType == CARD_NONE){
;
return;
}
//Serial.print("SD Card Type: ");
if(cardType == CARD_MMC){
;
} else if(cardType == CARD_SD){
;
} else if(cardType == CARD_SDHC){
;
} else {
;
}
uint64_t cardSize = SD.cardSize() / (1024 * 1024);
}
// SD Card
void isSD() {
zzzzzz = "";
zzzzzz = uid + "|" + sver + "|" + dateRTC + "|" + timeRTC + "|" + Status + "|" + TargetLon + "|" + TargetLat + "|" + latestHumidity + "|" + latestTempC + "|" + latestTempF + "|" + average + "|\r";
char msg[zzzzzz.length() + 1];
zzzzzz.toCharArray(msg, zzzzzz.length() + 1);
appendFile(SD, "/espdata.txt", msg );
}
// List Dir
void listDir(fs::FS &fs, const char * dirname, uint8_t levels){
dirname;
File root = fs.open(dirname);
if(!root){
return;
}
if(!root.isDirectory()){
return;
}
File file = root.openNextFile();
while(file){
if(file.isDirectory()){
file.name();
if(levels){
listDir(fs, file.name(), levels -1);
}
} else {
file.name();
file.size();
}
file = root.openNextFile();
}
}
// Write File
void writeFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path, const char * message){
path;
File file = fs.open(path, FILE_WRITE);
if(!file){
return;
}
if(file.print(message)){
;
} else {
;
}
file.close();
}
// Append File
void appendFile(fs::FS &fs, const char * path, const char * message){
//Serial.printf("Appending to file: %s\n", path);
path;
File file = fs.open(path, FILE_APPEND);
if(!file){
return;
}
if(file.print(message)){
;
} else {
;
}
file.close();
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// EEPROM with unique ID
EEPROM.begin(EEPROM_SIZE);
// Get Unit ID
GetUID();
// GPS Receiver
// Setup GPS
setupGPS();
// SHARP Display start & clear the display
display.begin();
display.clearDisplay();
isDisplayUID();
delay( 5000 );
// Initialize the LED Green
pinMode(iLEDGreen, OUTPUT);
// PCF8523 Precision RTC
setupRTC();
// Date and Time RTC
isRTC();
// RHT03 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
// Call rht.begin() to initialize the sensor and our data pin
rht.begin(RHT03_DATA_PIN);
// SD Card
setupSD();
// Rocker Switches
pinMode(iRow1, INPUT);
// EMF Meter (Single Axis)
setupEMF();
}
Follow Us
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: http://neosteamlabs.com/
Web: http://www.jlpconsultants.com/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Etsy: https://www.etsy.com/shop/NeoSteamLabs
Don Luc
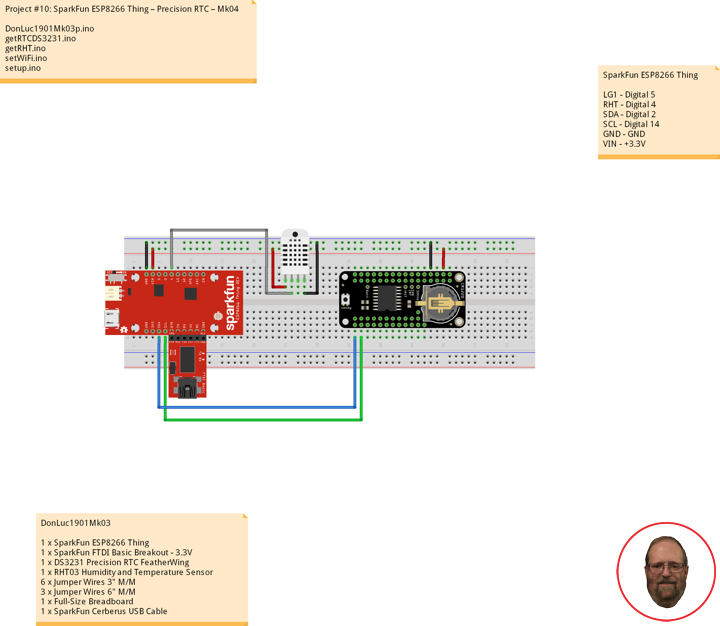
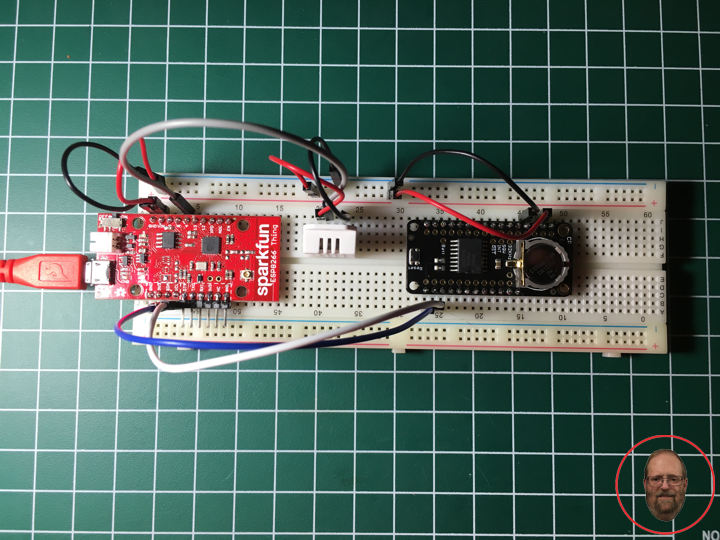
Project #10: ESP8266 Thing – Precision RTC – Mk04
DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
A Feather board without ambition is a Feather board without FeatherWings! This is the DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing: it adds an extremely accurate I2C-integrated Real Time Clock (RTC) with a Temperature Compensated Crystal Oscillator to any Feather main board. This RTC is the most precise you can get in a small, low power package. Most RTCs use an external 32kHz timing crystal that is used to keep time with low current draw.
With a CR1220 12mm lithium battery plugged into the top of the FeatherWing, you can get years of precision timekeeping, even when main power is lost. Great for datalogging and clocks, or anything where you need to really know the time.
DonLuc1901Mk03
1 x SparkFun ESP8266 Thing
1 x SparkFun FTDI Basic Breakout – 3.3V
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x RHT03 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
6 x Jumper Wires 3″ M/M
3 x Jumper Wires 6″ M/M
1 x Full-Size Breadboard
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
SparkFun ESP8266 Thing
LG1 – Digital 5
RHT – Digital 4
SDA – Digital 2
SCL – Digital 14
GND – GND
VIN – +3.3V
DonLuc1901Mk03p.ino
// ***** Don Luc Electronics *****
// Software Version Information
// Project #10: SparkFun ESP8266 Thing – DS3231 Precision RTC - Mk04
// 01-03
// DonLuc1901Mk03p.ino 01-03
// SparkFun ESP8266 Thing
// DS3231 Precision RTC
// RHT03 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
// Include Library Code
// WiFi
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
// RHT Humidity and Temperature Sensor
#include <SparkFun_RHT03.h>
// DS3231 Precision RTC
#include <RTClib.h>
#include <Wire.h>
// WiFi Definitions
const char WiFiAPPSK[] = "donlucmk01";
// Pin Definitions
const int LED_PIN = 5; // Thing's onboard, green LED
const int ANALOG_PIN = A0; // The only analog pin on the Thing
const int DIGITAL_PIN = 12; // Digital pin to be read
// WiFi
WiFiServer server(80);
// RHT Humidity and Temperature Sensor
const int RHT03_DATA_PIN = 4; // RHT03 data pin Digital 4
RHT03 rht; // This creates a RTH03 object, which we'll use to interact with the sensor
float latestHumidity;
float latestTempC;
float latestTempF;
// DS3231 Precision RTC
RTC_DS3231 RTC;
String sDate;
String sTime;
void loop()
{
// RHT03 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
isRHT03();
// DS3231 Precision RTC
timeRTC();
// Check if a client has connected
WiFiClient client = server.available();
if (!client) {
return;
}
// Read the first line of the request
String req = client.readStringUntil('\r');
Serial.println(req);
client.flush();
// Match the request
int val = -1; // We'll use 'val' to keep track of both the request type (read/set) and value if set.
if (req.indexOf("/led/0") != -1)
val = 0; // Will write LED low
else if (req.indexOf("/led/1") != -1)
val = 1; // Will write LED high
else if (req.indexOf("/read") != -1)
val = -2; // Will print pin reads
// Otherwise request will be invalid. We'll say as much in HTML
// Set GPIO5 according to the request
if (val >= 0)
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, val);
client.flush();
// Prepare the response. Start with the common header:
String s = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n";
s += "Content-Type: text/html\r\n\r\n";
s += "<!DOCTYPE HTML>\r\n<html>\r\n";
// If we're setting the LED, print out a message saying we did
if (val >= 0)
{
s += "LED is now ";
s += (val)?"on":"off";
}
else if (val == -2)
{ // If we're reading pins, print out those values:
s += "Date = ";
s += sDate;
s += "<br>";
s += "Time = ";
s += sTime;
s += "<br>";
s += "Analog Pin = ";
s += String(analogRead(ANALOG_PIN));
s += "<br>"; // Go to the next line.
s += "Digital Pin 12 = ";
s += String(digitalRead(DIGITAL_PIN));
s += "<br>"; // Go to the next line.
s += "Humidity and Temperature";
s += "<br>"; // Go to the next line.
s += "Humidity : ";
s += String(latestHumidity); // Humidity
s += "%";
s += "<br>"; // Go to the next line.
s += "Celsius: ";
s += String(latestTempC); // Temperature *C
s += "*C";
s += "<br>"; // Go to the next line.
s += "Fahrenheit: ";
s += String(latestTempF); // Temperature *F
s += "*F";
}
else
{
s += "Invalid Request.<br> Try /led/1, /led/0, or /read.";
}
s += "</html>\n";
// Send the response to the client
client.print(s);
delay(1);
Serial.println("Client disonnected");
// The client will actually be disconnected when the function returns and 'client' object is detroyed
}
getRHT.ino
// RHT03 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
void isRHT03(){
// Call rht.update() to get new humidity and temperature values from the sensor.
int updateRet = rht.update();
// The humidity(), tempC(), and tempF() functions can be called -- after
// a successful update() -- to get the last humidity and temperature value
latestHumidity = rht.humidity();
latestTempC = rht.tempC();
latestTempF = rht.tempF();
}
getRTCDS3231.ino
// DS3231 Precision RTC
void setupRTC() {
// DS3231 Precision RTC
RTC.begin();
if (! RTC.begin()) {
while (1);
}
DateTime now = RTC.now();
if (RTC.lostPower()) {
// Following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled
RTC.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
}
}
// timeRTC
void timeRTC() {
// DS3231 Precision RTC
sDate = "";
sTime = "";
DateTime now = RTC.now();
// sData
sDate += String(now.year(), DEC);
sDate += "/";
sDate += String(now.month(), DEC);
sDate += "/";
sDate += String(now.day(), DEC);
// sTime
sTime += String(now.hour(), DEC);
sTime += ":";
sTime += String(now.minute(), DEC);
sTime += ":";
sTime += String(now.second(), DEC);
}
setWiFi.ino
// WiFi
void setupWiFi()
{
// WiFi mode WIFI_AP
WiFi.mode(WIFI_AP);
// Append the last two bytes of the MAC (HEX'd) to "Thing-":
uint8_t mac[WL_MAC_ADDR_LENGTH];
WiFi.softAPmacAddress(mac);
String macID = String(mac[WL_MAC_ADDR_LENGTH - 2], HEX) +
String(mac[WL_MAC_ADDR_LENGTH - 1], HEX);
macID.toUpperCase();
String AP_NameString = "ESP8266 Thing " + macID;
char AP_NameChar[AP_NameString.length() + 1];
memset(AP_NameChar, 0, AP_NameString.length() + 1);
for (int i=0; i<AP_NameString.length(); i++)
AP_NameChar[i] = AP_NameString.charAt(i);
WiFi.softAP(AP_NameChar, WiFiAPPSK);
}
// init Hardware
void initHardware()
{
// Serial
Serial.begin(115200);
// LED Green
pinMode(DIGITAL_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW);
// RHT03 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
// Call rht.begin() to initialize the sensor and our data pin
rht.begin(RHT03_DATA_PIN);
// DS3231 Precision RTC
setupRTC();
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// Hardware
initHardware();
// WiFi
setupWiFi();
server.begin();
}
Don Luc
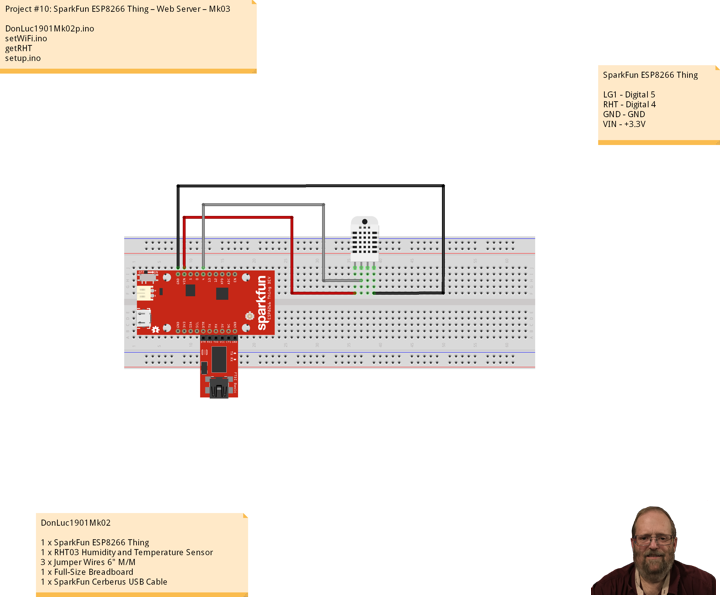
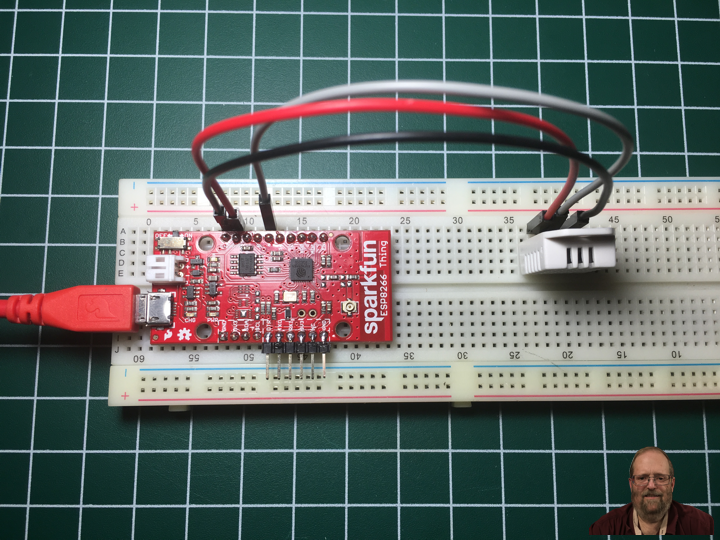
Project #10: ESP8266 Thing – Web Server – Mk03
AP Web Server
Not only can the ESP8266 connect to a WiFi network and interact with the Internet, but it can also set up a network of its own, allowing other devices to connect directly to it. This example demonstrates how to turn the ESP8266 into an access point (AP), and serve up web pages to any connected client.
After uploading this sketch, find another device that you can connect to a WiFi network – phone, laptop, etc. Look for a network called “Thing-XXXX”, where XXXX is the last 2 bytes of the Thing’s MAC address.
WiFi => Yes
ESP8266 Thing XXXX
He sketch sets the network’s password to “donlucmk01”.
After connecting to your Thing’s AP network, load up a browser and point it to 192.168.4.1/read. The Thing should serve up a web page showing you its ADC and digital pin 12 readings:
Analog Pin = XXX
Digital Pin: XXX
Humidity and Temperature
Humidity: XX.XX%
Celsius: XX.XX*C
Fahrenheit: XX.XX*F
LED Green
After that, give 192.168.4.1/led/0 (No) and 192.168.4.1/led/1 (Yes) a try, and keep an eye on the Thing’s green LED while you do.
RHT03 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
The RHT03 is a low cost humidity and temperature sensor with a single wire digital interface. The sensor is calibrated and doesn’t require extra components so you can get right to measuring relative humidity and temperature.
DonLuc1901Mk02
1 x SparkFun ESP8266 Thing
1 x SparkFun FTDI Basic Breakout – 3.3V
1 x RHT03 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
3 x Jumper Wires 6″ M/M
1 x Full-Size Breadboard
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
SparkFun ESP8266 Thing
LG1 – Digital 5
RHT – Digital 4
GND – GND
VIN – +3.3V
DonLuc1901Mk02p.ino
// ***** Don Luc Electronics *****
// Software Version Information
// Project #10: SparkFun ESP8266 Thing – AP Web Server - Mk02
// 01-02
// DonLuc1901Mk01p.ino 01-02
// SparkFun ESP8266 Thing
// AP Web Server
// RHT03 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
// Include Library Code
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h>
#include <SparkFun_RHT03.h>
// WiFi Definitions
const char WiFiAPPSK[] = "donlucmk01";
// Pin Definitions
const int LED_PIN = 5; // Thing's onboard, green LED
const int ANALOG_PIN = A0; // The only analog pin on the Thing
const int DIGITAL_PIN = 12; // Digital pin to be read
// WiFi
WiFiServer server(80);
// RHT Humidity and Temperature Sensor
const int RHT03_DATA_PIN = 4; // RHT03 data pin Digital 4
RHT03 rht; // This creates a RTH03 object, which we'll use to interact with the sensor
float latestHumidity;
float latestTempC;
float latestTempF;
void loop()
{
// RHT03 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
isRHT03();
// Check if a client has connected
WiFiClient client = server.available();
if (!client) {
return;
}
// Read the first line of the request
String req = client.readStringUntil('\r');
Serial.println(req);
client.flush();
// Match the request
int val = -1; // We'll use 'val' to keep track of both the request type (read/set) and value if set.
if (req.indexOf("/led/0") != -1)
val = 0; // Will write LED low
else if (req.indexOf("/led/1") != -1)
val = 1; // Will write LED high
else if (req.indexOf("/read") != -1)
val = -2; // Will print pin reads
// Otherwise request will be invalid. We'll say as much in HTML
// Set GPIO5 according to the request
if (val >= 0)
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, val);
client.flush();
// Prepare the response. Start with the common header:
String s = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n";
s += "Content-Type: text/html\r\n\r\n";
s += "<!DOCTYPE HTML>\r\n<html>\r\n";
// If we're setting the LED, print out a message saying we did
if (val >= 0)
{
s += "LED is now ";
s += (val)?"on":"off";
}
else if (val == -2)
{ // If we're reading pins, print out those values:
s += "Analog Pin = ";
s += String(analogRead(ANALOG_PIN));
s += "<br>"; // Go to the next line.
s += "Digital Pin 12 = ";
s += String(digitalRead(DIGITAL_PIN));
s += "<br>"; // Go to the next line.
s += "Humidity and Temperature";
s += "<br>"; // Go to the next line.
s += "Humidity : ";
s += String(latestHumidity); // Humidity
s += "%";
s += "<br>"; // Go to the next line.
s += "Celsius: ";
s += String(latestTempC); // Temperature *C
s += "*C";
s += "<br>"; // Go to the next line.
s += "Fahrenheit: ";
s += String(latestTempF); // Temperature *F
s += "*F";
}
else
{
s += "Invalid Request.<br> Try /led/1, /led/0, or /read.";
}
s += "</html>\n";
// Send the response to the client
client.print(s);
delay(1);
Serial.println("Client disonnected");
// The client will actually be disconnected when the function returns and 'client' object is detroyed
}
getRHT.ino
// RHT03 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
void isRHT03(){
// Call rht.update() to get new humidity and temperature values from the sensor.
int updateRet = rht.update();
// The humidity(), tempC(), and tempF() functions can be called -- after
// a successful update() -- to get the last humidity and temperature value
latestHumidity = rht.humidity();
latestTempC = rht.tempC();
latestTempF = rht.tempF();
}
setWiFi.ino
// WiFi
void setupWiFi()
{
// WiFi mode WIFI_AP
WiFi.mode(WIFI_AP);
// Append the last two bytes of the MAC (HEX'd) to "Thing-":
uint8_t mac[WL_MAC_ADDR_LENGTH];
WiFi.softAPmacAddress(mac);
String macID = String(mac[WL_MAC_ADDR_LENGTH - 2], HEX) +
String(mac[WL_MAC_ADDR_LENGTH - 1], HEX);
macID.toUpperCase();
String AP_NameString = "ESP8266 Thing " + macID;
char AP_NameChar[AP_NameString.length() + 1];
memset(AP_NameChar, 0, AP_NameString.length() + 1);
for (int i=0; i<AP_NameString.length(); i++)
AP_NameChar[i] = AP_NameString.charAt(i);
WiFi.softAP(AP_NameChar, WiFiAPPSK);
}
// init Hardware
void initHardware()
{
// Serial
Serial.begin(115200);
// LED Green
pinMode(DIGITAL_PIN, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, LOW);
// RHT03 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
// Call rht.begin() to initialize the sensor and our data pin
rht.begin(RHT03_DATA_PIN);
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// Hardware
initHardware();
// WiFi
setupWiFi();
server.begin();
}
Don Luc
Project #10: ESP8266 Thing – Blink – Mk02
Soldering
Plated through-hole soldering (PTH), flux-core solder alloys commonly used for electrical soldering are 60/40 Sn-Pb used principally in electrical/electronic work and TENMA soldering station temperature controlled digital.
Hardware Assembly
We’re getting ahead of ourselves. To connect the FTDI programmer to your Thing you’ll need to solder something to the Thing. What, exactly, you solder to the board depends both on how you’ll use it in your project, and how you’ll interface it with the programmer. When it comes to selecting a header (or wire) to solder, there are a variety of options. We’ve tried a lot of them with the Thing:
Or you can mix and match headers to best fit your needs. Right-angle male headers may help to interface between the FTDI and the Thing. Straight male headers are a good choice for low-profile connections. Straight female headers may help with connecting to I2C sensors. And, of course, wire can be soldered to any of the pins that have a long way to connect to something.
10 pin – Break Away Headers – Straight
4 pin – Break Away Headers – Straight
6 pin – Break Away Male Headers – Right Angle
Once you’ve soldered up at least the programming port, you’re ready to load some code onto the Thing.
Programming the Thing
The ESP8266 has a built-in serial bootloader, which allows for easy programming and re-programming. You don’t need a specialized, expensive programmer – just a simple, USB-to-Serial converter. The FTDI Basic’s 6-pin header matches up exactly to the Thing’s 6-pin serial port header. To set up for programming, simply connect the FTDI directly to this port – take care to match up the DTR and GND pins.
Blink
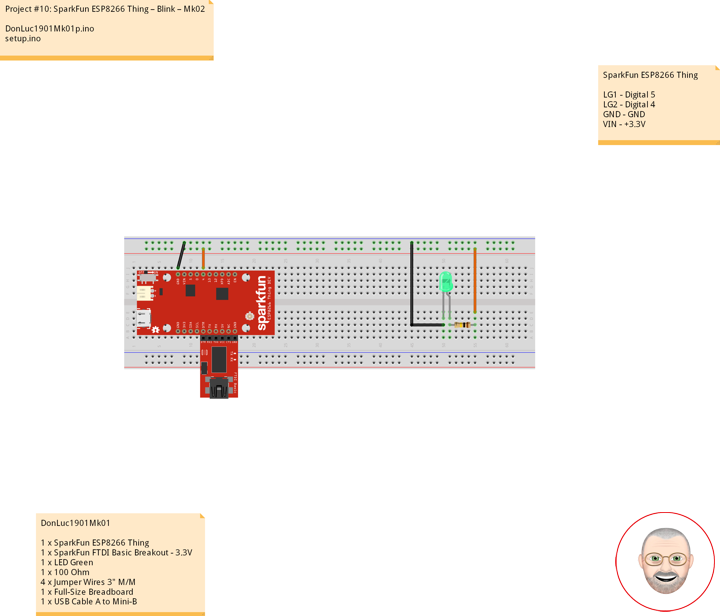
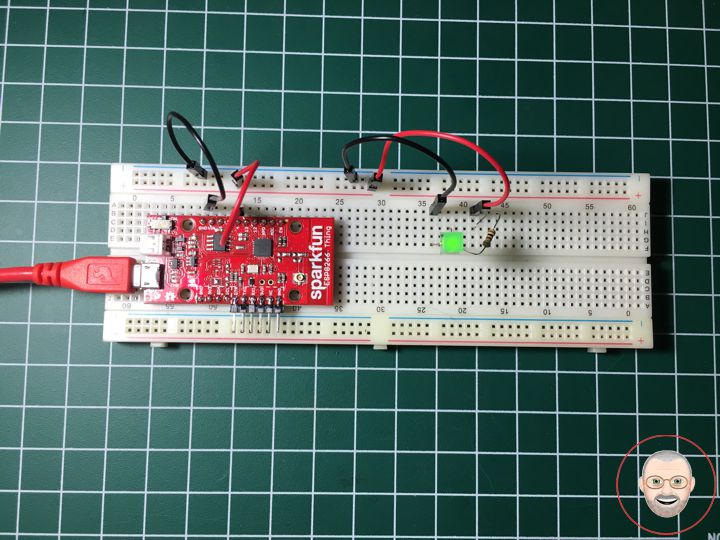
Let’s blink some LEDs and IoT (Internet our Thing). To verify that everything works Blink: toggle pin 5, which is attached to the onboard LED Green, toggle pin 4 which is LED Green.
DonLuc1901Mk01
1 x SparkFun ESP8266 Thing
1 x SparkFun FTDI Basic Breakout – 3.3V
1 x LED Green
1 x 100 Ohm
4 x Jumper Wires 3″ M/M
1 x Full-Size Breadboard
1 x USB Cable A to Mini-B
SparkFun ESP8266 Thing
LG1 – Digital 5
LG2 – Digital 4
GND – GND
VIN – +3.3V
DonLuc1901Mk01p.ino
// ***** Don Luc Electronics *****
// Software Version Information
// Project #10: SparkFun ESP8266 Thing – Blink - Mk02
// 01-01
// DonLuc1901Mk01p.ino 01-01
// SparkFun ESP8266 Thing
// Blink
// Include Library Code
#define ESP8266_LED 5 // LED Green
int iLEDGreen = 4; // LED Green
void loop()
{
// ESP8266_LED, iLEDGreen
digitalWrite(ESP8266_LED, LOW);
digitalWrite(iLEDGreen, LOW);
delay(2000);
digitalWrite(ESP8266_LED, HIGH);
delay(2000);
digitalWrite(ESP8266_LED, LOW);
delay(2000);
digitalWrite(iLEDGreen, HIGH);
delay(2000);
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup()
{
// LED
pinMode(ESP8266_LED, OUTPUT); // ESP8266_LED Green
pinMode(iLEDGreen, OUTPUT); // LED Green
}
Don Luc
Project #10: SparkFun ESP8266 Thing – Mk01
Description
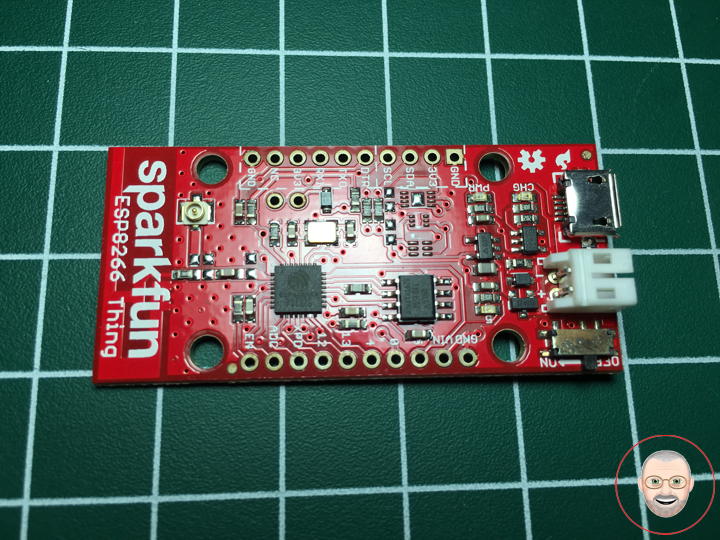
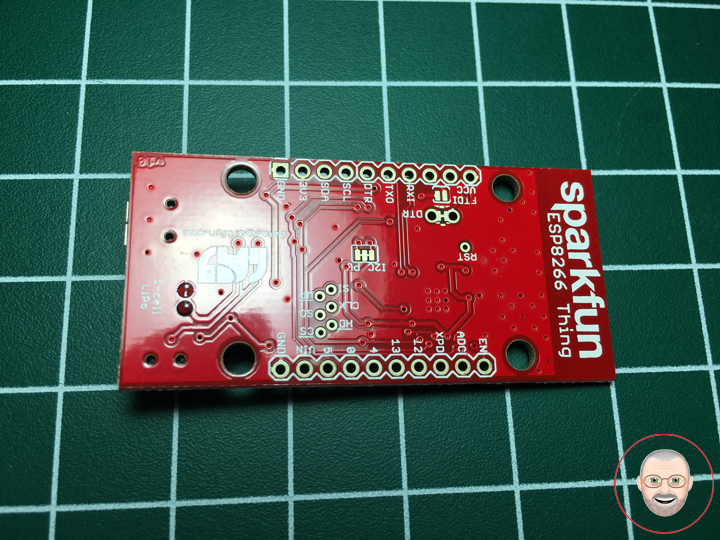
The SparkFun ESP8266 Thing is a breakout and development board for the ESP8266 WiFi SoC – a leading platform for Internet of Things (IoT) or WiFi-related projects. The Thing is low-cost and easy to use, and Arduino IDE integration can be achieved in just a few steps. We’ve made the ESP8266 easy to use by breaking out all of the module’s pins, adding a LiPo charger, power supply, and all of the other supporting circuitry it requires.
Why the name? We lovingly call it the “Thing” due to it being the perfect foundation for your Internet of Things project. The Thing does everything from turning on an LED to posting data with datastream, and can be programmed just like any microcontroller. You can even program the Thing through the Arduino IDE by installing the ESP8266 Arduino addon.
The SparkFun ESP8266 Thing is a relatively simple board. The pins are broken out to two parallel, breadboard-compatible rows. USB and LiPo connectors at the top of the board provide power – controlled by the nearby ON/OFF switch. LEDs towards the inside of the board indicate power, charge, and status of the IC. The ESP8266’s maximum voltage is 3.6V, so the Thing has an onboard 3.3V regulator to deliver a safe, consistent voltage to the IC. That means the ESP8266’s I/O pins also run at 3.3V, you’ll need to level shift any 5V signals running into the IC. A 3.3V FTDI Basic is required to program the SparkFun ESP8266 Thing, but other serial converters with 3.3V I/O levels should work just fine as well. The converter does need a DTR line in addition to the RX and TX pins.
Features
- All module pins broken out
- On-board LiPo charger/power supply
- 802.11 b/g/n
- Wi-Fi Direct (P2P), soft-AP
- Integrated TCP/IP protocol stack
- Integrated TR switch, balun, LNA, power amplifier and matching network
- Integrated PLLs, regulators, DCXO and power management units
- Integrated low power 32-bit CPU could be used as application processor
- +19.5dBm output power in 802.11b mode
Don Luc