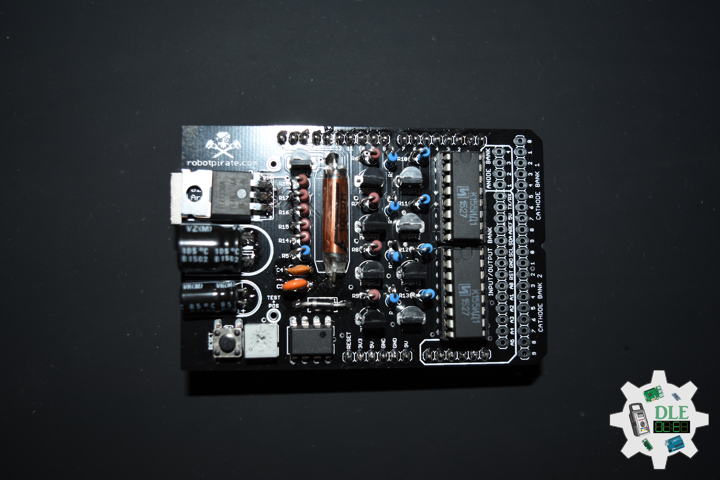
Nixie Clock
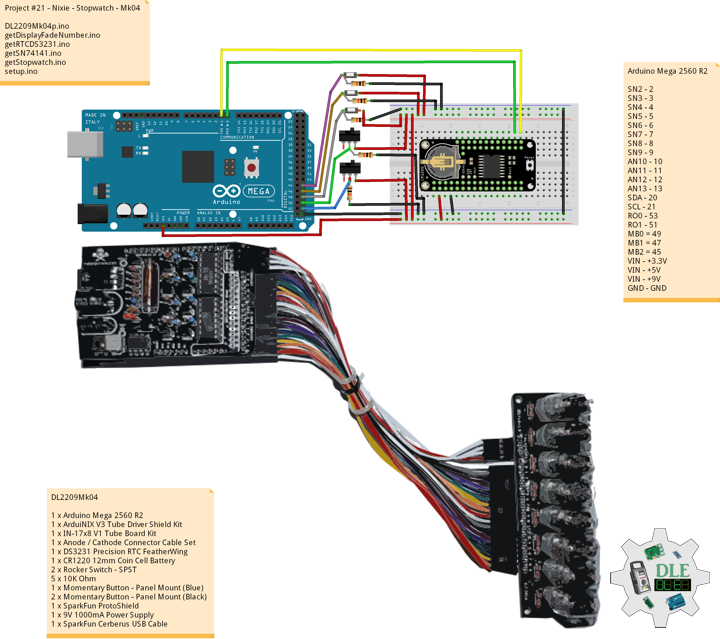
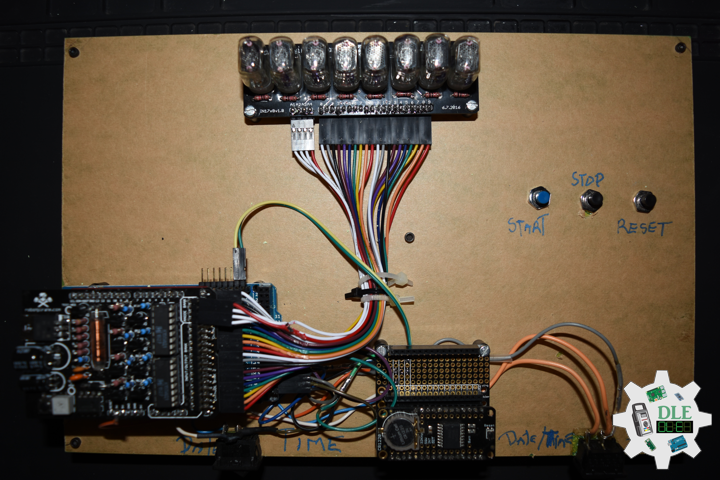
Project #21 – Nixie – Stopwatch – Mk04
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #NixieTube #Nixie #ArduiNIX #ArduinoMega2560 #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
Stopwatch
A stopwatch is a timepiece designed to measure the amount of time that elapses between its activation and deactivation. In manual timing, the clock is started and stopped by a person pressing a button. The timing functions are traditionally controlled by two buttons on the case. Pressing the top button starts the timer running, and pressing the button a second time stops it, leaving the elapsed time displayed. A press of the second button then resets the stopwatch to zero. The second button is also used to record split times or lap times. When the split time button is pressed while the watch is running it allows the elapsed time to that point to be read, but the watch mechanism continues running to record total elapsed time. Pressing the split button a second time allows the watch to resume display of total time.
DL2209Mk04
1 x Arduino Mega 2560 R2
1 x ArduiNIX V3 Tube Driver Shield Kit
1 x IN-17×8 V1 Tube Board Kit
1 x Anode / Cathode Connector Cable Set
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x CR1220 12mm Coin Cell Battery
2 x Rocker Switch – SPST
5 x 10K Ohm
1 x Momentary Button – Panel Mount (Blue)
2 x Momentary Button – Panel Mount (Black)
1 x SparkFun ProtoShield
1 x 9V 1000mA Power Supply
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
Arduino Mega 2560 R2
SN2 – 2
SN3 – 3
SN4 – 4
SN5 – 5
SN6 – 6
SN7 – 7
SN8 – 8
SN9 – 9
AN10 – 10
AN11 – 11
AN12 – 12
AN13 – 13
SDA – 20
SCL – 21
RO0 – 53
RO1 – 51
MB0 = 49
MB1 = 47
MB2 = 45
VIN – +3.3V
VIN – +5V
VIN – +9V
GND – GND
DL2209Mk04p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #21 - Nixie - Stopwatch - Mk04
21-04
DL2209Mk04p.ino
1 x Arduino Mega 2560 R2
1 x ArduiNIX V3 Tube Driver Shield Kit
1 x IN-17x8 V1 Tube Board Kit
1 x Anode / Cathode Connector Cable Set
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x CR1220 12mm Coin Cell Battery
2 x Rocker Switch - SPST
5 x 10K Ohm
1 x Momentary Button - Panel Mount (Blue)
2 x Momentary Button - Panel Mount (Black)
1 x 9V 1000mA Power Supply
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// Wire you to communicate with I2C/TWI devices
// Date and Time DS3231 RTC
#include "RTClib.h"
// SN74141 (1)
int ledPin_0_a = 2;
int ledPin_0_b = 3;
int ledPin_0_c = 4;
int ledPin_0_d = 5;
// SN74141 (2)
int ledPin_1_a = 6;
int ledPin_1_b = 7;
int ledPin_1_c = 8;
int ledPin_1_d = 9;
// Anode pins
int ledPin_a_1 = 10;
int ledPin_a_2 = 11;
int ledPin_a_3 = 12;
int ledPin_a_4 = 13;
// Fade
float fadeMax = 0.1f;
float fadeStep = 0.1f;
// Number Array
int NumberArray[8]={0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
int currNumberArray[8]={0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
float NumberArrayFadeInValue[8]={0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f};
float NumberArrayFadeOutValue[8]={5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f};
// Date and time functions using a DS3231 RTC
RTC_DS3231 RTC;
// Rocker Switch - SPST
// Rocker Switch 0
const int iRO0 = 53;
// State
int iRO0State = 0;
// Rocker Switch 1
const int iRO1 = 51;
// State
int iRO1State = 0;
// Momentary Button
const int iStartP = 49;
const int iStopP = 47;
const int iResetP = 45;
// Setting hours, minutes, secound and miliseconds to 0
int iH = 0;
int iM = 0;
int iS = 0;
int iMS = 0;
int iMSS = 0;
// Defines starting points
int iStart = 0;
int iStop1 = 0;
int iReset = 0;
// Get the high and low order values for hours,min,seconds.
int lowerHours = 0;
int upperHours = 0;
int lowerMins = 0;
int upperMins = 0;
int lowerSeconds = 0;
int upperSeconds = 0;
int lowerMiliseconds = 0;
int upperMiliseconds = 0;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "21-04";
void loop() {
// Read the state of the Switch value
iRO1State = digitalRead(iRO1);
// If it is the Switch State is HIGH
if (iRO1State == HIGH) {
// Stopwatch
isStart();
} else {
// Date ans Time
isTimeRTC();
}
}
getDisplayFadeNumber.ino
// Display Fade Number
void DisplayFadeNumberString()
{
// Anode channel 1 - numerals 0,4
SetSN74141Chips(currNumberArray[0],currNumberArray[4]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_1, HIGH);
delay(NumberArrayFadeOutValue[0]);
SetSN74141Chips(NumberArray[0],NumberArray[4]);
delay(NumberArrayFadeInValue[0]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_1, LOW);
// Anode channel 2 - numerals 1,5
SetSN74141Chips(currNumberArray[1],currNumberArray[5]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_2, HIGH);
delay(NumberArrayFadeOutValue[1]);
SetSN74141Chips(NumberArray[1],NumberArray[5]);
delay(NumberArrayFadeInValue[1]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_2, LOW);
// Anode channel 3 - numerals 2,6
SetSN74141Chips(currNumberArray[2],currNumberArray[6]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_3, HIGH);
delay(NumberArrayFadeOutValue[2]);
SetSN74141Chips(NumberArray[2],NumberArray[6]);
delay(NumberArrayFadeInValue[2]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_3, LOW);
// Anode channel 4 - numerals 3,7
SetSN74141Chips(currNumberArray[3],currNumberArray[7]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_4, HIGH);
delay(NumberArrayFadeOutValue[3]);
SetSN74141Chips(NumberArray[3],NumberArray[7]);
delay(NumberArrayFadeInValue[3]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_4, LOW);
// Loop thru and update all the arrays, and fades.
for( int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; i ++ ) //equal to & of digits
{
if( NumberArray[i] != currNumberArray[i] )
{
NumberArrayFadeInValue[i] += fadeStep;
NumberArrayFadeOutValue[i] -= fadeStep;
if( NumberArrayFadeInValue[i] >= fadeMax )
{
NumberArrayFadeInValue[i] = 2.0f;
NumberArrayFadeOutValue[i] = 4.0f; //affects the refresh cycle
currNumberArray[i] = NumberArray[i];
}
}
}
}
getRTCDS3231.ino
// DS3231 Precision RTC
// Setup RTC
void setupRTC() {
// DS3231 Precision RTC
RTC.begin();
if (! RTC.begin() ) {
while (1) delay(10);
}
if (RTC.lostPower()) {
// Following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled
RTC.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
// This line sets the RTC with an explicit date & time, for example to set
// August 2, 2021 at 13:53:0 you would call:
// RTC.adjust(DateTime(2022, 4, 26, 11, 39, 0));
}
}
// Date ans Time - isTimeRTC
void isTimeRTC() {
// Date and Time
DateTime now = RTC.now();
// Read the state of the Switch value
iRO0State = digitalRead(iRO0);
// If it is the Switch State is HIGH
if (iRO0State == HIGH) {
// Get the high and low order values for hours, minute, seconds
int lowerHours = now.hour() % 10;
int upperHours = now.hour() - lowerHours;
int lowerMins = now.minute() % 10;
int upperMins = now.minute() - lowerMins;
int lowerSeconds = now.second() % 10;
int upperSeconds = now.second() - lowerSeconds;
// 10 >= hours, minute, seconds
if( upperSeconds >= 10 ) upperSeconds = upperSeconds / 10;
if( upperMins >= 10 ) upperMins = upperMins / 10;
if( upperHours >= 10 ) upperHours = upperHours / 10;
if( upperHours == 0 && lowerHours == 0 )
{
upperHours = 1;
lowerHours = 2;
}
// Fill in the Number array used to display on the Nixie tubes
NumberArray[7] = upperHours;
NumberArray[6] = lowerHours;
NumberArray[5] = 0;
NumberArray[4] = upperMins;
NumberArray[3] = lowerMins;
NumberArray[2] = 0;
NumberArray[1] = upperSeconds;
NumberArray[0] = lowerSeconds;
} else {
// Get the high and low order values for year, month, day
int iYear = now.year() - 2000;
int lowerYear = iYear % 10;
int upperYear = iYear - lowerYear;
int lowerMonth = now.month() % 10;
int upperMonth = now.month() - lowerMonth;
int lowerDay = now.day() % 10;
int upperDay = now.day() - lowerDay;
// 10 >= year, month, day
if( upperDay >= 10 ) upperDay = upperDay / 10;
if( upperMonth >= 10 ) upperMonth = upperMonth / 10;
if( upperYear >= 10 ) upperYear = upperYear / 10;
// Fill in the Number array used to display on the Nixie tubes
NumberArray[7] = 2;
NumberArray[6] = 0;
NumberArray[5] = upperYear;
NumberArray[4] = lowerYear;
NumberArray[3] = upperMonth;
NumberArray[2] = lowerMonth;
NumberArray[1] = upperDay;
NumberArray[0] = lowerDay;
}
// Display
DisplayFadeNumberString();
}
getSN74141.ino
// SN74141
// SN74141 : Truth Table
//D C B A #
//L,L,L,L 0
//L,L,L,H 1
//L,L,H,L 2
//L,L,H,H 3
//L,H,L,L 4
//L,H,L,H 5
//L,H,H,L 6
//L,H,H,H 7
//H,L,L,L 8
//H,L,L,H 9
// isSetupSN74141
void isSetupSN74141(){
pinMode(ledPin_0_a, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_0_b, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_0_c, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_0_d, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_1_a, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_1_b, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_1_c, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_1_d, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_a_1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_a_2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_a_3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_a_4, OUTPUT);
}
// SetSN74141Chips
void SetSN74141Chips( int num2, int num1 )
{
// Set defaults
// Will display a zero.
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int c = 0;
int d = 0;
// Load the a,b,c,d.. to send to the SN74141 IC (1)
switch( num1 )
{
case 0:
a=0;
b=0;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 1:
a=1;
b=0;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 2:
a=0;
b=1;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 3:
a=1;
b=1;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 4:
a=0;
b=0;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 5:
a=1;
b=0;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 6:
a=0;
b=1;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 7:
a=1;
b=1;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 8:
a=0;
b=0;
c=0;
d=1;
break;
case 9:
a=1;
b=0;
c=0;
d=1;
break;
default:
a=1;
b=1;
c=1;
d=1;
break;
}
// Write to output pins.
digitalWrite(ledPin_0_d, d);
digitalWrite(ledPin_0_c, c);
digitalWrite(ledPin_0_b, b);
digitalWrite(ledPin_0_a, a);
// Load the a,b,c,d.. to send to the SN74141 IC (2)
switch( num2 )
{
case 0:
a=0;
b=0;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 1:
a=1;
b=0;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 2:
a=0;
b=1;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 3:
a=1;
b=1;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 4:
a=0;
b=0;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 5:
a=1;
b=0;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 6:
a=0;
b=1;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 7:
a=1;
b=1;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 8:
a=0;
b=0;
c=0;
d=1;
break;
case 9:
a=1;
b=0;
c=0;
d=1;
break;
default:
a=1;
b=1;
c=1;
d=1;
break;
}
// Write to output pins
digitalWrite(ledPin_1_d, d);
digitalWrite(ledPin_1_c, c);
digitalWrite(ledPin_1_b, b);
digitalWrite(ledPin_1_a, a);
}
getStopwatch.ino
// Stopwatch
// Setup Stopwatch
void isSetupStopwatch(){
// Switch
pinMode(iRO0, INPUT);
pinMode(iRO1, INPUT);
// Momentary Button
pinMode(iStartP, INPUT);
pinMode(iStopP, INPUT);
pinMode(iResetP, INPUT);
}
// Start
void isStart()
{
// Reading buton state iStart
iStart = digitalRead(iStartP);
if(iStart == HIGH)
{
// Calls the isStopWatch function
isStopWatch();
}
}
// Stop Watch
void isStopWatch()
{
// Miliseconds
iMS = iMS + 10;
if(iMS == 600)
{
iMS = 0;
iMSS = 0;
iS = iS + 1;
} else if (iMS == 60) { // 1
iMSS = iMSS + 1;
} else if (iMS == 120) { // 2
iMSS = iMSS + 1;
} else if (iMS == 180) { //3
iMSS = iMSS + 1;
} else if (iMS == 240) { // 4
iMSS = iMSS + 1;
} else if (iMS == 300) { // 5
iMSS = iMSS + 1;
} else if (iMS == 360) { // 6
iMSS = iMSS + 1;
} else if (iMS == 420) { // 7
iMSS = iMSS + 1;
} else if (iMS == 480) { // 8
iMSS = iMSS + 1;
} else if (iMS == 540) { // 9
iMSS = iMSS + 1;
}
// If state for counting up minutes
if( iS == 60)
{
iS = 0;
iM = iM + 1;
}
// If state for counting up hours
if( iM == 60)
{
iM = 0;
iH = iH + 01;
}
// Get the high and low order values for hours, minute, seconds, Miliseconds
int lowerHours = iH % 10;
int upperHours = iH - lowerHours;
int lowerMins = iM % 10;
int upperMins = iM - lowerMins;
int lowerSeconds = iS % 10;
int upperSeconds = iS - lowerSeconds;
int lowerMiliseconds = iMSS;
int upperMiliseconds = iMSS - lowerMiliseconds;
// 10 >= hours, minute, seconds, Miliseconds
if( upperSeconds >= 10 ) upperSeconds = upperSeconds / 10;
if( upperMins >= 10 ) upperMins = upperMins / 10;
if( upperHours >= 10 ) upperHours = upperHours / 10;
// Fill in the Number array used to display on the Nixie tubes
NumberArray[7] = upperHours;
NumberArray[6] = lowerHours;
NumberArray[5] = upperMins;
NumberArray[4] = lowerMins;
NumberArray[3] = upperSeconds;
NumberArray[2] = lowerSeconds;
NumberArray[1] = lowerMiliseconds;
NumberArray[0] = lowerMiliseconds;
// Display
DisplayFadeNumberString();
// Reading buton state Stop
iStop1 = digitalRead(iStopP);
// Checking if button is pressed
if(iStop1 == HIGH)
{
// Calls the isStopwatchStop function
isStopwatchStop();
}
else
{
// Calls the isStopWatch function
isStopWatch();
}
}
// Stopwatch Stop
void isStopwatchStop()
{
// Get the high and low order values for hours, minute, seconds, Miliseconds
int lowerHours = iH % 10;
int upperHours = iH - lowerHours;
int lowerMins = iM % 10;
int upperMins = iM - lowerMins;
int lowerSeconds = iS % 10;
int upperSeconds = iS - lowerSeconds;
int lowerMiliseconds = iMSS;
int upperMiliseconds = iMSS - lowerMiliseconds;
// 10 >= hours, minute, seconds, Miliseconds
if( upperSeconds >= 10 ) upperSeconds = upperSeconds / 10;
if( upperMins >= 10 ) upperMins = upperMins / 10;
if( upperHours >= 10 ) upperHours = upperHours / 10;
// Fill in the Number array used to display on the Nixie tubes
NumberArray[7] = upperHours;
NumberArray[6] = lowerHours;
NumberArray[5] = upperMins;
NumberArray[4] = lowerMins;
NumberArray[3] = upperSeconds;
NumberArray[2] = lowerSeconds;
NumberArray[1] = lowerMiliseconds;
NumberArray[0] = lowerMiliseconds;
// Display
DisplayFadeNumberString();
// Reading buton state iStart
iStart = digitalRead(iStartP);
if(iStart == HIGH)
{
// Calls the isStopWatch function
isStopWatch();
}
// Reading buton state
iReset = digitalRead(iResetP);
if(iReset == HIGH)
{
// Calls the isStopwatchReset function
isStopwatchReset();
loop();
}
if(iReset == LOW)
{
// Calls the isStopwatchStop function
isStopwatchStop();
}
}
// Stopwatch Reset
void isStopwatchReset()
{
// Seting hours to 0
iH = 0;
// Seting minutes to 0
iM = 0;
// Seting seconds to 0
iS = 0;
// Seting miliseconds to 0
iMS = 0;
// Seting miliseconds to 0
iMSS = 0;
// Fill in the Number array used to display on the Nixie tubes
NumberArray[7] = 0;
NumberArray[6] = 0;
NumberArray[5] = 0;
NumberArray[4] = 0;
NumberArray[3] = 0;
NumberArray[2] = 0;
NumberArray[1] = 0;
NumberArray[0] = 0;
// Display
DisplayFadeNumberString();
// Exiting the program and returning to the point where entered the program
return;
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// isSetupSN74141
isSetupSN74141();
// Setup Stopwatch
isSetupStopwatch();
// Setup RTC
setupRTC();
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor and E-Mentor
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2022 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: https://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
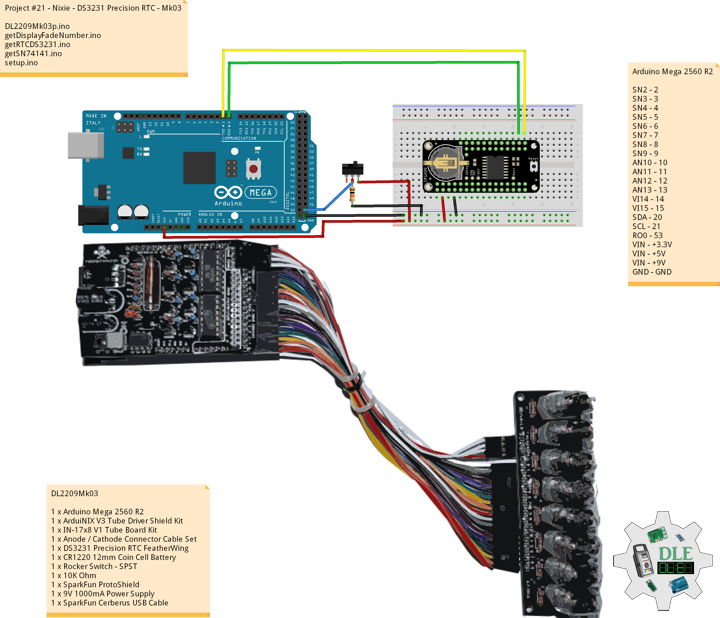
Project #21 – Nixie – DS3231 Precision RTC – Mk03
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #NixieTube #Nixie #ArduiNIX #ArduinoUNO #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
The datasheet for the DS3231 explains that this part is an extremely accurate I²C – Integrated RTC TCXO – crystal. This Real Time Clock (RTC) is the most precise you can get in a small, low power package. Most RTC’s use an external 32kHz timing crystal that is used to keep time with low current draw. That’s all well and good, but those crystals have slight drift, particularly when the temperature changes, the temperature changes the oscillation frequency very slightly but it does add up. This RTC is in a beefy package because the crystal is inside the chip. And right next to the integrated crystal is a temperature sensor. That sensor compensates for the frequency changes by adding or removing clock ticks so that the time keeping stays on schedule.
This is the finest RTC you can get, and now we have it in a compact, breadboard friendly breakout. With a coin cell plugged into the back, you can get years of precision time keeping, even when main power is lost. Great for datalogging and clocks, or anything where you need to really know the time.
DL2209Mk03
1 x Arduino Mega 2560 R2
1 x ArduiNIX V3 Tube Driver Shield Kit
1 x IN-17×8 V1 Tube Board Kit
1 x Anode / Cathode Connector Cable Set
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x CR1220 12mm Coin Cell Battery
1 x Rocker Switch – SPST
1 x 10K Ohm
1 x SparkFun ProtoShield
1 x 9V 1000mA Power Supply
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
Arduino Mega 2560 R2
SN2 – 2
SN3 – 3
SN4 – 4
SN5 – 5
SN6 – 6
SN7 – 7
SN8 – 8
SN9 – 9
AN10 – 10
AN11 – 11
AN12 – 12
AN13 – 13
VI14 – 14
VI15 – 15
SDA – 20
SCL – 21
RO0 – 53
VIN – +3.3V
VIN – +5V
VIN – +9V
GND – GND
DL2209Mk03p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #21 - Nixie - DS3231 Precision RTC - Mk03
21-03
DL2209Mk03p.ino
1 x Arduino Mega 2560 R2
1 x ArduiNIX V3 Tube Driver Shield Kit
1 x IN-17x8 V1 Tube Board Kit
1 x Anode / Cathode Connector Cable Set
1 x DS3231 Precision RTC FeatherWing
1 x CR1220 12mm Coin Cell Battery
1 x Rocker Switch - SPST
1 x 10K Ohm
1 x 9V 1000mA Power Supply
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// Wire you to communicate with I2C/TWI devices
// Date and Time DS3231 RTC
#include "RTClib.h"
// SN74141 (1)
int ledPin_0_a = 2;
int ledPin_0_b = 3;
int ledPin_0_c = 4;
int ledPin_0_d = 5;
// SN74141 (2)
int ledPin_1_a = 6;
int ledPin_1_b = 7;
int ledPin_1_c = 8;
int ledPin_1_d = 9;
// Anode pins
int ledPin_a_1 = 10;
int ledPin_a_2 = 11;
int ledPin_a_3 = 12;
int ledPin_a_4 = 13;
// NOTE: Grounding on virtual pins 14 and 15
// (analog pins 0 and 1) will set the Hour and Mins.
int iVirtual14 = 14;
int iVirtual15 = 15;
// Fade
float fadeMax = 0.1f;
float fadeStep = 0.1f;
// Number Array
int NumberArray[8]={0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
int currNumberArray[8]={0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
float NumberArrayFadeInValue[8]={0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f};
float NumberArrayFadeOutValue[8]={5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f};
// Date and time functions using a DS3231 RTC
RTC_DS3231 RTC;
// Rocker Switch - SPST
int iRO0 = 53;
// State
int iRO0State = 0;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "21-03";
void loop() {
// timeRTC
timeRTC();
}
getDisplayFadeNumber.ino
// Display Fade Number
void DisplayFadeNumberString()
{
// Anode channel 1 - numerals 0,4
SetSN74141Chips(currNumberArray[0],currNumberArray[4]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_1, HIGH);
delay(NumberArrayFadeOutValue[0]);
SetSN74141Chips(NumberArray[0],NumberArray[4]);
delay(NumberArrayFadeInValue[0]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_1, LOW);
// Anode channel 2 - numerals 1,5
SetSN74141Chips(currNumberArray[1],currNumberArray[5]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_2, HIGH);
delay(NumberArrayFadeOutValue[1]);
SetSN74141Chips(NumberArray[1],NumberArray[5]);
delay(NumberArrayFadeInValue[1]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_2, LOW);
// Anode channel 3 - numerals 2,6
SetSN74141Chips(currNumberArray[2],currNumberArray[6]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_3, HIGH);
delay(NumberArrayFadeOutValue[2]);
SetSN74141Chips(NumberArray[2],NumberArray[6]);
delay(NumberArrayFadeInValue[2]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_3, LOW);
// Anode channel 4 - numerals 3,7
SetSN74141Chips(currNumberArray[3],currNumberArray[7]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_4, HIGH);
delay(NumberArrayFadeOutValue[3]);
SetSN74141Chips(NumberArray[3],NumberArray[7]);
delay(NumberArrayFadeInValue[3]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_4, LOW);
// Loop thru and update all the arrays, and fades.
for( int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; i ++ ) //equal to & of digits
{
if( NumberArray[i] != currNumberArray[i] )
{
NumberArrayFadeInValue[i] += fadeStep;
NumberArrayFadeOutValue[i] -= fadeStep;
if( NumberArrayFadeInValue[i] >= fadeMax )
{
NumberArrayFadeInValue[i] = 2.0f;
NumberArrayFadeOutValue[i] = 4.0f; //affects the refresh cycle
currNumberArray[i] = NumberArray[i];
}
}
}
}
getRTCDS3231.ino
// DS3231 Precision RTC
// Setup RTC
void setupRTC() {
// DS3231 Precision RTC
RTC.begin();
if (! RTC.begin() ) {
while (1) delay(10);
}
if (RTC.lostPower()) {
// Following line sets the RTC to the date & time this sketch was compiled
RTC.adjust(DateTime(F(__DATE__), F(__TIME__)));
// This line sets the RTC with an explicit date & time, for example to set
// August 2, 2021 at 13:53:0 you would call:
// RTC.adjust(DateTime(2022, 4, 26, 11, 39, 0));
}
}
// timeRTC
void timeRTC() {
// Date and Time
DateTime now = RTC.now();
// Read the state of the Switch value
iRO0State = digitalRead(iRO0);
// If it is the Switch State is HIGH
if (iRO0State == HIGH) {
// Get the high and low order values for hours, minute, seconds
int lowerHours = now.hour() % 10;
int upperHours = now.hour() - lowerHours;
int lowerMins = now.minute() % 10;
int upperMins = now.minute() - lowerMins;
int lowerSeconds = now.second() % 10;
int upperSeconds = now.second() - lowerSeconds;
// 10 >= hours, minute, seconds
if( upperSeconds >= 10 ) upperSeconds = upperSeconds / 10;
if( upperMins >= 10 ) upperMins = upperMins / 10;
if( upperHours >= 10 ) upperHours = upperHours / 10;
if( upperHours == 0 && lowerHours == 0 )
{
upperHours = 1;
lowerHours = 2;
}
// Fill in the Number array used to display on the Nixie tubes
NumberArray[7] = upperHours;
NumberArray[6] = lowerHours;
NumberArray[5] = 0;
NumberArray[4] = upperMins;
NumberArray[3] = lowerMins;
NumberArray[2] = 0;
NumberArray[1] = upperSeconds;
NumberArray[0] = lowerSeconds;
} else {
// Get the high and low order values for year, month, day
int iYear = now.year() - 2000;
int lowerYear = iYear % 10;
int upperYear = iYear - lowerYear;
int lowerMonth = now.month() % 10;
int upperMonth = now.month() - lowerMonth;
int lowerDay = now.day() % 10;
int upperDay = now.day() - lowerDay;
// 10 >= year, month, day
if( upperDay >= 10 ) upperDay = upperDay / 10;
if( upperMonth >= 10 ) upperMonth = upperMonth / 10;
if( upperYear >= 10 ) upperYear = upperYear / 10;
// Fill in the Number array used to display on the Nixie tubes
NumberArray[7] = 2;
NumberArray[6] = 0;
NumberArray[5] = upperYear;
NumberArray[4] = lowerYear;
NumberArray[3] = upperMonth;
NumberArray[2] = lowerMonth;
NumberArray[1] = upperDay;
NumberArray[0] = lowerDay;
}
// Display
DisplayFadeNumberString();
}
getSN74141.ino
// SN74141
// SN74141 : Truth Table
//D C B A #
//L,L,L,L 0
//L,L,L,H 1
//L,L,H,L 2
//L,L,H,H 3
//L,H,L,L 4
//L,H,L,H 5
//L,H,H,L 6
//L,H,H,H 7
//H,L,L,L 8
//H,L,L,H 9
// isSetupSN74141
void isSetupSN74141(){
pinMode(ledPin_0_a, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_0_b, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_0_c, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_0_d, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_1_a, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_1_b, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_1_c, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_1_d, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_a_1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_a_2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_a_3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_a_4, OUTPUT);
// NOTE: Grounding on virtual pins 14 and 15
// (analog pins 0 and 1) will set the Hour and Mins.
// Set the vertual pin 14 (pin 0 on the analog inputs )
pinMode( iVirtual14, INPUT );
// Set pin 14 as a pull up resistor.
digitalWrite(iVirtual14, HIGH);
// Set the vertual pin 15 (pin 1 on the analog inputs )
pinMode( iVirtual15, INPUT );
// Set pin 15 as a pull up resistor.
digitalWrite(iVirtual15, HIGH);
}
// SetSN74141Chips
void SetSN74141Chips( int num2, int num1 )
{
// Set defaults
// Will display a zero.
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int c = 0;
int d = 0;
// Load the a,b,c,d.. to send to the SN74141 IC (1)
switch( num1 )
{
case 0:
a=0;
b=0;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 1:
a=1;
b=0;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 2:
a=0;
b=1;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 3:
a=1;
b=1;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 4:
a=0;
b=0;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 5:
a=1;
b=0;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 6:
a=0;
b=1;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 7:
a=1;
b=1;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 8:
a=0;
b=0;
c=0;
d=1;
break;
case 9:
a=1;
b=0;
c=0;
d=1;
break;
default:
a=1;
b=1;
c=1;
d=1;
break;
}
// Write to output pins.
digitalWrite(ledPin_0_d, d);
digitalWrite(ledPin_0_c, c);
digitalWrite(ledPin_0_b, b);
digitalWrite(ledPin_0_a, a);
// Load the a,b,c,d.. to send to the SN74141 IC (2)
switch( num2 )
{
case 0:
a=0;
b=0;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 1:
a=1;
b=0;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 2:
a=0;
b=1;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 3:
a=1;
b=1;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 4:
a=0;
b=0;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 5:
a=1;
b=0;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 6:
a=0;
b=1;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 7:
a=1;
b=1;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 8:
a=0;
b=0;
c=0;
d=1;
break;
case 9:
a=1;
b=0;
c=0;
d=1;
break;
default:
a=1;
b=1;
c=1;
d=1;
break;
}
// Write to output pins
digitalWrite(ledPin_1_d, d);
digitalWrite(ledPin_1_c, c);
digitalWrite(ledPin_1_b, b);
digitalWrite(ledPin_1_a, a);
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// isSetupSN74141
isSetupSN74141();
// Switch
pinMode(iRO0, INPUT);
// Setup RTC
setupRTC();
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor and E-Mentor
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2022 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: https://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
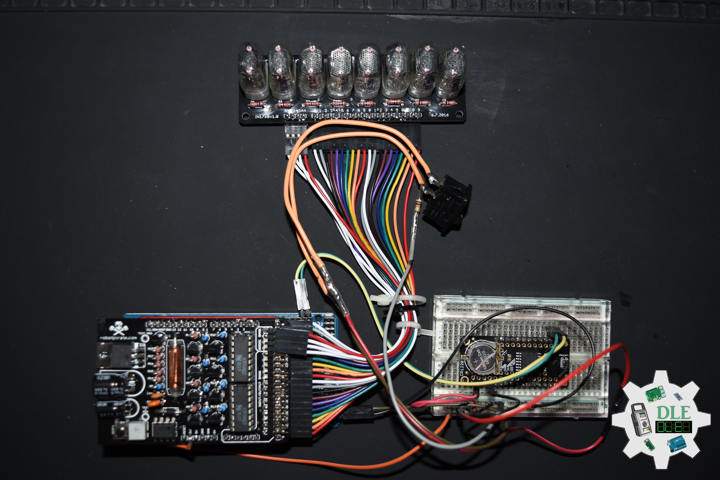
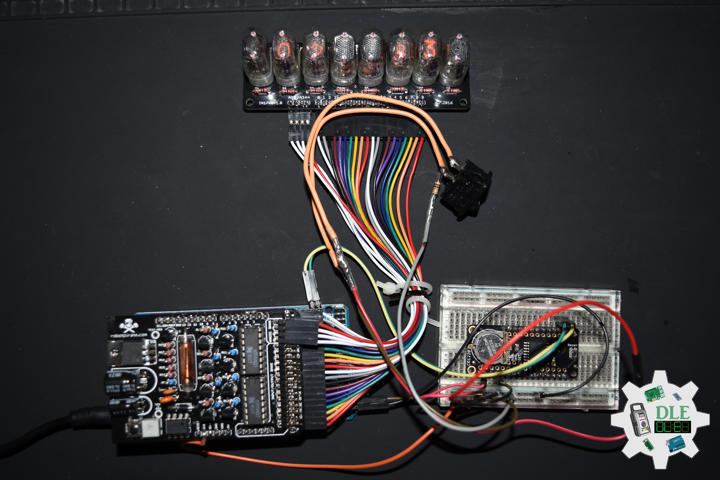
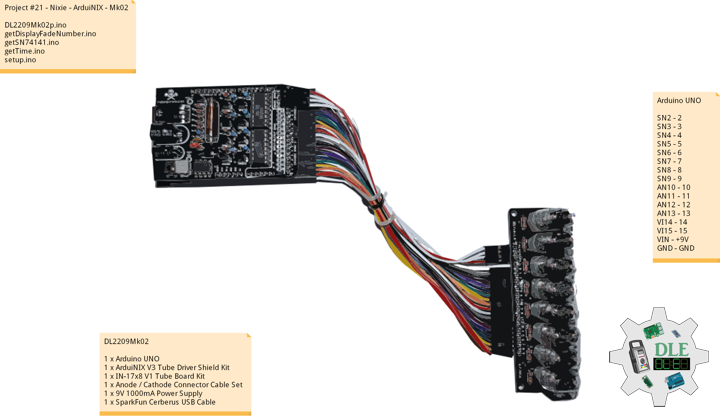
Project #21 – Nixie – ArduiNIX – Mk02
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #NixieTube #Nixie #ArduiNIX #ArduinoUNO #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
——
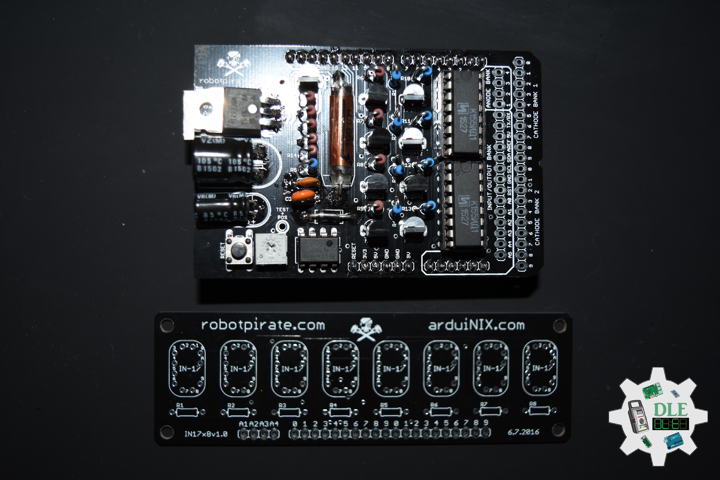
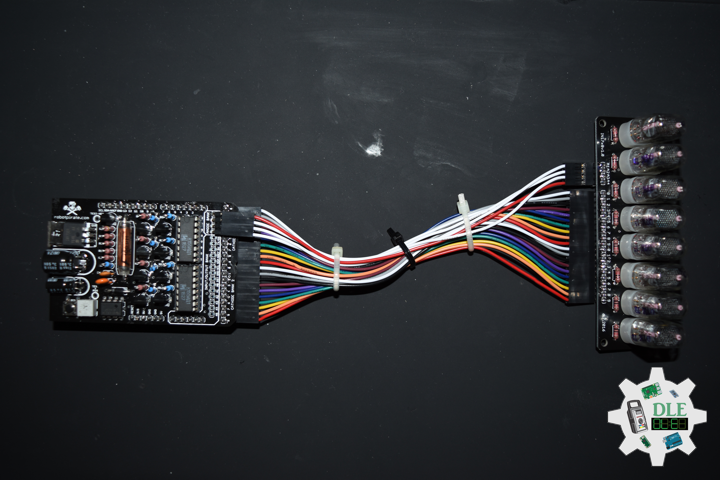
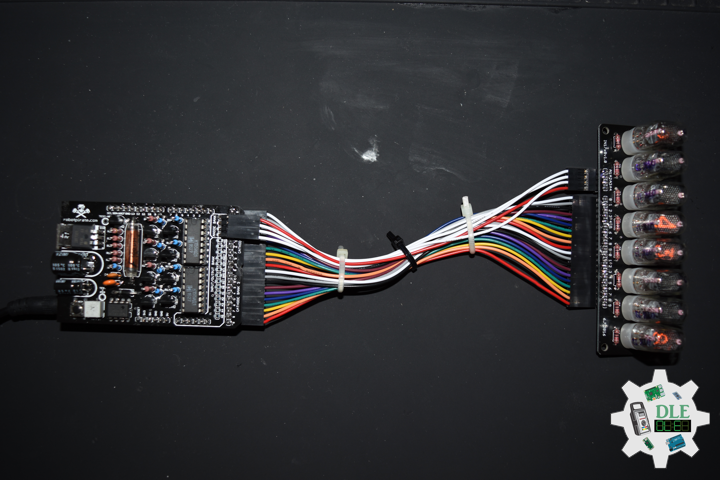
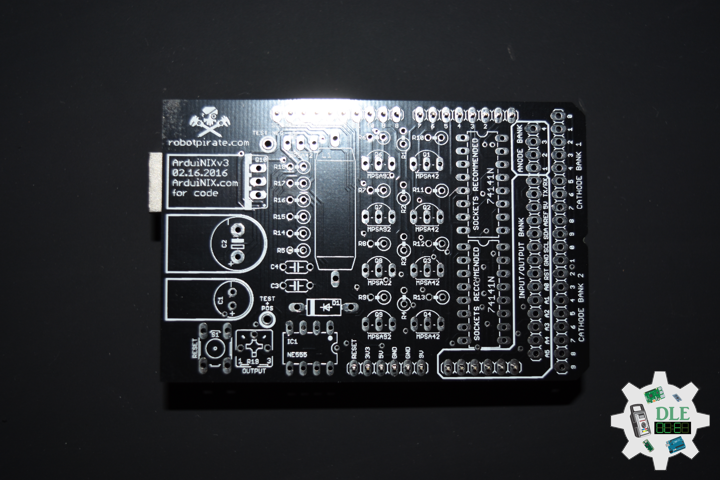
ArduiNIX
The ArduiNIX is an Arduino compatible shield which plugs right onto the top of the Arduino UNO board. ArduiNIX takes care of stepping power from 9 VDC wall adapter power supply up to a maximum of approximately 250 VDC to drive any and all Nixie tubes. ArduiNIX also provides Multiplexed display for up to 80 elements by using 4 anode channels and 20 cathode channels. Multiplexing increases the life expectancy of your Nixie tube investment.
Not only does the ArduiNIX provide a Nixie tube platform for standard clock functions, but it is also user programmable, meaning if you can program it using the arduino environment, you can make it happen on your Nixie display. Take special care when working with the ArduiNIX. The ArduiNIX Shield operates at high voltages. Be careful when handling it while it’s powered up. Normally the Arduino is safe to handle, but when used in conjunction with the ArduiNIX, voltages in excess of 200 volts may be achieved. Use caution. An IN-17 x 8 display board, and 8 x Russian IN-17 Nixie tubes.
DL2209Mk02
1 x Arduino UNO
1 x ArduiNIX V3 Tube Driver Shield Kit
1 x IN-17×8 V1 Tube Board Kit
1 x Anode / Cathode Connector Cable Set
1 x 9V 1000mA Power Supply
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
Arduino UNO
SN2 – 2
SN3 – 3
SN4 – 4
SN5 – 5
SN6 – 6
SN7 – 7
SN8 – 8
SN9 – 9
AN10 – 10
AN11 – 11
AN12 – 12
AN13 – 13
VI14 – 14
VI15 – 15
VIN – +9V
GND – GND
DL2209Mk02p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #21 - Nixie - ArduiNIX - Mk02
21-02
DL2209Mk02p.ino
1 x Arduino UNO
1 x ArduiNIX V3 Tube Driver Shield Kit
1 x IN-17x8 V1 Tube Board Kit
1 x Anode / Cathode Connector Cable Set
1 x 9V 1000mA Power Supply
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// SN74141 (1)
int ledPin_0_a = 2;
int ledPin_0_b = 3;
int ledPin_0_c = 4;
int ledPin_0_d = 5;
// SN74141 (2)
int ledPin_1_a = 6;
int ledPin_1_b = 7;
int ledPin_1_c = 8;
int ledPin_1_d = 9;
// Anode pins
int ledPin_a_1 = 10;
int ledPin_a_2 = 11;
int ledPin_a_3 = 12;
int ledPin_a_4 = 13;
// NOTE: Grounding on virtual pins 14 and 15
// (analog pins 0 and 1) will set the Hour and Mins.
int iVirtual14 = 14;
int iVirtual15 = 15;
// Fade
float fadeMax = 0.1f;
float fadeStep = 0.1f;
// Number Array
int NumberArray[8]={0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
int currNumberArray[8]={0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
float NumberArrayFadeInValue[8]={0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f};
float NumberArrayFadeOutValue[8]={5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f};
// Defines
// Sub seconds
long SSECS = 100;
// Milliseconds in a Sec
long SECS = 60;
// 60 Seconds in a Min.
long MINS = 60;
// 60 Mins in an hour
long HOURS = 60 * MINS;
// 24 Hours in a day. > Note: change the 24 to a 12 for non military time.
long DAYS = 12 * HOURS;
// Time from when we started
long runTime = 0;
// Default time sets. clock will start at 12:34:00.
// This is so we can count the correct order of tubes.
long clockHourSet;
long clockMinSet;
long clockSecSet;
//long clockSSecSet;
int HourButtonPressed = false;
int MinButtonPressed = false;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "21-02";
void loop() {
// Time
isTime();
}
getDisplayFadeNumber.ino
// Display Fade Number
void DisplayFadeNumberString()
{
// Anode channel 1 - numerals 0,4
SetSN74141Chips(currNumberArray[0],currNumberArray[4]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_1, HIGH);
delay(NumberArrayFadeOutValue[0]);
SetSN74141Chips(NumberArray[0],NumberArray[4]);
delay(NumberArrayFadeInValue[0]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_1, LOW);
// Anode channel 2 - numerals 1,5
SetSN74141Chips(currNumberArray[1],currNumberArray[5]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_2, HIGH);
delay(NumberArrayFadeOutValue[1]);
SetSN74141Chips(NumberArray[1],NumberArray[5]);
delay(NumberArrayFadeInValue[1]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_2, LOW);
// Anode channel 3 - numerals 2,6
SetSN74141Chips(currNumberArray[2],currNumberArray[6]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_3, HIGH);
delay(NumberArrayFadeOutValue[2]);
SetSN74141Chips(NumberArray[2],NumberArray[6]);
delay(NumberArrayFadeInValue[2]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_3, LOW);
// Anode channel 4 - numerals 3,7
SetSN74141Chips(currNumberArray[3],currNumberArray[7]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_4, HIGH);
delay(NumberArrayFadeOutValue[3]);
SetSN74141Chips(NumberArray[3],NumberArray[7]);
delay(NumberArrayFadeInValue[3]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_4, LOW);
// Loop thru and update all the arrays, and fades.
for( int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; i ++ ) //equal to & of digits
{
if( NumberArray[i] != currNumberArray[i] )
{
NumberArrayFadeInValue[i] += fadeStep;
NumberArrayFadeOutValue[i] -= fadeStep;
if( NumberArrayFadeInValue[i] >= fadeMax )
{
NumberArrayFadeInValue[i] = 2.0f;
NumberArrayFadeOutValue[i] = 4.0f; //affects the refresh cycle
currNumberArray[i] = NumberArray[i];
}
}
}
}
getSN74141.ino
// SN74141
// SN74141 : Truth Table
//D C B A #
//L,L,L,L 0
//L,L,L,H 1
//L,L,H,L 2
//L,L,H,H 3
//L,H,L,L 4
//L,H,L,H 5
//L,H,H,L 6
//L,H,H,H 7
//H,L,L,L 8
//H,L,L,H 9
// isSetupSN74141
void isSetupSN74141(){
pinMode(ledPin_0_a, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_0_b, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_0_c, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_0_d, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_1_a, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_1_b, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_1_c, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_1_d, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_a_1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_a_2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_a_3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_a_4, OUTPUT);
// NOTE: Grounding on virtual pins 14 and 15
// (analog pins 0 and 1) will set the Hour and Mins.
// Set the vertual pin 14 (pin 0 on the analog inputs )
pinMode( iVirtual14, INPUT );
// Set pin 14 as a pull up resistor.
digitalWrite(iVirtual14, HIGH);
// Set the vertual pin 15 (pin 1 on the analog inputs )
pinMode( iVirtual15, INPUT );
// Set pin 15 as a pull up resistor.
digitalWrite(iVirtual15, HIGH);
}
// SetSN74141Chips
void SetSN74141Chips( int num2, int num1 )
{
// Set defaults
// Will display a zero.
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int c = 0;
int d = 0;
// Load the a,b,c,d.. to send to the SN74141 IC (1)
switch( num1 )
{
case 0:
a=0;
b=0;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 1:
a=1;
b=0;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 2:
a=0;
b=1;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 3:
a=1;
b=1;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 4:
a=0;
b=0;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 5:
a=1;
b=0;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 6:
a=0;
b=1;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 7:
a=1;
b=1;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 8:
a=0;
b=0;
c=0;
d=1;
break;
case 9:
a=1;
b=0;
c=0;
d=1;
break;
default:
a=1;
b=1;
c=1;
d=1;
break;
}
// Write to output pins.
digitalWrite(ledPin_0_d, d);
digitalWrite(ledPin_0_c, c);
digitalWrite(ledPin_0_b, b);
digitalWrite(ledPin_0_a, a);
// Load the a,b,c,d.. to send to the SN74141 IC (2)
switch( num2 )
{
case 0:
a=0;
b=0;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 1:
a=1;
b=0;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 2:
a=0;
b=1;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 3:
a=1;
b=1;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 4:
a=0;
b=0;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 5:
a=1;
b=0;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 6:
a=0;
b=1;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 7:
a=1;
b=1;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 8:
a=0;
b=0;
c=0;
d=1;
break;
case 9:
a=1;
b=0;
c=0;
d=1;
break;
default:
a=1;
b=1;
c=1;
d=1;
break;
}
// Write to output pins
digitalWrite(ledPin_1_d, d);
digitalWrite(ledPin_1_c, c);
digitalWrite(ledPin_1_b, b);
digitalWrite(ledPin_1_a, a);
}
getTime.ino
// Time
void isTime(){
// Get milliseconds.
runTime = millis();
//int ssTime = millis();
int hourInput = digitalRead(iVirtual14);
int minInput = digitalRead(iVirtual15);
if( hourInput == 0 )
HourButtonPressed = true;
if( minInput == 0 )
MinButtonPressed = true;
if( HourButtonPressed == true && hourInput == 1 )
{
clockHourSet++;
HourButtonPressed = false;
}
if( MinButtonPressed == true && minInput == 1 )
{
clockMinSet++;
MinButtonPressed = false;
}
// Get time in seconds.
// Change this value to speed up or
// slow down the clock, set to smaller number such as 10, 1, or 100 for debugging
long time = (runTime) / 1000;
int sstime = (runTime) / 10;
// Set time based on offset..
// long hbump = 60*60*clockHourSet;
//long sbump = 60*60*60*clockHourSet; //change hourset to secondset
long hbump = 60*60*clockHourSet;
long mbump = 60*clockMinSet;
time += mbump + hbump;
// Convert time to days,hours,mins,seconds
long days = time / DAYS; time -= days * DAYS;
long hours = time / HOURS; time -= hours * HOURS;
long minutes = time / MINS; time -= minutes * MINS;
long seconds = time;
// long sseconds = 76;// time -= seconds * SECS;
long sseconds = runTime / SECS; time -= sseconds * SECS;
// Get the high and low order values for hours,min,seconds.
int lowerHours = hours % 10;
int upperHours = hours - lowerHours;
int lowerMins = minutes % 10;
int upperMins = minutes - lowerMins;
int lowerSeconds = seconds % 10;
int upperSeconds = seconds - lowerSeconds;
int lowerSSeconds = sseconds % 10;
//- lowerSSeconds;
int upperSSeconds = lowerSSeconds % 10; upperSSeconds = upperSSeconds /10;
if( upperSSeconds >= 10 ) upperSSeconds = upperSSeconds / 10;
if( upperSeconds >= 10 ) upperSeconds = upperSeconds / 10;
if( upperMins >= 10 ) upperMins = upperMins / 10;
if( upperHours >= 10 ) upperHours = upperHours / 10;
if( upperHours == 0 && lowerHours == 0 )
{
upperHours = 1;
lowerHours = 2;
}
// Fill in the Number array used to display on the tubes.
NumberArray[7] = upperHours;
NumberArray[6] = lowerHours;
NumberArray[5] = upperMins;
NumberArray[4] = lowerMins;
NumberArray[3] = upperSeconds;
NumberArray[2] = lowerSeconds;
NumberArray[1] = lowerSSeconds; //upperSSeconds;
NumberArray[0] = lowerSSeconds; //lowerSSeconds;
Serial.print(lowerSSeconds);
Serial.println();
// Display.
//DisplayFadeNumberString();
// Display.
DisplayFadeNumberString();
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// isSetupSN74141
isSetupSN74141();
// Open serial communications
Serial.begin(9600);
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor and E-Mentor
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2022 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: https://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
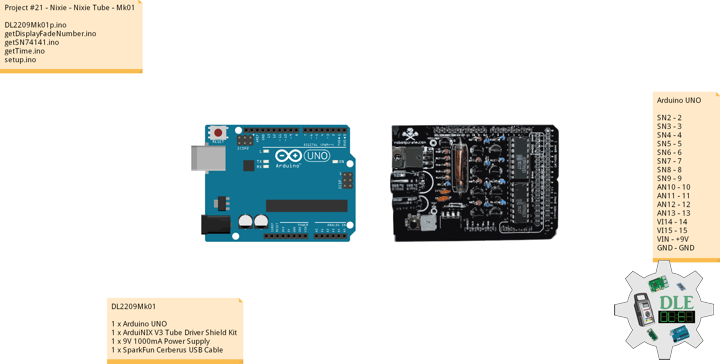
Project #21 – Nixie – Nixie Tube – Mk01
——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #NixieTube #Nixie #ArduiNIX #ArduinoUNO #Arduino #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
Nixie Tube
A Nixie tube, or cold cathode display, is an electronic device used for displaying numerals or other information using glow discharge. The glass tube contains a wire-mesh anode and multiple cathodes, shaped like numerals or other symbols. Applying power to one cathode surrounds it with an orange glow discharge. The tube is filled with a gas at low pressure.
The early Nixie displays were made by a small vacuum tube manufacturer called Haydu Brothers Laboratories, and introduced in 1955 by Burroughs Corporation, who purchased Haydu. The name Nixie was derived by Burroughs from “NIX I”, an abbreviation of “Numeric Indicator eXperimental No. 1”, although this may have been a backronym designed to justify the evocation of the mythical creature with this name.
Citing dissatisfaction with the aesthetics of modern digital displays and a nostalgic fondness for the styling of obsolete technology, significant numbers of electronics enthusiasts have shown interest in reviving Nixies.
DL2209Mk01
1 x Arduino UNO
1 x ArduiNIX V3 Tube Driver Shield Kit
1 x 9V 1000mA Power Supply
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
Arduino UNO
SN2 – 2
SN3 – 3
SN4 – 4
SN5 – 5
SN6 – 6
SN7 – 7
SN8 – 8
SN9 – 9
AN10 – 10
AN11 – 11
AN12 – 12
AN13 – 13
VI14 – 14
VI15 – 15
VIN – +9V
GND – GND
DL2209Mk01p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #21 - Nixie - Nixie Tube - Mk01
21-01
DL2209Mk01p.ino
1 x Arduino UNO
1 x ArduiNIX V3 Tube Driver Shield Kit
1 x 9V 1000mA Power Supply
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// SN74141 (1)
int ledPin_0_a = 2;
int ledPin_0_b = 3;
int ledPin_0_c = 4;
int ledPin_0_d = 5;
// SN74141 (2)
int ledPin_1_a = 6;
int ledPin_1_b = 7;
int ledPin_1_c = 8;
int ledPin_1_d = 9;
// Anode pins
int ledPin_a_1 = 10;
int ledPin_a_2 = 11;
int ledPin_a_3 = 12;
int ledPin_a_4 = 13;
// NOTE: Grounding on virtual pins 14 and 15
// (analog pins 0 and 1) will set the Hour and Mins.
int iVirtual14 = 14;
int iVirtual15 = 15;
// Fade
float fadeMax = 0.1f;
float fadeStep = 0.1f;
// Number Array
int NumberArray[8]={0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
int currNumberArray[8]={0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0};
float NumberArrayFadeInValue[8]={0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,0.0f};
float NumberArrayFadeOutValue[8]={5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f,5.0f};
// Defines
// Sub seconds
long SSECS = 100;
// Milliseconds in a Sec
long SECS = 60;
// 60 Seconds in a Min.
long MINS = 60;
// 60 Mins in an hour
long HOURS = 60 * MINS;
// 24 Hours in a day. > Note: change the 24 to a 12 for non military time.
long DAYS = 12 * HOURS;
// Time from when we started
long runTime = 0;
// Default time sets. clock will start at 12:34:00.
// This is so we can count the correct order of tubes.
long clockHourSet = 12;
long clockMinSet = 34;
long clockSecSet = 56;
long clockSSecSet = 12;
int HourButtonPressed = false;
int MinButtonPressed = false;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "21-01";
void loop() {
// Time
isTime();
}
getDisplayFadeNumber.ino
// Display Fade Number
void DisplayFadeNumberString()
{
// Anode channel 1 - numerals 0,4
SetSN74141Chips(currNumberArray[0],currNumberArray[4]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_1, HIGH);
delay(NumberArrayFadeOutValue[0]);
SetSN74141Chips(NumberArray[0],NumberArray[4]);
delay(NumberArrayFadeInValue[0]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_1, LOW);
// Anode channel 2 - numerals 1,5
SetSN74141Chips(currNumberArray[1],currNumberArray[5]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_2, HIGH);
delay(NumberArrayFadeOutValue[1]);
SetSN74141Chips(NumberArray[1],NumberArray[5]);
delay(NumberArrayFadeInValue[1]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_2, LOW);
// Anode channel 3 - numerals 2,6
SetSN74141Chips(currNumberArray[2],currNumberArray[6]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_3, HIGH);
delay(NumberArrayFadeOutValue[2]);
SetSN74141Chips(NumberArray[2],NumberArray[6]);
delay(NumberArrayFadeInValue[2]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_3, LOW);
// Anode channel 4 - numerals 3,7
SetSN74141Chips(currNumberArray[3],currNumberArray[7]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_4, HIGH);
delay(NumberArrayFadeOutValue[3]);
SetSN74141Chips(NumberArray[3],NumberArray[7]);
delay(NumberArrayFadeInValue[3]);
digitalWrite(ledPin_a_4, LOW);
// Loop thru and update all the arrays, and fades.
for( int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; i ++ ) //equal to & of digits
{
if( NumberArray[i] != currNumberArray[i] )
{
NumberArrayFadeInValue[i] += fadeStep;
NumberArrayFadeOutValue[i] -= fadeStep;
if( NumberArrayFadeInValue[i] >= fadeMax )
{
NumberArrayFadeInValue[i] = 2.0f;
NumberArrayFadeOutValue[i] = 4.0f; //affects the refresh cycle
currNumberArray[i] = NumberArray[i];
}
}
}
}
getSN74141.ino
// SN74141
// SN74141 : Truth Table
//D C B A #
//L,L,L,L 0
//L,L,L,H 1
//L,L,H,L 2
//L,L,H,H 3
//L,H,L,L 4
//L,H,L,H 5
//L,H,H,L 6
//L,H,H,H 7
//H,L,L,L 8
//H,L,L,H 9
// isSetupSN74141
void isSetupSN74141(){
pinMode(ledPin_0_a, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_0_b, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_0_c, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_0_d, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_1_a, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_1_b, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_1_c, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_1_d, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_a_1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_a_2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_a_3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ledPin_a_4, OUTPUT);
// NOTE: Grounding on virtual pins 14 and 15
// (analog pins 0 and 1) will set the Hour and Mins.
// Set the vertual pin 14 (pin 0 on the analog inputs )
pinMode( iVirtual14, INPUT );
// Set pin 14 as a pull up resistor.
digitalWrite(iVirtual14, HIGH);
// Set the vertual pin 15 (pin 1 on the analog inputs )
pinMode( iVirtual15, INPUT );
// Set pin 15 as a pull up resistor.
digitalWrite(iVirtual15, HIGH);
}
// SetSN74141Chips
void SetSN74141Chips( int num2, int num1 )
{
// Set defaults
// Will display a zero.
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int c = 0;
int d = 0;
// Load the a,b,c,d.. to send to the SN74141 IC (1)
switch( num1 )
{
case 0:
a=0;
b=0;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 1:
a=1;
b=0;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 2:
a=0;
b=1;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 3:
a=1;
b=1;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 4:
a=0;
b=0;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 5:
a=1;
b=0;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 6:
a=0;
b=1;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 7:
a=1;
b=1;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 8:
a=0;
b=0;
c=0;
d=1;
break;
case 9:
a=1;
b=0;
c=0;
d=1;
break;
default:
a=1;
b=1;
c=1;
d=1;
break;
}
// Write to output pins.
digitalWrite(ledPin_0_d, d);
digitalWrite(ledPin_0_c, c);
digitalWrite(ledPin_0_b, b);
digitalWrite(ledPin_0_a, a);
// Load the a,b,c,d.. to send to the SN74141 IC (2)
switch( num2 )
{
case 0:
a=0;
b=0;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 1:
a=1;
b=0;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 2:
a=0;
b=1;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 3:
a=1;
b=1;
c=0;
d=0;
break;
case 4:
a=0;
b=0;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 5:
a=1;
b=0;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 6:
a=0;
b=1;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 7:
a=1;
b=1;
c=1;
d=0;
break;
case 8:
a=0;
b=0;
c=0;
d=1;
break;
case 9:
a=1;
b=0;
c=0;
d=1;
break;
default:
a=1;
b=1;
c=1;
d=1;
break;
}
// Write to output pins
digitalWrite(ledPin_1_d, d);
digitalWrite(ledPin_1_c, c);
digitalWrite(ledPin_1_b, b);
digitalWrite(ledPin_1_a, a);
}
getTime.ino
// Time
void isTime(){
// Get milliseconds.
runTime = millis();
//int ssTime = millis();
int hourInput = digitalRead(iVirtual14);
int minInput = digitalRead(iVirtual15);
if( hourInput == 0 )
HourButtonPressed = true;
if( minInput == 0 )
MinButtonPressed = true;
if( HourButtonPressed == true && hourInput == 1 )
{
clockHourSet++;
HourButtonPressed = false;
}
if( MinButtonPressed == true && minInput == 1 )
{
clockMinSet++;
MinButtonPressed = false;
}
// Get time in seconds.
// Change this value to speed up or
// slow down the clock, set to smaller number such as 10, 1, or 100 for debugging
long time = (runTime) / 1000;
int sstime = (runTime) / 10;
// Set time based on offset..
// long hbump = 60*60*clockHourSet;
//long sbump = 60*60*60*clockHourSet; //change hourset to secondset
long hbump = 60*60*clockHourSet;
long mbump = 60*clockMinSet;
time += mbump + hbump;
// Convert time to days,hours,mins,seconds
long days = time / DAYS; time -= days * DAYS;
long hours = time / HOURS; time -= hours * HOURS;
long minutes = time / MINS; time -= minutes * MINS;
long seconds = time;
// long sseconds = 76;// time -= seconds * SECS;
long sseconds = runTime / SECS; time -= sseconds * SECS;
// Get the high and low order values for hours,min,seconds.
int lowerHours = hours % 10;
int upperHours = hours - lowerHours;
int lowerMins = minutes % 10;
int upperMins = minutes - lowerMins;
int lowerSeconds = seconds % 10;
int upperSeconds = seconds - lowerSeconds;
int lowerSSeconds = sseconds % 10;
//- lowerSSeconds;
int upperSSeconds = lowerSSeconds % 10; upperSSeconds = upperSSeconds /10;
if( upperSSeconds >= 10 ) upperSSeconds = upperSSeconds / 10;
if( upperSeconds >= 10 ) upperSeconds = upperSeconds / 10;
if( upperMins >= 10 ) upperMins = upperMins / 10;
if( upperHours >= 10 ) upperHours = upperHours / 10;
if( upperHours == 0 && lowerHours == 0 )
{
upperHours = 1;
lowerHours = 2;
}
// Fill in the Number array used to display on the tubes.
NumberArray[7] = upperHours;
NumberArray[6] = lowerHours;
NumberArray[5] = upperMins;
NumberArray[4] = lowerMins;
NumberArray[3] = upperSeconds;
NumberArray[2] = lowerSeconds;
NumberArray[1] = lowerSSeconds; //upperSSeconds;
NumberArray[0] = lowerSSeconds; //lowerSSeconds;
Serial.print(lowerSSeconds);
Serial.println();
// Display.
//DisplayFadeNumberString();
// Display.
DisplayFadeNumberString();
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// isSetupSN74141
isSetupSN74141();
// Open serial communications
Serial.begin(9600);
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor and E-Mentor
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2022 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: https://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc
Nixie Clock
“All-In-One” Arduino Nixie Clock
Detailed Description
The Arduino “All-In-One” Nixie Clock kit drives 6 IN-14 Nixie Tubes in a traditional “6 in a row” set up. It’s packed full of features, and at the end of the simple build you will have a beautiful IN-14 Nixie Clock. The board is small (150mm x 50mm), and is an easy to build and is a tried and tested design, with many hundreds of units sold.
This kit is based on an Arduino (Atmel ATMega) micro controller. You don’t need to own an Arduino to use this kit! It is self contained and runs without an external Arduino board.
The controller comes pre-programmed. You you can download, modify and upload the open source code if you wish.
This kit is ideal if you want to make an unusual or eye catching clock in a custom case.
Even better: The code is open source, with regular updates and new features.
WiFi Time Provider
If you already have a Clock with the battery-backed RTC (Real Time Clock) module, you can easily upgrade it to use the WiFi time provider module.
This gives you all the advantages of the WiFi kit. You need to have firmware V44 or later to use this.
You set the WiFi provider once once, and it never needs setting again, ever! It also allows you to configure the clock using a browser.
Don Luc