——
#DonLucElectronics #DonLuc #Synthesizer #UltrasonicSynth #Arduino #ArduinoProMini #Project #Fritzing #Programming #Electronics #Microcontrollers #Consultant
——
——
——
——
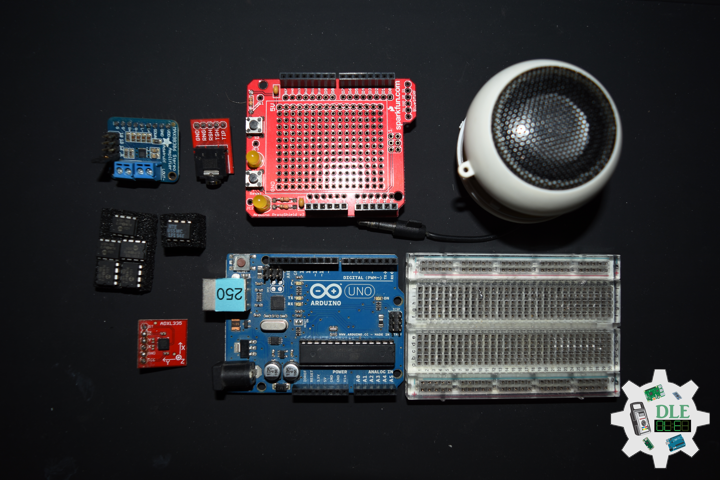
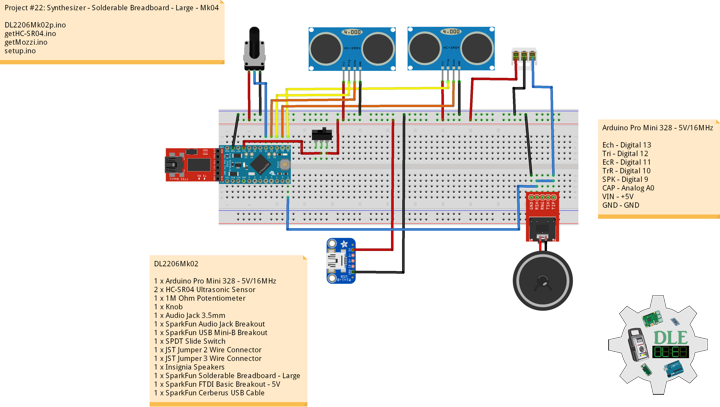
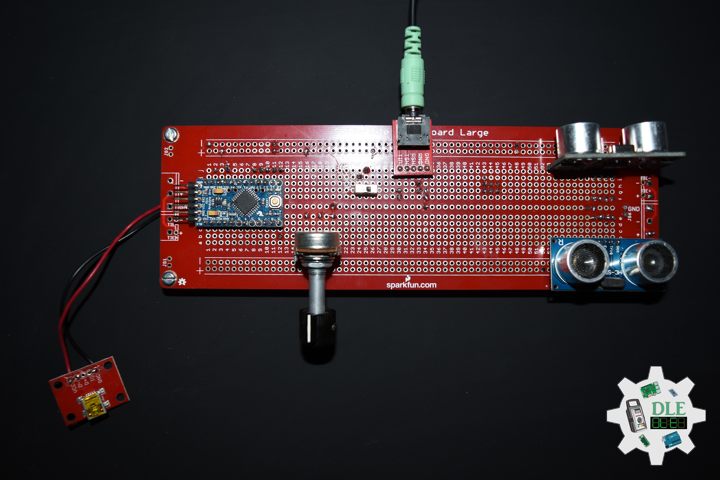
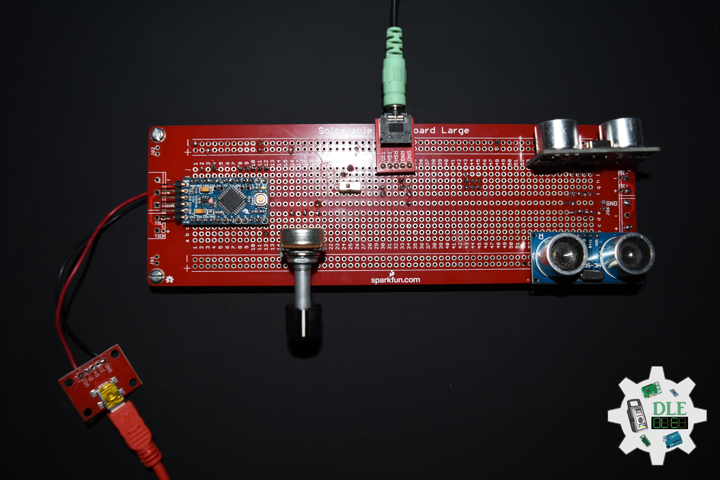
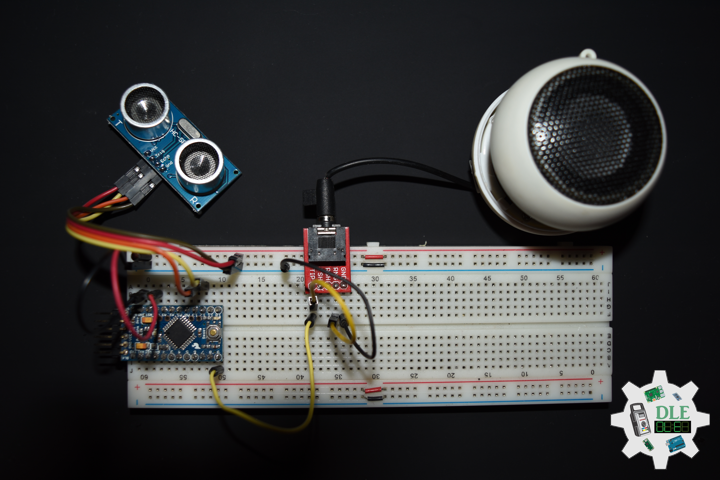
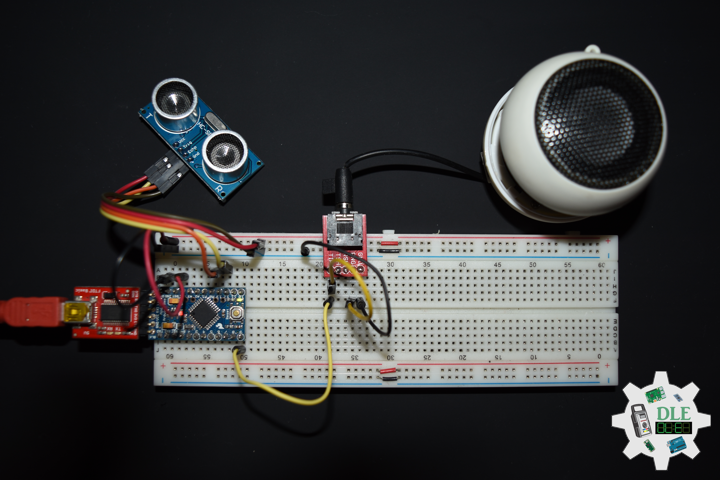
SparkFun Solderable Breadboard – Large
This is the Large SparkFun Solderable Breadboard. A bare PCB that is the exact size as our full-size breadboard with the same connections to pins and power rails. This board is especially useful for preserving a prototype or experiment you just created on a solderless breadboard by soldering all the pieces in place. The large solderable breadboard also includes real estate for screw terminal connectors and a trace down the center gutter for ground.
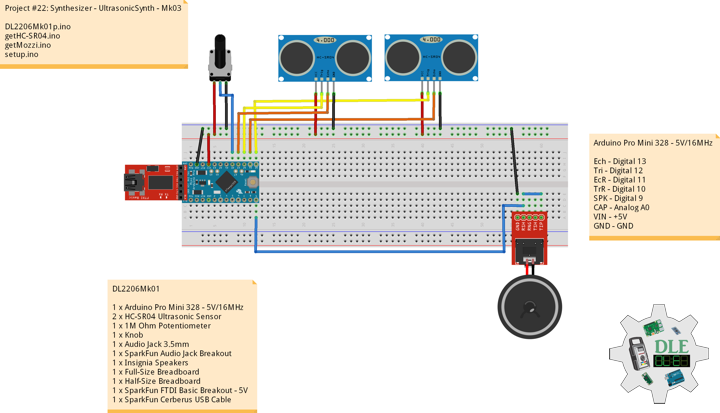
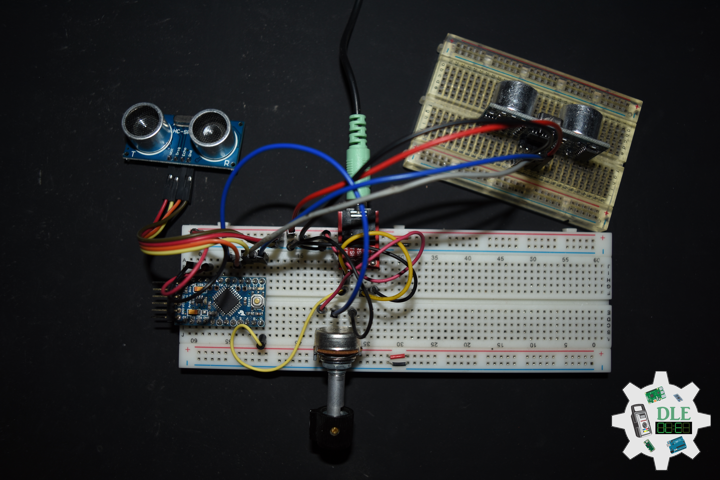
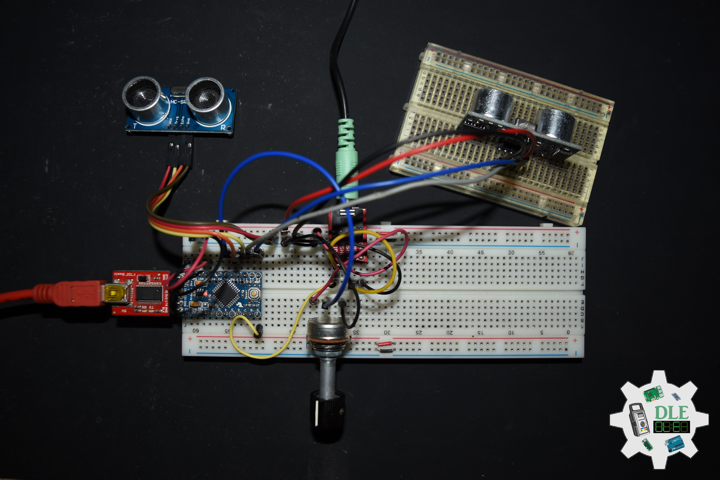
DL2206Mk02
1 x Arduino Pro Mini 328 – 5V/16MHz
2 x HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
1 x 1M Ohm Potentiometer
1 x Knob
1 x Audio Jack 3.5mm
1 x SparkFun Audio Jack Breakout
1 x SparkFun USB Mini-B Breakout
1 x SPDT Slide Switch
1 x JST Jumper 2 Wire Connector
1 x JST Jumper 3 Wire Connector
1 x Insignia Speakers
1 x SparkFun Solderable Breadboard – Large
1 x SparkFun FTDI Basic Breakout – 5V
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
Arduino Pro Mini 328 – 5V/16MHz
Ech – Digital 13
Tri – Digital 12
EcR – Digital 11
TrR – Digital 10
SPK – Digital 9
CAP – Analog A0
VIN – +5V
GND – GND
——
DL2206Mk02p.ino
/* ***** Don Luc Electronics © *****
Software Version Information
Project #22: Synthesizer - Solderable Breadboard - Large - Mk04
22-04
DL2206Mk02p.ino
1 x Arduino Pro Mini 328 - 5V/16MHz
2 x HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
1 x 1M Ohm Potentiometer
1 x Knob
1 x Audio Jack 3.5mm
1 x SparkFun Audio Jack Breakout
1 x SparkFun USB Mini-B Breakout
1 x SPDT Slide Switch
1 x JST Jumper 2 Wire Connector
1 x JST Jumper 3 Wire Connector
1 x Insignia Speakers
1 x SparkFun Solderable Breadboard - Large
1 x SparkFun FTDI Basic Breakout - 5V
1 x SparkFun Cerberus USB Cable
*/
// Include the Library Code
// Mozzi
#include <MozziGuts.h>
// Oscillator
#include <Oscil.h>
// Table for Oscils to play
#include <tables/cos2048_int8.h>
// Smoothing Control
#include <Smooth.h>
// Maps unpredictable inputs to a range
#include <AutoMap.h>
// Desired carrier frequency max and min, for AutoMap
const int MIN_CARRIER_FREQ = 22;
const int MAX_CARRIER_FREQ = 440;
// Desired intensity max and min, for AutoMap, note they're inverted for reverse dynamics
const int MIN_INTENSITY = 700;
const int MAX_INTENSITY = 10;
// Desired mod speed max and min, for AutoMap, note they're inverted for reverse dynamics
const int MIN_MOD_SPEED = 10000;
const int MAX_MOD_SPEED = 1;
// Maps unpredictable inputs to a range
AutoMap kMapCarrierFreq(0,1023,MIN_CARRIER_FREQ,MAX_CARRIER_FREQ);
AutoMap kMapIntensity(0,1023,MIN_INTENSITY,MAX_INTENSITY);
AutoMap kMapModSpeed(0,1023,MIN_MOD_SPEED,MAX_MOD_SPEED);
// Set the input for the knob to analog pin 0
const int KNOB_PIN = A0;
// Set the analog input for fm_intensity
int LDR1_PIN;
// Set the analog input for mod rate
int LDR2_PIN;
// Table for Oscils to play
Oscil<COS2048_NUM_CELLS, AUDIO_RATE> aCarrier(COS2048_DATA);
Oscil<COS2048_NUM_CELLS, AUDIO_RATE> aModulator(COS2048_DATA);
Oscil<COS2048_NUM_CELLS, CONTROL_RATE> kIntensityMod(COS2048_DATA);
// Brightness (harmonics)
int mod_ratio = 5;
// Carries control info from updateControl to updateAudio
long fm_intensity;
// Smoothing for intensity to remove clicks on transitions
float smoothness = 0.95f;
Smooth <long> aSmoothIntensity(smoothness);
// Trigger pin 12 to pitch distance sensor
const int iTrigPitch = 12;
// Echo Receive pin 13 to pitch distance sensor
const int iEchoPitch = 13;
// Define the useable range of the pitch sensor
const int pitchLowThreshold = 45;
const int pitchHighThreshold = 2;
// Stores the distance measured by the distance sensor
float distance = 0;
// Trigger pin 10 to rate distance sensor
const int iTrigRate = 10;
// Echo Receive pin 13 to pitch distance sensor
const int iEchoRate = 11;
// Define the useable range of the pitch sensor
const int rateLowThreshold = 45;
const int rateHighThreshold = 2;
// Stores the distance measured by the distance sensor
float rate = 0;
// Mini Speaker
int SPK = 9;
// Software Version Information
String sver = "22-04";
void loop() {
// Audio Hook
audioHook();
}
getHC-SR04.ino
// HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
// Setup HC-SR04
void setupHCSR04() {
// The trigger iTrig Pitch will output pulses of electricity
pinMode(iTrigPitch, OUTPUT);
// The echo iEcho will measure the duration of pulses coming back from the distance sensor
pinMode(iEchoPitch, INPUT);
// The trigger iTrig Rate will output pulses of electricity
pinMode(iTrigRate, OUTPUT);
// The echo iEcho will measure the duration of pulses coming back from the distance sensor
pinMode(iEchoRate, INPUT);
}
// Distance
float isDistance() {
// Variable to store the time it takes for a ping to bounce off an object
float echoTime;
// Variable to store the distance calculated from the echo time
float calculatedDistance;
// Send out an ultrasonic pulse that's 10ms long
digitalWrite(iTrigPitch, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(iTrigPitch, LOW);
// Use the pulseIn command to see how long it takes for the
// pulse to bounce back to the sensor
echoTime = pulseIn(iEchoPitch, HIGH);
// Calculate the distance of the object that reflected the pulse
// (half the bounce time multiplied by the speed of sound)
calculatedDistance = echoTime * 0.034 / 2;
// Send back the distance that was calculated
return calculatedDistance;
}
// Rate
float isRate() {
// Variable to store the time it takes for a ping to bounce off an object
float echoTime;
// Variable to store the distance calculated from the echo time
float calculatedDistance;
// Send out an ultrasonic pulse that's 10ms long
digitalWrite(iTrigRate, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(iTrigRate, LOW);
// Use the pulseIn command to see how long it takes for the
// pulse to bounce back to the sensor
echoTime = pulseIn(iEchoRate, HIGH);
// Calculate the distance of the object that reflected the pulse
// (half the bounce time multiplied by the speed of sound)
// cm = 58.0
calculatedDistance = echoTime * 0.034 / 2;
// Send back the distance that was calculated
return calculatedDistance;
}
getMozzi.ino
// Mozzi
// Update Control
void updateControl(){
// Variable to store the distance measured by the sensor
distance = isDistance();
// Low Threshold
if ( distance >= pitchLowThreshold) {
// pitchLowThreshold
distance = pitchLowThreshold;
}
// High Threshold
if ( distance < pitchHighThreshold){
// pitchHighThreshold
distance = pitchHighThreshold;
}
// Variable to store the distance measured by the sensor
rate = isRate();
// Low Threshold
if ( rate >= rateLowThreshold) {
// rateLowThreshold
rate = rateLowThreshold;
}
// High Threshold
if ( rate < rateHighThreshold){
// rateHighThreshold
rate = rateHighThreshold;
}
// Read the knob
// Value is 0-1023
int knob_value = mozziAnalogRead(KNOB_PIN);
// Map the knob to carrier frequency
int carrier_freq = kMapCarrierFreq(knob_value);
// Calculate the modulation frequency to stay in ratio
int mod_freq = carrier_freq * mod_ratio;
// Set the FM oscillator frequencies
aCarrier.setFreq(carrier_freq);
aModulator.setFreq(mod_freq);
// Read the light dependent resistor on the width
LDR1_PIN = distance;
int LDR1_value = LDR1_PIN;
int LDR1_calibrated = kMapIntensity(LDR1_value);
// Calculate the fm_intensity
// Shift back to range after 8 bit multiply
fm_intensity = ((long)LDR1_calibrated * (kIntensityMod.next()+128))>>8;
// Read the light dependent resistor on the speed
LDR2_PIN = rate;
int LDR2_value= LDR2_PIN;
// Use a float here for low frequencies
float mod_speed = (float)kMapModSpeed(LDR2_value)/1000;
kIntensityMod.setFreq(mod_speed);
}
// Update Audio
int updateAudio()
{
// Update Audio
long modulation = aSmoothIntensity.next(fm_intensity) * aModulator.next();
return aCarrier.phMod(modulation);
}
setup.ino
// Setup
void setup() {
// Setup HC-SR04
setupHCSR04();
// Delay
delay( 200 );
// Mozzi Start
startMozzi();
}
——
People can contact us: https://www.donluc.com/?page_id=1927
Technology Experience
- Single-Board Microcontrollers (PIC, Arduino, Raspberry Pi,Espressif, etc…)
- IoT
- Robotics
- Camera and Video Capture Receiver Stationary, Wheel/Tank and Underwater Vehicle
- Unmanned Vehicles Terrestrial and Marine
- Research & Development (R & D)
Instructor and E-Mentor
- IoT
- PIC Microcontrollers
- Arduino
- Raspberry Pi
- Espressif
- Robotics
Follow Us
J. Luc Paquin – Curriculum Vitae – 2022 English & Español
https://www.jlpconsultants.com/luc/
Web: https://www.donluc.com/
Web: https://www.jlpconsultants.com/
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/neosteam.labs.9/
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/channel/UC5eRjrGn1CqkkGfZy0jxEdA
Twitter: https://twitter.com/labs_steam
Pinterest: https://www.pinterest.com/NeoSteamLabs/
Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/neosteamlabs/
Don Luc